* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BSC 1005L - MDC Faculty Web Pages
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
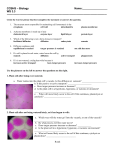
BSC 1005L (General Education Biology Laboratory, Professor Chiappone) LAB#4: DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS, PLANT CELLS, AND TONICITY (Symbiosis, 2007) PRACTICE QUIZ #4 QUESTIONS 1. Diffusion is an example of ______. (a) phagocytosis (b) exocytosis (c) active transport (d) endocytosis (e) passive transport 2. Diffusion ______. (a) is the result of the potential energy of atoms (b) is driven by an input of cellular energy (c) requires an input of cellular energy (d) occurs when particles spread from areas where they are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated (e) proceeds until equilibrium is reached 3. Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires ______ and moves a substance ______ its concentration gradient. (a) energy and transport proteins . . . down (b) energy . . . down (c) transport proteins . . . down (d) energy and transport proteins . . . against (e) transport proteins . . . against 4. Osmosis can be defined as ______. (a) the diffusion of water (b) the diffusion of nonpolar molecules (c) active transport (d) the diffusion of a solute (e) endocytosis 5. A balloon permeable to water but not to glucose contains a 10% glucose solution. A beaker contains a 5% glucose solution. Which of the following is true? (a) The solution in the beaker is hypertonic relative to the solution in the balloon. (b) The solution in the balloon is isotonic; the solution in the beaker is hypertonic. (c) When placed in the beaker, the balloon will lose water by osmosis. (d) When placed in the beaker, the balloon will experience neither a net gain nor a net loss of water. (e) The solution in the balloon is hypertonic relative to the solution in the beaker. 6. When two solutions that differ in solute concentration are placed on either side of a selectively permeable membrane, and osmosis is allowed to take place, the water will ______. (a) exhibit a net movement to the side with lower water concentration (b) exhibit a net movement to the side with higher water concentration (c) exhibit a net movement to the side with lower solute concentration (d) exhibit an equal movement in both directions across the membrane (e) not cross the membrane Page 1 of 4 7. A cell that neither gains nor loses water when it is immersed in a solution is ______. (a) isotonic to its environment (b) hypertonic to its environment (c) hypotonic to its environment (d) metabolically inactive (e) dead 8. Some protozoans have special organelles called contractile vacuoles that continually eliminate excess water from the cell. The presence of these organelles tells you that the environment ______. (a) is isotonic to the protozoan (b) is hypotonic to the protozoan (c) is hypertonic to the protozoan (d) contains a higher concentration of solutes than the protozoan (e) none of the above 9. You are adrift in the Atlantic Ocean and, being thirsty, drink the surrounding seawater. As a result, ______. (a) you quench your thirst (b) your cells lyse, due to the excessive intake of salt (c) your cells become turgid (d) you dehydrate yourself (e) none of the above 10. If placed in tap water, an animal cell will undergo lysis, whereas a plant cell will not. What accounts for this difference? (a) expulsion of water by the plant cell's central vacuole (b) the relative impermeability of the plant cell membrane to water (c) the relative impermeability of the plant cell wall to water (d) the fact that plant cells are isotonic to tap water (e) the relative inelasticity and strength of the plant cell wall 11. In a hypotonic solution, plant cells will ______. (a) undergo plasmolysis (b) pump out excess water (c) become flaccid (d) burst (e) become turgid 12. Which of the following processes could result in the net movement of a substance into a cell, if the substance is more concentrated in the cell than in the surroundings? (a) active transport (b) facilitated diffusion (c) diffusion (d) osmosis (e) plasmolysis Page 2 of 4 13. Active transport ______. (a) uses ATP as an energy source (b) can move solutes against their concentration gradient (c) requires the cell to expend energy (d) can involve the transport of ions (e) all of the above 14. Examine the cells below. Cells with a higher concentration of ions than the surrounding medium tend to ______. (a) stay about the same size and shape (b) expand (c) shrink (d) undergo mitosis (e) merge with other cells 15. The concentration of solute affects the rate of osmosis? (a) False (b) True 16. What would you expect to happen to a tomato plant if you watered the soil around it heavily with brine? (a) Nothing would happen. (b) The plant would wilt. (c) The plant would exhibit increased turgidity (stiffness). (d) The plant would get up and walk away. 17. A solution that contains less dissolved material such as salts and sugars than does an organism living is ______ to that organism. (a) iso-osmotic (b) tonic (c) hyper-osmotic (d) hypo-osmotic (e) turgid Page 3 of 4 18. A solution that contains more dissolved material such as salts and sugars than does an organism living is ______ to that organism. (a) iso-osmotic (b) tonic (c) hyper-osmotic (d) hypo-osmotic (e) turgid 19. What would you happen to the central vacuole of the cells of a freshwater plant place in salt water? (a) Nothing would happen. (b) The central vacuole would increase in size. (c) The central vacuole would decrease in size due to the loss of water. (d) The central vacuole would get up and walk away. 20. What is the name for differential diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane? (a) tonicity (b) diffusion (c) turgidity (d) active transport (e) osmosis Page 4 of 4