* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12 Units of Heredity
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
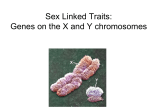
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
3/4/13 Chapter 12 12. Units of Heredity Units of Inheritance • Genes • Sex-‐linked traits • Pedigrees • Anuploidy • Chromosomal mutaCons 2 1 3/4/13 QuesCons: • What kind of traits are heritable? • How can we tract heritable diseases within families? • What are some ways chromosomal changes can cause mutaCons? 3 Heredity • Trait inheritance • The transmission of traits from parents to children • Inherit genes (units of heredity) from parents • Inherit traits from parents 4 2 3/4/13 GeneCc Disorders • GeneCc disorders may be recessive or dominant • What is the probability that two carriers of the recessive Sickle Cell Anemia gene (Ss) will have a child with sickle cell anemia? • What is the probability that someone with the dominant HunCngton disease gene (Hh) will have a child with HunCngton disease? 5 Inheritance of recessive genes • Sickle Cell Anemia – Recessive trait – Need two copies ¼ (25%) chance of having a child with sickle cell anemia 6 3 3/4/13 Inheritance of dominant genes • HunCngton’s disease – Dominant trait – Need one copy ½ (50%) chance of having a child with HunCngton’s 7 Sex-‐linked genes • Found on the X chromosome (usually) • X-‐linked disorders mostly affect male children. Why? • Examples: red-‐green colorblindness, hemophilia 8 4 3/4/13 Inheritance of colorblindness • Normal mom (XXb) x Normal dad (XY) • The mom is a carrier for colorblindness 9 X Chromosome InacCvaCon • Females have 2 the copies of x-‐ chromosome genes • SomeCmes have to turn off the second chromosome for normal expression – Barr Body 10 5 3/4/13 Mosaics -‐ Calico Cats Xo/-‐ = Orange Xb/-‐ = Black -‐/-‐ = White; Double InacCvaCon Calico X-‐ Inactivation, University of Miami 11 GeneCc disorders • Why are recessive disorders more common among relaCvely inbred populaCons? • Achondroplasia (dwarfism) – is caused by a dominant allele • If two parents are “lijle people” (or dogs), will all children also be affected? Explain. 12 6 3/4/13 Pedigree • Family tree showing inheritance • Useful in tracking phenotypic expression • However: – Requires mulC-‐ generaCon data – MulCple individuals per generaCon 13 Pedigree • Allows us to infer carriers of different alleles • Based on the expression in earlier and later generaCons 14 7 3/4/13 15 Aa x Aa A a A a Aa aa AA Aa Outcome: • 1 Homozygous dominant (not albino • 2 Heterozygous (not albion, but carriers) • 1 Homozygous recessive (albino) 16 8 3/4/13 17 Royal Families of Europe 18 9 3/4/13 Aneuploidy • Having an extra copy of a chromosome 19 Aneuploidy (Trisomy 21) 20 10 3/4/13 Polyploidy • More than two complete sets of chromosomes • Triploid • Tetraploid 21 Importance to Fish farming • Triploid fish – Low reproducCon rate – Low success of ferClizaCon – High growth rate 22 11 3/4/13 23 Aneuploidy and Cancer • Aneuploidy can occur during mitosis – Has less of an effect because cells can be eliminated (final check point of mitosis) • However if it goes unchecked can lead to cancer forming cells – Loss of cell cycle control 24 12 3/4/13 Chromosomal structural changes • Physical changes can also lead to mutaCon – By changing the geneCc informaCon stored in the chromosome. Dele=on Inversion Transloca=on Duplica=on 25 DeleCon • Segment of DNA removed • Chromosome is now missing some genes • If passed along offspring will have only a single copy of deleted genes; express mutaCons 26 13 3/4/13 DeleCon – FainCng Goats • Temporary Muscle Rigidity – Missing gene causes muscles to temporarily lock when startled • Congenital Myotonia • Also found in humans, and other mammals 27 28 14 3/4/13 Inversion • SecCon of a chromosome is taken out and flipped • Can affect genes being turned on and off correctly 29 Williams Syndrome • Impressive verbal & social skills • Lack social inhibiCon • “Elfin” Syndrome – Because of resemblance to good natured elf/fairy characters in folklore – Grin • May suffer for a range of Developmental issues – Severity varies with the size of the inversion 30 15 3/4/13 Balanced TranslocaCon • Crossing-‐over between non-‐ homologus chromosomes • ReorganizaCon of genes on chromosomes • Responsible for some cancers 31 Unbalanced TranslocaCon • When passed along to offspring • Cause extra/ missing copies of genes • Without causing Aneuploidy 32 16 3/4/13 DuplicaCon • SecCons of the chromosome are copied – Inserted next to the original • Or into another chromosome (translocaCon) 33 Tandem Repeats • Duplicated regions oren can keep duplicaCng • Causing a build up of repeats • Short repeats in order are called tandem repeats • An increasing number of repeats within one gene (Runx-‐2) create a longer snout • Bull Terriers over 60 years 34 17 3/4/13 Tandem Repeats Lots of DuplicaCons Few DuplicaCons 35 Point MutaCons • A Single NucleoCde Change – InserCon/DeleCon – Switch • Can have a large effect on phenotype • More in the next chapter… 36 18 3/4/13 QuesCons: • What kind of traits are heritable? • How can we tract heritable diseases within families? • What are some ways chromosomal changes can cause mutaCons? 37 19