* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download diffusion lab - traceypd2013
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
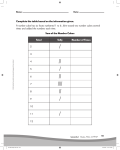
Tracey Zhang 3B Pictures Cell Division Worksheet 2. What evidence is there that HCl diffuses into the cubes? From the agar cubes, it can be seen that the HCl diffused into it because the pink color of the cube shrunk (by approximately 1 cm per dimension). This is important because before the cube was placed in HCl, almost the whole cube was pink. This pink color is caused by phenolphthalein, which is pink only in the presence of a base and not an acid. However, after placing it in HCl, an acid, the pink color began shrinking, meaning that the phenolphthalein is in the presence of an acid, namely HCl. 3. What happens to the diffusion rate as a cell gets larger? The diffusion rate remains the same because for each cube, HCl penetrated only 1 cm in each dimension after 10 minutes. Thus, the diffusion rate of each cube stayed the same, showing that size does not affect the diffusion rate. 4. What happens to the surface area-‐to-‐volume ratio as a cell gets larger? As the cell gets larger, the surface area-‐to-‐volume ratio becomes much smaller, with the ratio shrinking from 6:1 (at dimensions of 1 cm x 1cm x 1 cm) to 2:1 (at dimensions of 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm). This occurs because the volume is growing at a rate faster than the surface area. 5. Propose a hypothesis to explain why large organisms have developed from more cells rather than larger cells. Large organisms developed from more cells rather than large cells because a larger cell places more demands on its DNA. Furthermore, the cell’s volume eventually exceeds the surface area of the cell, which is unhealthy for the cell because its volume determines the rate the cell uses up materials. A larger cell means that it uses up material at a quicker rate. However, the surface area, or the cell membrane, is not increasing as quickly as a volume. The cell membrane is where all the necessary materials enter. The different rates at which the surface area and volume increases at consequently means that the surface area cannot keep up with the burgeoning demands of the cell. Thus, it becomes more efficient for cells to divide themselves up rather than grow at an unlimited pace.