* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 1 Cells Powerpoint Worksheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
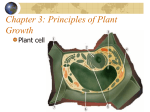
The cell Topic 1 Introduction • • • • • • The study of cells is called Cytology The cell is the smallest functional unit of life Cell theory Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cell parts and their functions Normal cell reproduction 1.1 Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of _______________________. 2. Cells are the ___________ units of life. 3. All cells come from ______________ cells Contributors to part 1 • ________________first described cells in 1665 using microscope he built. • A few years later, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek sees living cells and calls the______________. • In 1838, Matthias Schleiden states that ____________ are made of cells. • In 1839, Theodor Schwann states that animals are made of cells. Contributors to part 3 • _____________, in the 1880’s, chicken broth experiment showed that living organisms would not _______________y appear. Functions of life • All organisms, whether single cell (unicellular) or multicellular, carry out all the functions of life. • Metabolism nutrition • Growth excretion • Reproduction • Response • Homeostasis • Metabolism – all the ________ ________that occur in an organism. Energy conversion • Growth may be limited but is always there. • Reproduction involves ____________ molecules being passed to offspring. • Responses to __________ in the environment. • Homeostasis is maintenance of constant internal ________________. • Nutrition provides compounds to convert to ____________. • Excretion is the ________ of unneeded or toxic chemicals from an organism. Cells and Size • Cells are small enough to usually need a microscope to study them. • _____________ microscope is the most common and uses light passing through the cells to see them. • ______________ microscopes use electrons to form an image and have greater magnification than light microscopes. Relative size • • • • • • Cells (eukaryotes) 100 micrometers um Organelles 10 um Bacteria 1 um Viruses 100 nanometers nm Membranes 10 nm Molecules 1 nm Calculating size • Formula Magnification = size of the________/ actual size Limiting cell size • The surface area of a cell, compared to the volume of the cell, limits how large a cell will get. • The amount of_____________a cell needs to take in, as well as the amount of ________ and heat that a cell needs to get rid of, depends on the ___________ of the cell. • The surface of the cell, the ______________, controls how fast this can occur. • As a cell gets larger in volume, its surface area also increases, but at a much ________ rate. • Volume involves ________ the radius while surface area involves __________ the radius. • This means that the larger a cell gets, the smaller the surface area to volume ratio. • Eventually, the volume gets so large that the surface area can’t handle the traffic in and out and the cell stops ____________. Cell reproduction and Differentiation • Single cell (unicellular) organisms need to reproduce to create new organisms. • Multicellular organisms need to create new cells to grow and replace _____________ or old cells. • New cells in multicellular organisms need to ______________, which means change into a particular type of cell. • All cells have the same DNA, but they use or ______________ different parts of it to become different types of cells. • Once they become specialized, some cells (nerve, muscle) lose the ability to _________ themselves. • Different types of cells can accomplish more as a group than they could as individuals, the group can do more than the sum of its parts. • This is referred to as an __________ __________ Stem Cells • There are cells within organisms that retain their ability to ________ and ____________ into different types of cells. • These cells are called Stem Cells • Scientists discovered pluripotent or____________stem cells in the early 1980s. • Stem cells can produce different types of cells and also more stem cells. Stem Cell Research • ____________ _________is using stem cells to grow cells to replace cells damaged through disease or accident. • ____________ and ___________ are two diseases being treaded with nerve cells grown from stem cells. • Pancreatic cells are being grown to treat Diabetes Tissue specific Stem Cells • Certain tissue types have their own stem cells. • _____________ treated with blood stem cells. • ______________ disease treated with photo receptor cells in the eye. Ethical issues • Pluripotent stem cell research is being done using stem cells from embryos through _____________fertilization. • Some argue that this is taking a life. 1.2 Cell Structure Prokaryotes • • • • Much ______ than eukaryotes- 1 um or less. Much _______than eukaryotes- no organelles. Appeared on Earth ________. __________ are the major members of this group. Prokaryote structures • • • • • • Cell wall Plasma membrane Flagella – not all have them Pili Ribosomes Nucleoid region Cell Wall and Plasma Membrane • Cell wall ________ and maintains _____ of cell • Made of a carbohydrate-protein material called _____________________. • Plasma membrane is just _______the cell wall. • Controls movement of material in and out of the cell and plays a role in binary fission. • Inside the membrane is the cytoplasm. No ________________ in cytoplasm. Pili and flagella • Pili are hair like growths on the outside of the cell, used for _____________ as well as reproduction. • Some prokaryotes have a flagellum or flagella (plural) which are longer than pili and are used for ________________. Ribosomes • All Prokaryotes have them. • Site of ____________ synthesis. • Smaller than Eukaryote ribosomes, 70s vs 80s Nucleoid Region • The area (no compartment) where the _________ circular DNA chromosome is located. • Prokaryote DNA is not attached to __________ like eukaryote DNA are. • Some prokaryotes also contain _________, small circular pieces of DNA that are separate from the main chromosome. • Plasmids replicate independently of the main chromosome and are not needed for day to day activities. Binary Fission • Prokaryotes divide by process called binary fission. • First the chromosome (DNA) is ___________. • The two daughter chromosomes attach to different areas of the plasma membrane. • The cell elongates, fibers called ___________separate the two chromosomes, then the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryote Animal Cell Eukaryotes • Size ranges from 5-100 um • Contain ______________, membrane bound structures which perform specific functions for the cell. Eukaryote Plant Cell Eukaryote Organelles • • • • • • • • • Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Lysosomes ( not usually found in plant cells) Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Nucleus Chloroplasts ( only in plants and algae) Centrosomes vacuoles • Cytoplasm – the area inside the plasma membrane. The fluid part is called the ___________. • Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – A series of tubes/channels that _____________ materials throughout the cell. • Two types – Smooth ER and Rough ER Smooth ER • • • • • • Contains ____________ on its surface which: Production of lipids and phospholipids Production of _______ hormones Detoxification of drugs in the _________ Storage of ___________ ions in muscle cells Release of glucose by _________ Rough ER • Contain ____________ on their surface which give a rough appearance. • The ribosomes of the Rough ER make proteins to be transported _______ of the cell. • There are ribosomes not attached to the Rough ER which float freely in the cytosol. • These ________ ribosomes make proteins to be used by the cell. • Ribosomes are composed of two units of _______ that are made in the nucleolus Lysosomes • Lysosomes – sacs of ___________ (hydrolytic) enzymes, made by the __________________, that help break down proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. • They attach to old organelles or materials brought into the cell by _________________. Golgi Apparatus • Made of flattened sacs called ____________. • It collects, modifies, packages and distributes materials made by the cell. • The _____ side of the Golgi apparatus is near the Rough ER and it receives the products of the ER. • These products leave the Golgi Apparatus in small sacs called __________, at the _______ side. Mitochondria • Rod shaped organelle close in size to a ________ • Contain their own DNA, a _________ _________chromosome, similar to bacterial cells. • Contain their own ___________ that are 70s, similar to bacteria. • They have a _________ membrane, the outer being smooth and the inner having many folds called ___________. • Inside the inner membrane is called the _______. Mitochondria • The area between the two membranes is called the inner membrane space. • The folds (cristae) allow for increased ________ ______ for the reactions of the mitochondria to take place. • The reactions of the mitochondria are called ___________ ____________and create molecules called _____. Mitochondria Nucleus • _________ membrane enclosed area, called the nuclear envelope, where the DNA is located. • Contains _______ to allow movement into and out of the nucleus. • DNA is in pieces called _______________. • Different ___________ have different numbers of chromosomes. • DNA is the ___________ material of the cell and allows traits to be passed to offspring. • When not dividing, DNA is in a form called ____________, which is DNA and proteins called ____________. • Where the DNA wraps around 8 histones, an area is formed called a ________________. • Most eukaryote cells have a single nucleus. • Some, like _____ ______cells, have no nucleus. • Most nuclei also contain a dark area called a ____________ which makes ribosomes. Chloroplast • Found only in algae and plant cells (_________________). • Surrounded by a double membrane and about the size of a bacteria. • Has its own DNA and 70s ribosomes, just like the Mitochondria. • Contain flattened sacs called ____________ where the light absorption part of __________________ occurs. • Thylakoids are in stacks called Grana/ Granum • The fluid part of the chloroplast is called ____________ which contains enzymes for photosynthesis. • Like Mitochondria, Chloroplasts can reproduce themselves independently of a cell. Chloroplast Centrosome • Found in all eukaryotic cells. • Consists of a pair of ______________ at right angles to each other. • Centrioles make _____________ which provide structure and allow movement. • Also important for cell division. • Some higher evolved plants produce microtubules even though they lack centrioles. • Located close to the ____________. Vacuoles • Membrane bound ____________ organelles made by the Golgi Apparatus. • Store many different substances including food, water, waste, and toxins. • Plant cells have a huge one filled with water and enzymes, allows __________ for the plant. Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Eukaryote Plant vs Animal cells • Plant cell Animal cell cell wall no cell wall chloroplasts no chloroplasts Large central vacuole small or no vacuoles carbs stored as starch carbs stored as glycogen no centrioles centrioles Fixed angular shape rounded shape Extracellular Matrix (ECM) • Surrounds the outside of animal cells, composed of ___________ fibers and glycoproteins. • Allows cells to __________ to each other. • Allows ___________________ and coordinated action between cells ECM 1.3 Membrane Structure History • Since 1915, scientists have known membranes are made of _________ and ______________. • In 1935, Davson-Danielli model suggested a phospholipid __________ covered on both sides by a thin layer of protein. • In 1972, Singer-Nicolson model suggested proteins were inserted into the phospholipid bilayer and not a continuous layer. • They believed the phospholipids were ______, meaning they were very loosely attached to each other and could move around, and the proteins formed a _________ pattern within the bilayer. • Most of the new evidence came from the use of the ____________ microscope. Phospholipids • The main “backbone” of the membrane is made of a __________ layer of phospholipids. • Each phospholipid is composed of a three carbon molecule called _____________. • Two of the carbons have ______ ______(lipid) molecules attached to them. • The third carbon is attached to a highly _______ alcohol/phosphate group. • The fatty acids are non-polar and not soluble in water. (__________________) • The alcohol/phosphate group is polar and soluble in water. (______________) • This causes the phospholipids to align themselves with their polar “heads” ________ and their non-polar “tails” ___________. Phospholipid Cholesterol • Membranes must be fluid or __________ to function properly. • At various locations in the hydrophobic, or tail region of animal cells, there are cholesterol molecules. • They allow membranes to be properly flexible at a large range of __________________. • _______ membranes do not have cholesterol. Proteins • It is the proteins found in and on the membranes that allow for the great ________ of membrane function. • There are two major types of membrane proteins, __________ and ______________. • Integral proteins are ________________, meaning they have both polar and non-polar regions. Proteins • These proteins will have their non –polar hydrophobic regions near the ________ of the membrane (by the tails) and their polar hydrophilic regions near the edges. • Peripheral proteins are attached to the __________ of the membrane, often attached to an integral protein. Protein Functions • There are many different proteins which have 6 general functions: • Sites for __________ binding – have a specific shape exposed to the outside that will only fit a specific hormone. When hormone attaches, it changes the ______ of the protein, relaying a message inside the cell • Enzymatic action – proteins act as enzymes to catalyze reactions, attached to outside or inside of the membrane • Cell adhesion – allow cells to attach to each other permanently or temporarily. Gap and tight junctions Protein Function • Cell to cell communication - proteins with ______________ attached that provide identification for different species. • Channel for ____________ transport – allow substances to travel through the membrane from ________________concentration. • Pump for active transport – moves substances through membrane by changing shape using _____ for energy. Moves from ____________ 1.4 Membrane Transport • Passive and Active Transport Passive Transport • Does ______ require energy • Movement is from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Usually referred to as moving ________the concentration gradient. • Osmosis (water), or diffusion Simple Diffusion • Particles moving from high to low concentration. In biology, usually across a ________________. • Examples: ____________ moving from the blood into cells, __________ ________ moving from cells into the blood. Facilitated Diffusion • Movement across a membrane is facilitated by a __________ carrier ___________. • Carrier protein changes __________ but does not require energy. Osmosis • Osmosis is a type of diffusion that involves the passive movement of __________ across a partially ______________ membrane. • Water will move from an area of lower solute concentration (______________) to an area of higher solute concentration (_____________). Ease of movement • The _____ and ________ of a molecule determines how easily it can cross a membrane. • Small, non-polar molecules cross _________ (gases) • Large, polar molecules cross hardest.(______ and _________) Active Transport • Requires work to be performed and therefor requires ___________ (ATP) • It is the movement of a substance __________ the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. • Example: animal cells have a high concentration of ___inside and high _____outside. Sodium-Potassium Pump • 5 stages involved in moving Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradients: 1- A specific integral protein binds to ___sodium ions inside the cell 2. The binding of the sodium to the protein causes_________________to occur. ATP becomes ____. 3- Phosphorylation causes the protein to change shape, __________ the Na+ from the cell 4- ____ Phosphate ions outside the cell bind to the protein, which causes the _________ of the phosphate. 5- The loss of the phosphate returns the protein to its original shape, __________ the K+ into the cell. The Na+ P+ pump is used extensively in _______ signal transport. Endo and Exocytosis • These are processes that allow ___________ substances in and out of cells. • Endo is into the cell, while exo is out of the cell. • Both processes depend on the _________ of the cell membrane. Endocytosis • The membrane of a cell surrounds and engulfs an object, leaving it within a ____________ inside the cell. Exocytosis • The opposite of endocytosis, how the cell exports proteins is a good example of how this works. • 1- Proteins produced by ribosomes on the _________enter the lumen (inside) of the ER • 2- Protein exits the ER inside a _________ and enters the cis end of the Golgi Apparatus. • 3- As protein moves through Golgi, it is _________ then exits the trans end inside a vesicle. • 4. This vesicle moves to the cell membrane and fuses to release (__________) the protein from the cell. • https://youtu.be/DuDmvlbpjHQ 1.5 The Origin of Cells • • • • Cell Theory: All organisms are made of ____________cells Cells are the ___________ unit of life All cells come from other pre-existing cells • There are some problems with and exceptions to this theory. • How did the first cell arise? • _____________ showed that cells don’t spontaneously arise. His experiment: • He boiled nutrient broth • He put sterile broth into 3 flasks, one open, one closed and one with a water trap type seal. He allow time for _____________. • A sample from each flask was transferred to solid growth media (petri dish) and incubated. • The only flask that showed growth was the __________ one. Exceptions to normal • Multi ___________ cells of striated muscle, fungal hyphae and giant algae. • Very large cells with no compartments • ___________ • Where did the first cells come from. Before that discussion, we need to understand the transition from simple prokaryotes to complex eukaryotes. Endosymbiotic Theory • Presented by Lynn Margulis in 1981 • About 2 billion years ago, a ___________ cell began living inside another cell that had engulfed it (_______________) • This eukaryotic cell and the bacterial cell began a ______________ relationship. • Over time, the bacteria cell evolved into a __________________. Evidence • Mitochondria are: about the size of bacteria • divide by binary fission • divide independently of their cell. • have their own 70s ribosomes • have their own DNA, single strand loop like bacteria • have a double membrane from being engulfed. • ______________ also show the same evidence for endosymbiotic theory. • The protist ________ gets its energy by ingesting organic matter. When it eats algae, it starts photosynthesis to get energy. • The slug Elysia chlorotica is brown and eats things for energy when it is __________. • As adults they are green due to eating algae and using them to do ________________. • _______of mitochondria more closely resembles that of bacteria than eukaryotes. 1.6 Cell Division • The life of a cell is described by the _______ _______. • In most cases, a cell will ______, then divide into two identical cells called__________cells. • The cell cycle has a growth part as well as a division part. Cell Cycle Interphase • ____________ phase of most cell cycles • Composed of three parts, G1 (Gap 1) , S and G2 (Gap 2). • G1 major event is _________ of the new cells. • S major event is _____________ of the DNA • G2 major events are further growth as well as preparing for __________ (M phase). DNA starts to condense, organelles are copied, microtubules begin to form. Cyclins • Cyclins are _________ that help control a cells movement through the cell cycle. • Cyclins bind to cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), enabling them to act as ____________. • These enzymes allow the cell to move from G1 to S and from G2 to M. • Some cells will stop at G1 and stay there (G0), such as _________ and muscle cells. Mitosis – Nuclear division • During Mitosis, the replicated chromosomes are divided into two ___________ groups in preparation for cell division (_____________). • The two new cells should be identical to each other and are called _____________ cells. • Prior to Mitosis beginning, the DNA _______ to form chromosomes. • Chromatin – nucleosomes- solenoids – looped domains - supercoil chromosomes • During Interphase, each DNA molecule is wrapped around histone proteins to form _____________. • Nucleosomes coil into solenoids, then form looped domains and finally supercoil to chromosomes. • After replication, during the S phase of interphase, each chromosome has an identical twin, attached to the original by a____________. Each molecule is called a ______________ and together they are called _________ chromatids. Phases of Mitosis • • • • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Prophase • ____________ fibers continue to supercoil and form _______________. • Nuclear envelope (membrane) ____________ and _____________ disappears. • Mitotic ____________ (fibers) forms. • Each chromosome has a region of its centromere called a ______________ that the fibers attach to. • Centrosomes move to opposite poles Metaphase • Chromosomes move to the _______ (equator) of the cell, this is called the metaphase ______. • The chromosomes __________ lie on the plate • The microtubules, or spindle fibers do this. • The centrosomes are now at opposite poles. Anaphase • The shortest phase begins when the two sister chromatids of each chromosome ________. • The chromatids, now chromosomes, move toward _________ poles, toward centrosomes. • The shortening of the microtubules causes the movement. • At the end of this phase, each pole of the cell has a complete, ________ set of chromosomes. Telophase • • • • • • Chromosomes are at the ________. Nuclear envelope reforms Chromosomes begin to __________. _____________ reappears Spindle fibers disappear The cell elongates and is ready for ______________ Cytokinesis • In animal cells, a ___________ furrow forms • In plant cells, a cell _________ forms • Both processes result in the cell being divided into two ___________ cells with identical nuclei • Growth, development of embryos, tissue repair and asexual reproduction all involve ____________ Animal cell Plant cell Cancer • Cancer is when the cell cycle runs out of control. • The mass of cells created is called a __________. • A __________ tumor is located at the original site of formation. • A secondary tumor forms as a result of ______________ or spreading to other areas. • Mitotic ________ is ratio of cells undergoing mitosis compared to the number not. The larger the number, the faster the cancer is growing. Causes of Cancer • Areas of a gene can change (mutate) to become ______________. • Oncogenes contribute to cancer formation. • Oncogenes can be formed by outside agents called ______________. • Cigarette smoke is a mutagen. • There is a _____________ correlation between smoking and cancer.