* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxidative Phosphorylation
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
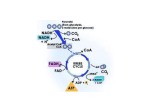
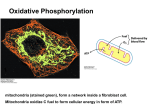
Introduction to METABOLISM Metabolism is the sum of all chemical changes occurring in a cell , tissue or the body It is composed of pathways Pathway is a multistep sequence of reactions in which the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction Each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme (may be with help of a coenzyme) A B C D E F G 1 2 3 4 5 6 Different pathways can intersect forming a network of chemical reactions. K T A B Pathways can be classified as either : catabolic (degredative) or anabolic (synthetic) C D L U M V E Glycolysis, an example of a metabolic pathway Metabolic map is a map that shows components of a pathways of metabolism It is useful in tracing connections between pathways metabolic map of intermediary metabolism Example of a metabolic map Catabolic & Anabolic Reactions Catabolic Reactions • Catabolic reactions break down complex molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides and lipids to few simple molecules • Serve to: yield energy in the form of ATP from the degradation of energyrich fuel molecules Allow molecules in the diet (or nutrient molecules stored in the cells) to be converted into building blocks needed for the synthesis of complex molecules Anabolic Reactions •Anabolic pathways form complex end products from simple precursors i.e. synthesis of glycogen from glucose & proteins from amino acids • Requires energy provided by breakdown of ATP to ADP & Pi ANABOLIC large complex organic molecules are constructed from small molecules Biosynthetic CATABOLIC Decomposition of large complex molecules into small molecules Degradative Reductive Oxidative Energy Required Energy Liberated Diverging Converging Catabolism (converging) Many Few Anabolism Few (diverging) Many Macromolecules Nutrients Proteins Polysaccharides Lipids Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Fats Proteins ATP Catabolism (oxidative, exergonic) NADPHChemical NADPH ATP End products H2O, CO2, NH3 GTP NADPH energy ATP NADH Anabolism (reductive, endergonic) Precursor Molecules Amino acids Sugars Fatty acids Nitrogenous bases Catabolism and anabolism are always related. Amphibolic Pathway Amphi = Dual, amphibolic: dual pathway For example, Krebs cycle is mainly a catabolic cycle, but with some anabolic features. e.g. part of Krebs cycle is used for the synthesis of glucose from amino acids Therefore, Krebs cycle is amphibolic Stages of Catabolism • Citric acid cycle produces NADH & FADH2 • Electrons flow from NADH & FADH2 in the mitochondria (electron transport chain) generates energy in the form of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). Adenosine triphosphate ATP (carrier of energy) ATP ADP + Pi ADP AMP + Pi Pi Pi Pi Mitochondria BATTERY OF THE CELL site for generating ATP Through Electron Transport Chain & Oxidative Phosphorylation In Electron Transport Chain in the mitochondria • Flow of electrons from NADH & FADH2 (through electron carriers CoQ & cytochromes) to oxygen yields energy • This energy is used for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (phosphorylation) Flow of electrons NADH ATP PHOSPHORYLATION OXIDATION NADH Oxidative Phosphorylation (in mitochondria) Oxidation: electron flow in electron transport chain (with production of energy) Phosphorylation: phosphorylation of ADP to ATP Diet Carbohydrates Glycogen (liver & Sk. Ms.) Glucose GLYCOLYSIS (in cytoplasm) Lactate Pyruvate in mitochondria CATABOLISM OF CARBOHYDRATES Acetyl CoA Citric Acid Cycle (in mitochondria) NADH & FADH2 Electron transport chain (flow of electrons) Formation of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation) Triglycerides Fatty acids Lipid Catabolism Acetyl CoA Citric acid cycle ATP Energy Protein Catabolism Amino Acid Protein amino group (nitrogen) incorporated into other Compounds (e.g. urea) excreted DEAMINATION (a-ketoacid) (carbon skeleton) catabolised synthesis of other compounds acetyl CoA Citric Acid Cycle ATP (energy)