* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chloroplast Mitochondria Cell Membrane Golgi Apparatus Cell Wall
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
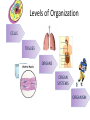
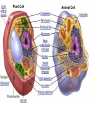
Chloroplast Cytoplasm Mitochondria Nucleus Cell Membrane Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Ribosomes Vacuole Cell Structure and Function **by the end of this lesson you WILL be able to name all parts of the cell seen above All living things are composed of cells. The cell is the basic structural unit of all life. All organisms are made up of cells and all the substances of an organism are products of the cell. More than three hundred years ago an English scientists Robert Hooke (1635-1703) observed some by the name of ________________ thin slices of cork. In Hooke’s report, mircographia, he described what he had seen through his microscope. Hooke Tiny cavities Each said that the cork was a mass of “_____________”. cavity was surrounded by walls which reminded him of a Bee’s Honeycomb so he called these structures cells. ____________________, It was not until the early 1800’s that the first specific ideas about cells were presented. In 1831, a British botanist, Robert Brown observed a cell structure he called the _______________, Nucleus In 1831, a French biologists, Dujardin (Doo__________. Zhar-Dan), was observing living cells and found the substance we now call the protoplasm. In 1839, two german biologists, Matthias Scleiden (Shly-den) and Theodore Schwann (Shvahn), along with the help of many other scientists, developed what we now call the Cell Theory “____________”. Cell Theory 1. All plants and animals are composed of cells and cell products 2. All life functions are performed by individual cells or groups of cells. 3. Cells come from other cells by reproduction. Levels of Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEMS ORGANISM Definition of a Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing LIFE functions 2 Types of Cells Prokaryotic Cell a. Do not have structures surrounded by membranes and do not contain a nucleus b. Few internal structures c. One-celled organisms, ex. Bacteria Eukaryotic Cells • Structures are surrounded by membrane and has a nucleus • Many internal structures • Multi-cellular organisms; humans, plants Plant Cell Animal Cell 2. Eukaryotic a. Contain organelles surrounded by membranes b. Most living organisms Chloroplast Cytoplasm Mitochondria Nucleus Cell Membrane Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Ribosomes Vacuole CELL MEMBRANE •Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell •Double layer •Found in plant and animal cells Plant cell Click to return to main page Animal Cell CELL WALL •Most commonly found in plant cells and bacteria •Supports and protects cells Click to return to main page NUCLEUS “Da Boss” •Brain of cell •Directs cell activities •Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane •Contains genetic materialDNA Nuclear membrane Nucleolus NUCLEOLUS •Inside nucleus •Contains RNA to build proteins NUCLEAR MEMBRANE •Surrounds nucleus •Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus Click to return to main page CYTOPLASM •jelly-like substance •Surrounded by cell membrane •Chemical reactions with in the cell take place here Click to return to main page Lysosome •Garbage Truck •Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal Click to return to main page ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM •The Highway •Transports materials around cell •Smooth type: no ribosome's •Rough type: ribosome's embedded in surface Click to return to main page RIBOSOMES •Each cell contains thousands •Make proteins •Found on ER or floating in the cytoplasm •Ribosome=Rib protein Click to return to main page ATP H2O MITOCHONDRIA •Produces energy through digestion •Recycles and decomposes foods of cell •“Power house” of cell Click to return to main page GOLGI BODIES •Stores and releases chemicals in the cell •Moves materials within the cell and out of cell Click to return to main page VACUOLE •Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal •Stores water and other substances •Bigger in plant cell then animal cell Water Vacuole Click to return to main page O₂ Glucose CHLOROPLASTS •Usually found in plant cells •Contains green chlorophyll •Where photosynthesis takes place Click to return to main page