* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Notes All organisms are made of cells. Osmosis is the
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
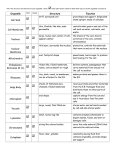
Unit 2 Notes All organisms are made of cells. Osmosis is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion is the movement of material across the cell membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Facilitated transport is the movement of material across a membrane through a protein channel from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Active Transport is the movement of material through a protein channel from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration and requires the use of energy. Passive Transport is the movement of material into or out of the cell without expending any energy. Endocytosis is the process by which the cell membrane envelops material too large to pass directly through the membrane or protein channel. Exocytosis is the process by which a cell expels waste or cell products too large to pass directly through its membrane or protein channels. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable boundary that controls what enters (nutrients and cell products) and leave (cell products and waste) in a cell. Nucleus is an organelle that contains and protects the cell’s DNA, one type of genetic information. The cytoplasm is the area inside the cell consisting of gelatin-like material and the internal cell structures, with the exception of the nucleus, that supports the cell. The chloroplast is an organelle that produces carbohydrates through the process of photosynthesis. The mitochondrion is an organelle that uses carbohydrates to produce cellular energy. An organelle is a membrane-bound cell structure that has its own specialized function. Cell require nutrients to grow. Once cells reach their optimal size, they must divide to maintain efficiency in obtaining and transporting nutrients. Cells divide as a means of replacing worn out, damaged cells, repairing tissue, and help a tissue, organ, and organism grow. The abundance or lack of nutrients influences cell growth, division, and processes. Cell growth and division allows us to sustain life. Cells use nutrients to produce other materials needed by the cell to function, sustain tissue, organ, and organism health and life.