* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Secondary Wall
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
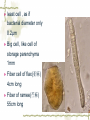
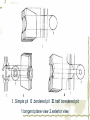
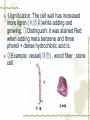
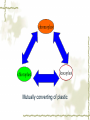
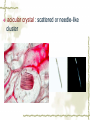
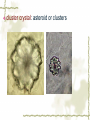
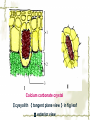
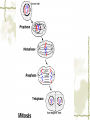
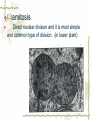
First Chapter Plant Cells one Form and Structure of Plant Cells ★Definition The structural and functional unit of a tissue , and consequently of the plant body itself , is known as a cell . Some species or kind of plants consist of single cell , but large type are make up of uncountable millions , or even billions , of these structural units. Chlamydomonas Nostoc commune Vauch 1.Shape and Size of Plant Cells It has various shapes and sizes. Cell , which distribute in differ part of frond and perform differ function , has differ form and size . plant cell , commonly 10~100μm(diameter) least cell , as if bacterial diameter only 0.2μm Big cell , like cell of storage parenchyma 1mm Fiber cell of flax(亚麻) 4cm long Fiber of ramee(苎麻) 55cm long 2.Basic Structure and Function of Plant cells Definition Microscopic structure: there can be seen the cell structure with microscope, called microscopic structure. Submicroscopic structure: there can be seen the cell structure with electron microscope , termed submicroscopic structure. Microscopic structure 1. nuclear membrane 2. nucleolus 3.chromosome 4. Cell wall 5. plasmalemma 6. vacuole membrane 7. vacuole 8. Chloroplast 9.Mitochondria 10.microtuble 11. Endoplasmic reticulum submicroscopic 1.Cell wall 2.nuclear membrane structure 3.nucleochylema 4.nucleolus 5.plasmalemma 6.Cytoplasm 7.vacuole membrane 8.chloroplast 9.vacuole 12.Ribosome 13.14.microbody15. golgi body 一、cell wall ★ constitute 二、protoplast 三、ergastic substance 一、 Cell Wall Layers intercellular layer primary wall secondary wall Intercellular Layer: It is thin layers owned in common between cell wall and cell wall . Primary Wall: By cellulose(纤维素) , hemicellulose(半纤维素) and pectin(果胶) material that protoplasm secrete, increase in interior side of intercellular layer. Secondary Wall: After the cell wall stops growing, are accumulating some materials coming into being in the interior of the primary wall on each gradually, make the cell wall increase and take shape on concentric storey thick. Ⅰ. pit simple pit bordered pit half bordered pit Ⅱ.plasmodesmata(胞间连丝复数) Pit The secondary wall does not increase thick evenly , leave some and has not increased the thick part in a lot of places during the process of thickenning, called the pit. Ⅰ.Simple pit Ⅱ.bordered pit Ⅲ.half boredered pit 1.tangent plane view 2.exterior view Bordered pit of pine’s stem and Radix et Rhizoma Rhei Ⅱ.plasmodesmata There are a lot of very thin protoplasm silks that cross and come into being the very small hole on the primary wall and get in touch each other among the cells, this kind of protoplasm silk is called plasmodesmata. Plasmodesmata of Persimmon core Ⅲ. Specification of Cell Walls lignification suberization cutinization mucilagization mineralization 1.lignification: The cell wall has increased more lignin (木质素)while adding and growing. ①Distinguish: it was stained Red when adding meta benzene and three phenol + dense hydrochloric acid is. ②Example: vessel(导管) , wood fiber , stone cell. 2. suberization: Have increased the fat phellem(木 栓质) in the cell wall. ①Distinguish :it was dyed Red when adding Sudan Ⅲ test solution(TS) is. ②Example: Brown outer bark trunk outside. 3. cutinization:Fat cutin(角质) except not being pack the cell wall , form a layer of cuticles outside epidermis of stem often. ①Distinguish :it was dyed when adding Sudan Ⅲ test solution is orange. ②Example: The seed of the castor-oil(蓖麻 油) plant , stem peel of the sugarcane(甘蔗). 4.mucilagization: Cellulose and such composition as the pectin ,etc. in the cell wall change but forms the mucus(黏液). ①Distinguish :it was stained Red when adding Red reagent of ruthenium(钌红) . ②Example: In the epidermis cells of plantain(车前) , linseed(亚麻). 5. mineralization: Contain the silicon or the calcium ,etc. in the cell wall. ①Distinguish :The silicon can be dissolved in the hydrogen fluoride(HF), but does not dissolve in the acetic acid (醋酸)or denser sulphuric acid(浓硫酸). ②Example:Gramineous(禾本科) Stem and leaf ②protoplast cytoplasm nuclear membrance nucleus nuclear sap nucleolus chromatin plastids Organelle chloroplast leucoplast chromoplast vacuoles There are all life matter in the cell, called protoplast . Chloroplast:green little grains(leaf) leucoplast:achromatous(无色的) and global grains (immature organ ) Chromoplast:anomalous red,yellow,and orange grains(flower,fruit,seed) Three kinds of plastid can convert mutually. Vacuoles:there are many little vacuoles in the delicate cell , but in mature ones there is only one big vacuole can be seen which occupied most part of the cell. Mutually converting of plastic ③Ergastic Substance The vegetable cell in the life process, produces various non- life matter as a result of the metabolism activity, called Ergastic Substance. Ⅰ.starch grain: hilum , annular striation lamellae reserve starch: ①simple starch grain ②compound starch grain ③half compound starch grain 1.2.3.4.simple starch grain (1.lambdoidal(人字形的) hilum 2.short gap(短缝状) ) 5.compound starch grain Ⅱ.Inulins Fan-shaped and yellow Ⅲ.Proteins(aleurone grain) Those are composed together by protein crystal , spherical albuminous(多胚乳) body and amorphous(无定型的) stuffed gelatin. Add one drop iodine-potassium iodide TS , the protein turns yellow. Ⅳ.Fats and Fatty Oils Add several drops of Sudan Ⅲ TS(试液) oil droplet contained in the cell stained red. Ⅴ.Crystals ① calcium oxalate crystal solitary crystal : square-shaped, diamond, rectangle or double-conical octahedrons(双锥八面 体) acicular crystal : scattered or needle-like cluster cluster crystal: asteroid or clusters crystal sand: irregular, polyhedrons columnar crystal : long is cylindrical, the length approximately is above diameter 4 times ② calcium carbonate crystal (cysyolith钟乳体): like a string of grape [locate in Moraceae(桑科) or Acanthaceae(爵床科)] Calcium carbonate crystal Ⅰcysyolith ( tangent plane view )in fig leaf Ⅱ exterior view Besides , physiological active substance like enzyme , vitamin , auxin , antibiotic , tannins,etc. Two Division of Plant cells Cell division is necessary and play important role for embryo to little frond to mature frond( possessing root , stem and leaf , flower , fruit , seed). Three types:(一)mitosis (二)amitosis (三)meiosis ㈠mitosis ①interphase : the cytoplasm is denser , the nucleus is big , nuclear menbrane with the nuclear sap can be seen clearly. ②prophase There inside the nucleus emerge condensed granulose chromatin and then gradually become the clubbed chromosome. ③metaphase: the nuclear membrane , the nuclear sap disappear , the chromosome and the spindle fibers connect with each other , and arrange in the surface of the equator. ④anaphase: the centromere detaching ,each pair of chromatids set apart from the equatorial plate to move to the two poles, thereby to compose the independent daughter chromosome respectively. ⑤telophase : the two daughter chromosomes arrive at the two poles , chromosome gradually fall into slender , emerging of the nuclear membrane with nuclear sap again . Meanwhile , divide into two cells in the two poles. Mitosis 1.Interphase 2-4.prophase 5.metaphase 6-7.anaphase 8.telophase 9.two daughter cells ㈡amitosis Direct nuclear division and it is most simple and common type of division . (in lower plant) ㈢meiosis one especial mitosis , as a result , divide into four cells in process of sexual reproductive. 1.第一次分裂前期2.第一次分裂中期3.第一次分裂后期 4.第一次分裂末期5.第二次分裂前期 6.第二次分裂前期7.第一次分裂中期8.第二次分裂后期 9.第二次分裂末期10.胞质分裂 Review Questions 一.Definition Pit , plasmodesmata , protoplast , ergastic substance 二.simple answer 1.How about the composing of the cell wall? 2.what are included in cell wall characteristics? 3.which types has crystal?