* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma Membrane and Cell Transport Clicker Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
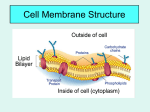
1. The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) surrounding every cell is composed primarily of ______. A.DNA B.Protein C. Carbohydrates D.Phospholipids A phospholipid molecule: composed of a phosphate group and two fatty acid tails. 2. The phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in a bilayer (double layer). How are the phospholipid molecules arranged in this bilayer? A.The nonpolar (hydrophobic) ends of the molecules faces inwards B.The polar (hydrophilic) ends of the molecules faces inwards C.The fatty acid tails of the molecules faces inward D.Both A and C E.Both B and C The hydrophilic phosphate groups facing outwards helps the cell interact with the watery environment on both sides of the membrane. The hydrophobic fatty acid tails in the interior of the membrane help create a barrier for many molecules to allow control of movement. 3. Channels through the phospholipid membrane are formed by A.Proteins B.DNA C.Cellulose D.Cholesterol 4. The term permeability means A.The ability of a substance to bend B.The ability of a substance to allow gases or liquids to pass through C.The ability of a substance to dissolve D.The ability of a substance to exist for a long time with out deteriorating. Permeable surface Impermeable surface (not permeable) 5. In diffusion, molecules move from _________________ concentration in a process that __________________ additional energy. A.high to low; requires B.high to low: does NOT require C.low to high; requires D.low to high; does NOT require Additional energy is not required, because diffusion occurs due to the random motion of the molecules. 6. A hypotonic solution is one that A. contains a higher concentration of solutes (dissolved particles) B. contains an equal concentration of solutes C. contains a lower concentration of solutes. D. is at a higher temperature E. is at a lower temperature Prefix reminders: Hypo = below Hypothermia is to have a body temperature below normal. Hyper= above Hyperactive is to have high energy. Iso= equal An isoceles triangle has two equal sides. 7. If a cell with a 0.7 %sucrose concentration inside is placed in a solution that has a 0.5% sucrose concentration, the process of osmosis will occur. In this case, A.sucrose will move into the cell B.sucrose will move out of the cell C.the cell will expand due to water gain D.the cell will shrink due to water loss E.both A and C F.both B and D 0.7 % sucrose O.5% sucrose Sucrose is too large to move through the selectively membrane. (Osmosis is occurring is a hint to this since it means the movement of water.) Remember that while the solutions are described in terms of the solute concentration it is the water that moves. The solution that has a lower solute concentration, has a higher water concentration. Water will move from the hypotonic (low solute / higher water) towards the hypertonic (higher solute /lower water) 0.7 %sucrose (99.3% water) 0.5% sucrose(99.5% water) The shell-less egg in fresh water (hypotonic) gained mass (water). Water Corn Syrup Paramecium living in fresh water ponds has to constantly pump out the water that flows into the cell. 8. If a cell with a 0.9% salt concentration inside is placed in a 1% salt solution, osmosis occurs. Which of the following will happen A. the cell will shrink due to water loss B. salt will move out of the cell C. the cell will expand due to water gain D. salt will move out of the cell E. both A and D F. both B and C 0.9 % salt 1% salt Salt is an ionic compound that can not move through the nonpolar barrier of the phospholipid membrane (without specialized channels). In osmosis, water will move in the direction of the higher SOLUTE (lower water) concentration. Thus hypertonic solutions, such as one high in salt, causes cells to lose water. • Drinking salt water will dehydrate our cells • Plants will wilt in a hypertonic solution. 9. Which kind(s) of solution outside of a cell could cause it to swell and potentially lyse (burst open)? A. a hypertonic solution B. a hypotonic solution C. an isotonic solution D. both A and C E. both B and C 10. A saline (salt) solution is used for fluid infusions into the blood stream. This solution needs to be ____ with blood cells. A. hypotonic B. hypertonic C. isotonic 11. In an isotonic solution A. the cell swells B. the cell shrinks C. there is NO movement of water in or out of the cell D. an equal amount of water moves into the cell as moves out 12. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, A. there is no NET movement of water B. there is a dynamic equilibrium C. there is a static equilibrium D. both A and B E. both A and C Net change = Inputs- Outputs. No net change when inputs and outs are balanced. Dynamic equilibrium= an equilibrium (balance) is when there is motion but the inputs equal the outputs. 13. When a substance is secreted from a cell in a process in which a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane to release the substance to the outside, it is called A. endocytosis B. exocytosis C. osmosis D. halitosis 14. O2 is a small, nonpolar molecule. If it is present outside the cell in high concentration it can enter the cell by A. Diffusion through the membrane B. Passive transport C. Active transport D. A and B E. A and C 15. Glucose is a larger polar molecule. If it is present outside of the cell in high concentration, it can enter the cell by A. Facilitated diffusion B. Passive transport C. Active transport D. A and B E. A and C 16. An amino acid (a large polar molecule) is present outside the cell in low concentration. It can be brought into the cell by A. Facilitated diffusion through specialized channels B. Passive transport C. Active transport D. A and B E. A and C In facilitated diffusion, a channel allows the substance to move through the membrane. But no energy is provided, so it is a type of passive transport and it can only move the substance from high concentration to low concentration. Active transport is required to move from low to high concentration. • High to low only • Can move from low to high 17. When a white blood cell engulfs a bacterium, the process of _________ has occurred. A.Endocytosis B.Exocytosis C.Osmosis D.Dialysis 18. What will happen for the following setup in which two different liquids are separated by a selectively-permeable membrane. The dots represent solute particles that can not move through the membrane. A.Water will move to the right B.Water will move to the left C.The system will remain in (lower concentration of water) 1. D 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. C 8. A 9. B 10.C 11.D 12.D 13.B 14.D 15.D 16.C 17.A 18.A