* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction - San Jose State University
Myron Ebell wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
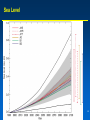
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
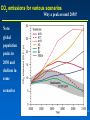
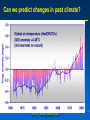
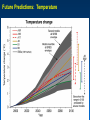
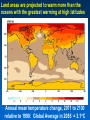
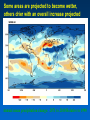
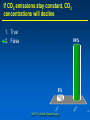
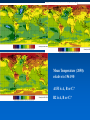
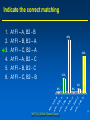
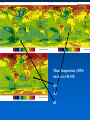
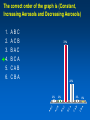
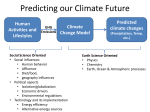
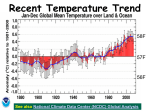
MET 112 Global Climate Change - Lecture 12 Future Predictions Eugene Cordero San Jose State University Outline Scenarios Global Models Future Predictions 1 MET 112 Global Climate Change Climate Change and humans Anthropogenic increases in – greenhouse-gas concentrations – sulfate aerosols due to anthropogenic emissions Emission scenarios have been developed Changes in solar irradiance and volcanic aerosols – Unpredictable and difficult to model 3 MET 112 Global Climate Change Q: How do we predict what the future climate will be like? A: We use global models of the earth system Sequence of Steps 1. Estimate future GHGs concentration 2. Using future GHG levels, calculate what future climate (e.g. temp, precip) will be like. 3. Assess the uncertainty of the predictions Calculation of Future CO2 Concentrations CO2 Emissions -How much is going into atmosphere Carbon Cycle Model – Simulates atmosphere-biosphere and atmosphere-ocean interactions CO2 Concentration How much remains in MET 112 Globalatmosphere Climate Change 8 Carbon Cycle Models Atmosphere/ocean and atmosphere/biosphere interactions not well understood Model calculations contain uncertainty; the largest uncertainty: – Future uptake of carbon by the biosphere – Future uptake of carbon by the oceans 10 MET 112 Global Climate Change Past and Projected Future CO2 (ppm) Parts per million Concentrations (Back-Up) Observations Model projections 12 MET 112 Global Climate Change What factors affect future CO2 levels? Global Population Type of energy generation – Fossil intensive – Renewable energy Growth of Economy Type of Economy – Material based – Service and information based Cooperation among countries – More homogeneous - share technologies – More isolated - larger divide between rich/poor countries Scenarios Emission Scenarios: Developed to account for range of possible future worlds SRES (special report on emission scenarios) Scenarios (1) Scenarios (2) A1 storyline – World of rapid economic growth – Population peaks 2050 – Different branches dependent on energy type/use A1FI – Fossil intensive – continued dependence on coal/oil A1T – Non-fossil intensive energy use (Technology) A1B – Balance between fossil and non-fossil A2 storyline – Heteorogenous world –technologies are not shared across borders, – population continues to increase 18 MET 112 Global Climate Change Scenarios (3) B1 storyline – Similar population as A1 – Global exchange/cooperation – Change in economic structures from product oriented to service oriented. – Focus on social and economic sustainability B2 storyline – Population like A2 – Similar environmental and social focus – More regionally oriented (not as much exchange between countries). MET 112 Global Climate Change 20 CO2 emissions for various scenarios Why a peak around 2050? Note: global population peaks in 2050 and declines in some scenarios 22 MET 112 Global Climate Change Projected CO2 Concentrations for Various Scenarios Note that even the low-emission scenarios result in greatly increased CO2 concentrations by the year 2100 – Max concentration (of scenarios shown): 970 ppm – Min concentration (of scenarios shown): 550 ppm – (Compare with current value: 370 ppm) 26 MET 112 Global Climate Change Climate Model A climate model is a mathematical representation of the physical processes that control climate – Basically everything that affects climate – Sun, atmosphere (greenhouse gases, aerosols), hydrosphere, land surface, cryosphere Equations are very complicated – Some of the world’s largest supercomputers are running climate models 28 MET 112 Global Climate Change Model Schematic Changes in greenhouse-gas concentrations and changes in albedo due to aerosols Climate Model Climate change (i.e. temperature, MET 112 Global Climate Change precipitation etc.) 30 Model Sensitivity Models (like the atmosphere) are sensitive systems. They can respond differently to the same radiative forcing, e.g., a doubling of CO2 – This means that different models give different answers to the same problem – Thus, we use a range of models to determine the range of possible future scenarios. 32 MET 112 Global Climate Change Model Verification: Can it be done? Before you can trust any of these models, they must be verified. – We can use past climate as a test. If your model can simulate the past climate, then there is a reasonable chance that the model can accurately predict future climate. 34 MET 112 Global Climate Change Can we predict changes in past climate? 35 MET 112 Global Climate Change Volcanoes, changes in solar radiation etc. Volcanoes, solar and humans Human emissions (CO2 etc.) What conclusions can you infer from these model experiments? 1. 2. These experiments demonstrate that .. no . ar e N at u ra l fa c to rs fa c ra l at u N to rs ar e th e of in g MET 112 Global Climate Change la r.. . la s en th e of Th e w ar m w ar m e Th 0 of 70 ... ... 0% 0% 0% 0% in g 1. The warming of the entire 20th century is largely due to humans 2. The warming of the last 50 years is largely due to humans. 3. Natural factors are largely responsible for the warming of the 20th century 4. Natural factors are not important in the early 20th century, but more important in the last part of the 20th century. 39 Climate models MET 112 Global Climate Change 2. .. ic t pr ed tt y di c on l pr e an C th e 20 th ... er ... an ic tv Sh ow tu no re A 0 of 70 th a se fu l ol c fo r pr ed . .. 4. he 3. an 2. Are not useful for predicting the temperature changes observed during the 20th century. Show that volcanic eruptions and changes in sunlight are responsible for most of the changes observed over the 20th century. Can predict the 20th century observed temperature changes with natural factors only. Can only predict the 20th century observed temperature changes when they include both 0% 0% 0% 0% human and natural contributions. C 1. 40 What conclusions can you infer from these model experiments? 1. Models can reasonably predict temperature variations over the last 150 years. 2. Most of the observed warming in the past 50 years is attributable to human activities. Future Predictions: Temperature 42 MET 112 Global Climate Change Notes on Temperature Projections Projected Warming: 2000 – 2100 ranges from ~1.4°C to ~5.8°C. Curves represent warming produced for seven scenarios by a model with average sensitivity. Each bar on the right represents a range of warming produced – by models of differing sensitivies for a specific scenario. 44 MET 112 Global Climate Change Land areas are projected to warm more than the oceans with the greatest warming at high latitudes Annual mean temperature change, 2071 to 2100 relative to 1990: Global Average in 2085 = 3.1oC Some areas are projected to become wetter, others drier with an overall increase projected Annual mean precipitation change: 2071 to 2100 Relative to 1990 Sea Level 49 MET 112 Global Climate Change Sea Level Rise Annual mean precipitation change: 2071 to 2100 Relative to 1990 50 MET 112 Global Climate Change Recent Sea Level Changes 51 MET 112 Global Climate Change Future predictions: main changes in climate Higher temperatures - especially on land – Arctic shows the largest warming Hydrological cycle more intense – More rain overall Sea levels rise – Why? Changes at regional level –hard to predict More intense weather (extremes) – Floods, MET droughts etc. Change 112 Global Climate 53 Questions 1. Based on the A1FI scenario, what is the predicted CO2 concentration, temperature change and sea level change in 2100? 2. Based on the A1T scenario, what is the predicted CO2 concentration, temperature change and sea level change in 2100? 3. Explain the differences. 54 MET 112 Global Climate Change Based on the A1FI scenario, what is the predicted CO2 concentration in 2100? 550 ppm 650 ppm 750 ppm 850 ppm 950 ppm 94% m 0 pp m 85 0 pp m 75 0 pp m 65 0 pp m pp 0 MET 112 Global Climate Change 2% 0% 95 4% 0% 55 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 55 Based on the A1T scenario, what is the predicted temperature change in 2100? +1.5C +2.5C +3.5C +4.5 0C -1.5C 73% 21% MET 112 Global Climate Change 5C 2% -1 . 0 C 0% 4. 5 5C +3 . 5C 2% +2 . 5C 2% +1 . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 56 Based on the A1FI scenario, by the year 2100, sea level will increase by approx 1m 0.5m 0.3m 0.1m 0m 100% MET 112 Global Climate Change 0% 0m 0% 0. 1m 0. 3m 0% 0. 5m 0% 1m 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 57 If CO2 emissions stay constant, CO2 concentrations will decline 1. True 2. False 94% MET 112 Global Climate Change ls e Fa Tr ue 6% 58 A B C Mean Temperature (2050): relative to 1961-90 A1FI is A, B or C? B2 is A, B or C? Indicate the correct matching A1FI – A, B2 - B A1FI – B, B2 – A A1FI – C, B2 – A A1FI – A, B2 – C A1FI – B, B2 - C A1FI – C, B2 – B 49% 34% 13% 4% MET 112 Global Climate Change A B 1F I– C, B 2 2 B, B I– – -C C A 1F A, B 2 – A – A 1F I– C, B 2 – I– 1F A A 1F I– B, B 2 2 A, B I– 1F 0% A -B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 60 Mean Temperature (2050): relative to 1961-90 A1F A2 B2 A B C Constant Aerosols ____ Increasing aerosols____ Decreasing aerosols____ 62 MET 112 Global Climate Change The correct order of the graph is (Constant, Increasing Aerosols and Decreasing Aerosols) ABC ACB BAC BCA CAB CBA 72% 22% C B A 0% B C A A B C C A B C A B 2% B 2% C 2% A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A B C Constant Aerosols Increasing aerosols Decreasing aerosols 64 MET 112 Global Climate Change Gateway to IPCC data IPCC Data Distribution Centre http://ipcc-ddc.cru.uea.ac.uk/ 65 MET 112 Global Climate Change Therefore, stabilizing emissions is not enough to reduce the radiative forcing Based on above, how much will emissions have to decline in %MET to 112 stabilize CO2 Global Climate Change at 550ppm? 68