* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell parts worksheet
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
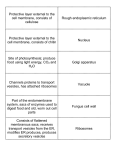
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre – stores, modifies, and packages proteins for export out of cell. Lysosome: has a single membrane, pinched off from Golgi body, contains hydrolytic enzymes for intracellular digestion and cell destruction (suicide bags). Nucleus – contains chromosomes coiled together as chromatin Nuclear pore: allows materials into nucleus, allows mRNA to leave nucleus Free floating ribosomes: site of protein synthesis Nucleolus: where rRNA is produced Nuclear membrane (envelope): double layer protective membrane Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis. Cytoplasm: mainly water Rough endoplasmic reticulum: contains ribosomes on surface. Cell membrane: selectively permeable Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: no ribosomes on surface, where steroid hormones and some carbohydrates are synthesized. Mitochondrion (pl. mitochondria): Double layer membrane, site of many of the chemical reactions involved in energy (ATP) production. Glycogen - stored glucose for energy. Glucose is converted to ATP mainly in the mitochondria. Glycogen found in large quantities in muscle and liver cells Organelles: Specialized structures within cells such as the nucleus, mitochondrion, ER etc. These are usually made of plasma membranes, exception - ribosomes do not have a membrane. Watch the video: Overview of Cell Organelles Nucleus: Largest organelle in the cell, enclosed by a double layer membrane. Control center of cell - controls metabolic functioning of cell & determines cell’s characteristics. Contains chromatin - DNA and proteins - during cell division, chromatin condenses to form individual chromosomes. The two most important chemicals in the nucleus are DNA and RNA. Nucleolus: Dark circular body in the nucleus - specialized area of chromatin which produces rRNA (ribosomal RNA) which is a component of ribosomes. Therefore, nucleolus helps produce ribosomes. Nuclear Pores: Openings in nuclear envelope (membrane) to allow large molecules to pass from nucleoplasm to the cytoplasm. Chromatin: The genetic material of the cell – made of DNA and proteins. During cell division, chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes. Human sex cells have 23 chromosomes. Watch the video: DNA Organization in the Nucleus Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane Components of Cell Membrane: 1. Phospholipids - two layers of phospholids form a cell membrane. Arrangement of phospholipids gives the membrane its fluid properties - membrane flexible Arrangement of phospholipids gives membrane its selectively permeable properties. Polar heads prevent charged particles (H+, Na+, Cl-, amino acids, glucose) from diffusing through phospholipid bilayer. Allow non polar molecules (O2, CO2) and small polar (non-charged) molecules like H2O to diffuse through phospholipid bilayer. Hydrophilic head = polar + water ‘loving’ Therefore, head is soluble in water 2 hydrophobic tails (fatty acids) = non-polar + water ‘hating’ Therefore, tails are not soluble in water 2. Embedded proteins-wholly or partially embedded within phospholipid bilayer, give structure. Functions of embedded proteins: a) Carrier proteins - form protein pores, these allow small charged ions (H+, Na+, Cl-) and large polar molecules (glucose, amino acids) to diffuse in/out of cell. Act as “pumps” actively transporting molecules in/out of cell. (ions, glucose, amino acids) b) Cell recognition proteins - with glycolipids and glycoproteins, give cell its distinctive antigens or surface features. 3. Glycolipids - carbohydrate attached to phospholipid. Glycoproteins - carbohydrate attached to embedded protein Both serve in cell recognition (antigens) and receptor (docking) sites on cell membrane. (e.g. for protein hormones) These 2 components are found on cell membrane only, not on other membranes inside cell. 4. Cholesterol - help maintain structure and fluidity of membrane Watch the video: Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure Ribosomes: Made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein, are not enclosed in a membrane. Site of protein synthesis. Found attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum or free floating in cytoplasm. Attached ribosomes - produce proteins for export (exocytosis) out of cell Free ribosomes - produce proteins to be used inside cell Polysomes – a group of ribosomes that translates (reads) a mRNA during protein synthesis. Endoplasmic Reticulum: Forms a membranous system of tubular canals that begins at the nuclear membrane and branches throughout cytoplasm Rough ER - have ribosomes attached to surface acts as transport of polypeptides (made at ribosomes) through cell. Rough ER - where protein folding occurs Smooth ER - does not have ribosomes attached - acts as transport (like rough ER) Smooth ER - contains enzymes to detoxify drugs and alcohol (liver cells) and synthesize lipids like steroid hormones (Cells of ovary and testes produce steroid sex hormones) Detoxify = inactivate potentially harmful drugs (including alcohol) by converting them to water soluble compounds that can be eliminated from the body in urine. Golgi apparatus (Golgi Body) Concentrically folded membrane, not continuous with nuclear membrane. Receives transport vesicles from ER. Functions as: 1. Sorting and repackaging centre - package protein into secretory vesicles so protein can be secreted out of cell through cell membrane (exocytosis) or so protein incorporated into cell membrane. 2. Modification of polypeptides (e.g. adding glycogen/sugar chains to protein). 3. Produce lysosomes (contain proteins which are hydrolytic enzymes. Vacuoles: Membrane bound often fluid filled cavities which act as storage sites in cell. Vesicles: Small vacuoles that can be made at ER, Golgi apparatus or from the folding of the cell membrane as in endocytosis. Types of vesicles 1. Transport vesicles - made at ER and transport polypeptides to Golgi apparatus. 2. Secretory vesicles - made at Golgi apparatus and transport to cell membrane for secretion out of cell by exocytosis. Lysosomes: Special type of vesicle made at Golgi apparatus. Contains hydrolytic enzymes for digestion within cell. Functions: 1. Attach to vacuoles and release hydrolytic enzymes to digest contents of vacuole. 2. “Suicide bags” - release enzymes to destroy cell (cell suicide). Watch the video: Intra-cellular Digestion of Unwanted Substances Example of lysosome function When white blood cells (macrophages) engulf bacteria or cellular debris these materials are incorporated into a vacuole. Lysosomes attach to these endocytic vacuoles and release hydrolytic enzymes which digest materials in vacuole, therefore, digesting engulfed materials. Watch the video: Phagocytosis Protein Production and Transport Proteins are made at the ribosome and are passed into the ER where they fold into their tertiary (globular) structure. These proteins are packaged into vesicles and sent to the Golgi apparatus where they are modified and repackaged at the Golgi apparatus. Pathway 1 – shows protein packaged into secretory vesicles and protein is secreted from cell. Pathway 2 – shows protein packaged into vesicle & protein is embedded in cell membrane. Pathway 3 – shows special vesicles called lysosomes that stay in the cell and that contain hydrolytic enzymes. Watch the video: Protein Pathways in the Cell Flagella Cilia a whip like tail used for motility (movement) human sperm cell structures - the tail is also called a flagella tiny hairs that project from the cell membrane used mainly as sweepers in the human body found in the trachea and bronchi (air ways) to sweep out debris before it can reach the lungs also found in the Fallopian tubes in female to sweep egg towards the uterus Mitochondria: (singular: mitochondrion) Sometimes referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. Folded inner membrane increases surface area for chemical reactions to take place. Organelle where aerobic cellular respiration occurs. Most of the ATP - energy currency of cells - is produced here Micrograph of Mitochondrion Cytoskeleton a cellular scafold or skeleton contained within the cytoplasm - made out of protein maintains cell shape, protects the cell, enables cellular movement and plays important roles in intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles) Cell size: To increase the surface area to volume ratio - many tissues and cells (and components of cells) are highly folded. Example - inner membrane of mitochondria, lining of intestine and stomach and alveoli. When cells grow too big their surface area to volume ratio decreases, therefore, cells divide before they become to big to supply nutrients by diffusion. Watch the video: Cell Size