* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.3 Cell Membrane (p. 81) 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
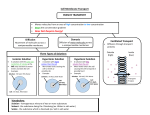
Name _____________________________ Bio PreAP/GT 3.3 Cell Membrane (p. 81) Cell Membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. The cell membrane, or the _____________ membrane, forms a boundary between a cell and the outside environment and controls the passage of materials into and out of the cell. • A phospholipid molecule has three parts: o Head composed of ____________ __________ and _____________ Charged [polar] ________________ - forms _______________ bonds with water o 2 ____________ ___________ tails Nonpolar ________________ – attracted to each other and repelled by water o Arranged as a ______________ polar _________________ on the outside nonpolar ______________ in the middle • Sketch figure 3.1 in the space provided. Label, proteins, protein channel, phospholipid, cholesterol and carbohydrate chain • • • Embedded in the plasma membrane are cell surface ____________ that allow larger materials to pass into and out of the cell. o These proteins are called _____________. ________ _________ _______ describes arrangement of molecules in membrane. o Flexible; not rigid o Membrane behaves as a fluid ______________ ________________ - membrane allows some, but not all, materials to cross. Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell membrane. • _____________ – protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response. o Recognizes and binds to only certain molecules – ligand. o Causes them to change shape. • _____________ receptor – within the cell • _____________ receptor –located in the cell membrane 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport. • ________________ transport – movement of molecules across a cell membrane _________________ energy input from the cell o _____________________ - movement of molecules in a fluid or gas from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. It take place wherever there is a difference in __________________ within the solution. __________________ _______________ - difference in concentration Particles of a solute and solvent are constantly moving from areas of _______ concentration to areas of ___________ concentration. These particles continue to move until the concentrations are equal or reach . . . ______________________. o ____________________ - diffusion of water molecules from high to low across a semipermeable membrane If a solution has a higher concentration of dissolved particles, then it will have a _________concentration of water molecules in the same solution the increased pressure that results from an increase of water is called ______________ ___________________ Refer to the figures below to answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. concentration of sucrose is higher in compartment ? concentration of water is higher in compartment ? osmosis occurs with movement from _?_ into _?_ diffusion of sucrose will/will not occur. level of column A will increase/ decrease/ remain the same. level of column B will increase/ decrease/ remain the same. *A column of fluid develops which creates a pressure that prevents the solution from increasing its volume further. Osmotic pressure has the effect of pushing water molecules of compartment A back into B. At this point, the number of water molecules moving in and out of compartment A is equal, so _______________________ exists. A. The cell solution is said to be ____________________ when there is a ______________ concentration of solute in the environment than that in the cell. Thus, the environment solution is said to be ____________. Water will move _______________ the cell. This is the shrinking of the cell due to water leaving the cell. . . _______________________________. B. The cell solution is said to be ____________________ when there is a _______________ concentration of solute in the environment than that in the cell. Thus, the environment solution is said to be _____________. Water will move ___________ the cell. This is the bursting of the cell due to water entering the cell. . . ______________________________. C. A cell is said to be _________________ when the concentration of solutes in the environment and in the cell are the _________________. Equal amounts of water will move _____________ and _________________ the cell. o Do you understand Osmosis? Cell (compared to beaker) hypertonic or hypotonic Beaker (compared to cell) hypertonic or hypotonic Which way does the water flow? in or out of cell o ________________ _________________ - diffusion of molecules across a membrane through transport proteins. Examples: Flasks X, Y, and Z contain solutions with different concentrations of the solute NaCl. Flask X has 0.5% NaCl, Y has 0.9% NaCl, and Z has 1.5% NaCl. Red blood cells (0.9% NaCl) will be placed in each flask. Flask X _____% of NaCl in flask _____% of water in flask _____% of NaCl in red blood cells _____% of water in red blood cells The environment solution is _______ and the cell solution is __________ , therefore water will move ______ the cell. Flask Y _____% of NaCl in flask _____% of water in flask _____% of NaCl in red blood cells _____% of water in red blood cells The environment solution is _______ and the cell solution is __________ , therefore water will move ________ the cell. Flask Z _____% of NaCl in flask _____% of water in flask _____% of NaCl in red blood cells _____% of water in red blood cells The environment solution is _______ and the cell solution is __________ , therefore water will move _____ the cell. 3.5 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Proteins can transport materials against a concentration gradient. • • • Cells must have a way to maintain concentrations of important food molecules at a level different from the concentration level outside the cell. Active transport uses __________ to transport particles through a membrane _________ the concentration gradient. An example of an active transport channel is the _____________-______________ pump. ____________ is required. o ___________________ is the taking in of particles into a cell by engulfing them in a membrane. o Two types: _________________________ is the taking in of liquid or dissolved materials. _________________________ is the taking in of large solid materials. o ____________________ is the removal of wastes out of a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane