* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate_Change_Power_Point
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
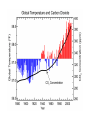
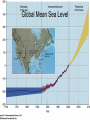
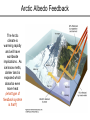
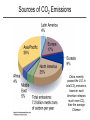
Climate Change Amy Urling Science Teacher Northfield High School Hurricane Irene (August 2011) Ms. Urling’s Disclaimer • Be careful where you get your information: (for example: don’t rely on websites such as DHMO.org) • All of the information presented in this Power Point are facts and come from: – – – – science textbooks scientific government organizations scientific peer-reviewed journals or Ms. Urling’s own observations. • Watch the video: http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/101videos/global-warming-101 In 2011, there were more than a dozen weather events costing more than $1 billion Tornadoes Glacier National Park - Montana • In 1850, Glacier National Park had 150 glaciers. Today it has only 25. • Scientists predict all the glaciers will be gone by 2020 Mt. Kilimanjaro Glacier Bay National Park - Alaska Margerie Glacier Glacier Bay National Park (July 2009) Ecotourism Urling 09 Denali National Park - Alaska The tree line in Denali National Park has increased in elevation. Taiga forests are now found where tundra used to be prevalent. Urling 09 Taiga Urling 09 Tundra Changes in Ecology Because of warmer winters in the West, pine beetles are killing large areas of forests in Wyoming, Montana, Colorado, California and Idaho Urling 08 Flat Creek Ranch, Wyoming – August 2008 Global Mean Sea Level Polar Bears and Disappearing Sea Ice Polar bears were the first species listed on the Endangered Species List (2008) due to the effects of global warming Why do we look at long term trends and not just 3 – 4 years of data? Polar Bears and Disappearing Sea Ice Polar bears were the first species listed on the Endangered Species List (2008) due to the effects of climate change Arctic Albedo Feedback The Arctic climate is warming rapidly and will have worldwide implications. As ice/snow melts, darker land is exposed which absorbs even more heat (what type of feedback system is that?) Weather vs. Climate • Weather: day-to-day variations in temperature, air pressure, wind, humidity, and precipitation – all mediated by the atmosphere • Climate: result of long-term weather patterns in a region • Climate Change: does not involve daily changes in weather – it involves changes in long-term weather patterns! • Climate Change vs. Global Warming??? Misconceptions About Climate Change Some people might say that global warming isn’t true because: • It snowed on April 27, 2010. • Vermont had a really cold summer last year. • There was only one major hurricane this year. • This past winter was colder compared to the year before. Other Factors Affecting Global Temperatures • Cloud cover: cooling • Particulates: cooling • Volcanic activity: cooling – When Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines in 1991, sulfur dioxide and other gases emitted into the atmosphere circled the globe, reduced sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface, and decreased levels of protective ozone for 15 months Natural Causes of Climate Change • Why does climate change naturally? – The Earth is like a wobbling top with an elliptical orbit around the sun. • Three kinds of changes occur. – (1) Earth is unable to keep its poles at a constant angle in relation to the sun. The wobble makes a complete cycle in 26,000 years. – (2) The tilt of wobble also varies over a period of 41,000 years – (3) The elliptical orbit around the sun also changes. Sometimes it is a more extreme ellipse; other times it is closer to a circle and this occurs over 100,000 years. CO2 Data from Mauna Loa, Hawaii 401.52 Why does the graph have a zig-zag pattern? How Do We Know What Temperatures and Gas Levels Were Like in the Past? • Tiny bubbles of ancient atmosphere in ice cores extracted from ancient glaciers • Analyzing radioisotopes in rocks and fossils • Plankton ocean sediment • Pollen • Tree rings • Historical records Carbon Dioxide and Temperature Levels of CO2 correlate directly with temperature Sources of CO2 Emissions China recently passed the U.S. in total CO2 emissions, however, each American releases much more CO2 than the average Chinese Intergovernmental Panel of Climate Change (IPCC) • Established in 1988 by the United Nations and World Meteorological Organization to document past climate changes and project future changes based on science. 195 countries are members. • Issued reports indicating that: – It's "extremely likely (95% probability)," that human influence, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, has been the dominant cause of global warming over the past several decades. – Warming is “unequivocal,”. The Earth is the hottest it has been in 400 years. – Arctic temperatures are rising faster than the rest of the Earth. – Glaciers and sea ice are melting at increasing rates. – Not-so-permanent permafrost is melting, releasing CO2 and CH4 – Sea level is rising and oceans are becoming more acidic. – Warmer oceans will fuel stronger storms. – Plants and animals are more vulnerable than humans. – We must phase out fossil fuels by 2100. IPCC Assessments • Global climate change IS occurring • Human activities ARE influencing global climate change • The Earth’s temperature will increase by 2.4 – 5.4°C (4.5 – 9.7°F) by 2100 (some areas may become warmer, some areas may become colder). • Global impacts will be unprecedented and severe – Heat waves more frequent and last longer – Widespread water concerns – increase in extremes (floods and droughts) – Rising sea levels – Increase in storm intensities – Significant losses in crop yields – Mass migration of people – 2–20% of species are likely to be at increased risk of extinction – Human health effects (diseases) Potential Effects of Climate Change • Rising Sea Levels – A major warming could increase sea levels because of : • 1. Expansion of liquid water as water warms • 2. Melting of ice sheets on land whose waters then flow into the ocean. – About half the people on Earth live in coastal areas. – As population rises, the number of people vulnerable to coastal flooding increases. • Rise in sea level could: – Threaten island nations (like the Maldives) – Increase coastal erosion on open beaches and cause property loss. – Lead to loss of coastal wetlands – Threaten ground water supply in coastal communitie The world’s smallest nation, Tuvalu, is only 4.5 meters above sea level More Potential Effects of Climate Change • Agricultural Productivity – Globally, agriculture production is likely to increase in some regions and decline in others. – Some areas may become ore arid. – A climate shift could have serious negative effects on food production. • Human Health Effects – Health status of millions of people could potentially be affected through • Increases in malnutrition • Increased deaths, diseases, and injury due to extreme weather events • Increased diarrhea diseases • Increased frequency of insect-born diseases How could climate change affect Vermont? • • • • • • • • • The Facts About Dealing With Climate Change • • • • The problem is occurring on a global level The effects will last a long time The problem is a long-term political issue The harmful and beneficial impacts are not spread evenly • Many actions that might reduce the threat of climate change, such as phasing out fossil fuels, are controversial because they can disrupt economies and lifestyles • It’s definitely an uphill battle Comment on one of the following quotes: “It’s about time for denial to come to an end. We’re no longer talking about theory, about computer models of what might happen. We’re talking about what is happening, all around the world, with almost unimaginable speed” Bill McKibben (world-famous environmental writer from Middlebury, VT) “If scientists are right about global warming, then acting to slow climate change is acting responsibly. If they are wrong, then we will have reduced air pollution, protected human health, reduced dependence on foreign oil, made the U.S. economy less vulnerable to oil shocks, and become a worldwide leader in new energy technologies. What are we waiting for?” Fred Krupp president of Environmental Defense