* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download memory drsidra
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
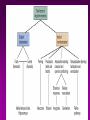
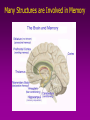
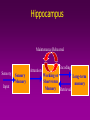
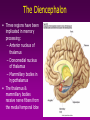
Memory Gateway to Learning Introduction • • • • What is memory? Positive and Negative Memory What is learning? Importance:Reward and punishment – Role of hippocampus – Survival • Areas for storage: – spinal cord reflexes – Higher centers • Neural basis of memory – Strength of synapse • Consolidation • Condification Stages of memory • Encoding-information for each memory is assembled from the different sensory systems and translated into whatever form necessary to be remembered. This is presumably the domain of the association cortices . • Consolidation• Storage• Retrieval- There is more than we can tell… How many stripes did you see on the cat? Mechanism of presynaptic facilitation underlying behavioral sensitization 1. Serotonin is released by modulatory interneuron and binds to GPCR Classification • Short term (working memory) • Intermediate term • Long term Mechanism of long-term synaptic enhancement Number of Neurons and Their Connectivities Often Change Significantly During Learning • Learning” is achieved in adult human beings and animals by modification of numbers of neurons in the memory circuits • Use it or lose it! Many Structures are Involved in Memory Implicit memory • Procedural memory – skills and habits, which, once acquired, become unconscious and automatic. • Priming – is facilitation of recognition of words or objects by prior exposure to them. An example is improved recall of a word when presented with the first few letters of it. Implicit memory • In nonassociative learning, – the organism learns about a single stimulus. • In associative learning, – the organism learns about the relation of one stimulus to another. Working Memory Sensory Input Sensory Memory Attention Working or Short-term Memory Hippocampus Maintenance Rehearsal Sensory Input Sensory Memory Attention Encoding Working or Long-term Short-term memory Memory Retrieval Implicit Memory • Does not require conscious awareness Amnesia - Loss of Memory • Retrograde amnesia – loss of memory for the time period before a trauma – typically is gradational from essentially complete loss just before trauma to less and less complete loss earlier and earlier before trauma • Anterograde amnesia – inability to form new memories Causes of Amnesia • Causes – concussion, chronic alcoholism, encephalitis, brain tumor, stroke • Transient amnesia – Probably caused by interruptions in cerebral blood flow – Blows to head, physical stress, drugs Bilateral removal of the hippocampus – Studied patients with surgical interventions to treat epilepsy – Bilateral removal of the hippocampus and neighboring regions of the temporal lobe • Most famous case was “H.M.” The Diencephalon • Three regions have been implicated in memory processing: – Anterior nucleus of thalamus – Dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus – Mammillary bodies in hypothalamus • The thalamus & mammillary bodies receive nerve fibers from the medial temporal lobe Effects of lesion • Lesion in dorsomedial thalamus: – Cognitive ability normal but memory impaired – Caused moderate retrograde amnesia and profound anterograde amnesia • Short term memory and preservation of old memories was intact. • Suggests that both the temporal lobe and parts of the thalamus may be involved in the formation of long-term declarative memories. Neocortex and Working Memory • Humans have much more prefrontal cortex than any other animals • Pathways: – Medial temporal lobe >> hypothalamus >> anterior nucleus of thalamus >> cingulate cortex – Medial temporal lobe >> dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus >> frontal cortex • Experiments suggest that frontal cortex is involved with working memory for problem solving and planning of behavior