* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
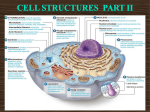
Download Chapter Three Review #2 KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Chapter Three Review #2 Q’s KEY 1. Golgi Body looks like stacks of three to twenty slightly curved sacs. See picture. 2. The main function of the GOLGI APPARATUS is to receive in-coming proteins and lipids, then modify them, sort them and re-package them into vesicles and ship them off. "Shipping and receiving warehouse" 3. A vesicle is a very small membranous transport sac. A vacuole is also membranous sac but it is much larger and more often used for storage. 4. Definitely Plant – As it possesses – Cell Wall, Chloroplast and a Large Central Vacuole. 5. Vesicles form when membrane pinches off to form a sac. This can happen at E.R, Golgi, and pinching in at the Cell Membrane. 6. Lysosomes are produced when hydrolytic enzymes are packaged up and blebbed off of the Golgi Apparatus. 7. Lysosomes store and release HYDROLYTIC ENZYMES. – They run hydrolysis on macromolecules to break them into their monomers. Lysosomes are often involved with the digestion of : Bacteria, In-coming Macromolecules and also the cell itself during Apoptosis – Programmed cell death or organelle breakdown. 8. Ribosomes are manufactured back in the NUCLEOLUS. 9. MITOCHONDRION – Mitochondria (plural) 10. CELLULAR RESPIRATION takes place in Mitochondria. So ATP is generated during cellular respiration. ATP provides energy for all cell processes. 11. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy Release Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + ENERGY 12. These folds are necessary for increasing Surface Area. This extra surface area is required to house all of the enzymes that are required to run cellular respiration. 13. These shelf-like folds are called CRISTAE 14. Matrix 15. Cytoskeleton is a vast network of filaments and tubules. This cytoskeleton is responsible for: - Maintaining Cell Shape - Allow for organelle movement - Anchor things in place Allow for motile structures and key process like cell division. 16. The key building structures for building the cytoskeleton are : A microfilament (Actin) consists of two filamentous proteins twisted around each other in a helical manner. Microtubules form when filamentous proteins called TUBULIN spiral up to form a cylinder. 17. TUBULIN 18. 9 + 0 Arrangement 9 + 2 Arrangement 19. Sperm cell – Base of Flagellum will be site of BASAL BODY (9 + 0) while shaft of Flagellum will be (9 + 2) arrangement. 20. The function of the basal body (9 + 0) is for anchorage and these basal bodies direct the organization of microtubules into the shaft ( 9 + 2) in cilium and flagella 21. Motor- operated side arms are found between microtubules. 22. Flagella are used for cellular locomotion. In humans the male gamete (Sperm) need to be motile. 23. Lysosomal enzymes would digest a neutral fat down into a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids if it was a triglyceride. Practice Quiz: 1. B 2. This Mitochondrion will produce – ATP,CO2 and H2O. ANSWER = D 3. B 4. C 5. D – For ATP