* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 2A – Structure and Function - Spring
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
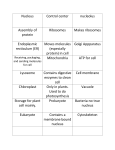
Ch. 2A – Structure and Function Lesson 1 – Cells and Life (pgs. 42-47) *Scientists whose discoveries led to the development of Cell Theory: Robert Hooke – English scientist who used a microscope to view cork cells; gave cells their name (1665) Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Dutch scientist who viewed unicellular organisms in pond water (1674) Matthias Schleiden – German scientist who looked at plant cells (1838) Theodor Schwann – German scientist who looked at animal cells (1839) Rudolph Virchow – German doctor who proposed all cells come from preexisting cells (1855) Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from preexisting cells. Basic Cell Substances *Water main ingredient in any cell; makes up 70% or more of a cell’s volume surrounds cells helps maintain homeostasis by insulating cells dissolves substances so they can move into and out of cells *Macromolecules – substances formed by joining many small molecules together, like cars of a train; enable cells to function Nucleic acids – long chains of nucleotides joined together; contain genetic information Proteins – long chains of amino acid molecules; play a role in structural support, transport, chemical breakdown of substances, and communication in a cell Lipids – large macromolecules that do not dissolve in water; play a role in energy storage, protective membranes, and communication in a cell Carbohydrates – made up of one, two, or a long chain of sugar molecules; play a role in energy storage, structural support, and communication in a cell Lesson 2 – The Cell (pgs. 50-57) (Ch. 2A - Structure and Function continued…) Cell Shape and Movement Cell membrane – flexible covering that protects the inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell Cell wall (plants, fungi, bacteria, some protists) – a stiff structure outside the cell membrane Cell appendages o Flagella – tail-like appendages that whip back and forth to move the cell o Cilia – short, hair-like structures that move a cell or move molecules away from a cell Cytoplasm – fluid inside a cell that contains salts and other molecules Cytoskeleton – network of threadlike proteins that are joined together to form a framework inside the cell to give it shape and help it move Cell Types Prokaryotic – cells without a nucleus; genetic material is not surrounded by a membrane; most are unicellular (ex. bacteria cells) Eukaryotic – cells have a nucleus; genetic material surrounded by a membrane; larger than prokaryotic cells (ex. plants, animals, fungi, protists) Organelles – structures in cells surrounded by membranes; have specialized functions Nucleus – part of a eukaryotic cell that directs cell activities and contains genetic information stored in DNA (which is organized into structures called chromosomes) o Nucleolus – found in the nucleus; makes ribosomes Manufacturing Molecules Ribosomes – make proteins; not surrounded by a membrane Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – spreads from nucleus throughout most of the cytoplasm o Rough – has ribosomes on its surface o Smooth – no ribosomes; makes lipids such as cholesterol and helps remove harmful substances from the cell Processing energy • Mitochondria – release energy during chemical reactions; this energy is stored in high-energy molecules called ATP o ATP – fuel for cellular processes like growth, cell division, and material transport Chloroplasts (plants and some protists) – membrane-bound organelles that use light energy to make food – a sugar called glucose, which contains stored energy—from water and carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis Processing, Transporting, and Storing Molecules Golgi apparatus – prepares and packages proteins into vesicles; looks like a stack of pancakes o Vesicles – tiny, ball-like organelles that transport substances from one area of a cell to another Lysosomes (animal cells) – contain substances that help break down and recycle cellular components Vacuoles – organelles that store food, water and waste material; plant cells usually have one large vacuole; some animal cells have many small vacuoles