* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the calvin cycle
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
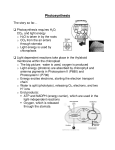
Menu Lesson Print Name Class Date SECTION 6-2 REVIEW T HE C ALVIN C YCLE VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. Calvin cycle 2. carbon fixation 3. stoma 4. C4 pathway HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work. 5. CAM MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The Calvin cycle begins when CO2 combines with a five-carbon carbohydrate called a. RuBP. b. PGA. c. PGAL. d. NADPH. 2. For every three molecules of CO2 that enter the Calvin cycle, the cycle produces one molecule of a. RuBP. b. PGA. c. PGAL. d. NADPH. 3. Organic compounds that can be made from the products of the Calvin cycle include a. only carbohydrates. b. only amino acids. c. only lipids. d. carbohydrates, amino acids, and lipids. 4. C3 and C4 plants differ in terms of the number of a. steps in the Calvin cycle. b. carbon atoms in the compound that CO2 is initially incorporated into. c. carbon atoms in the end product of the Calvin cycle. d. ATP molecules used in the Calvin cycle. 5. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis a. continues to decrease. b. continues to increase. c. initially decreases and then levels off. d. initially increases and then levels off. Modern Biology Study Guide 33 Menu Lesson Print Name Class Date SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. How many molecules of ATP and NADPH are used in each turn of the Calvin cycle? 2. Using (CH2O) as the general formula for a carbohydrate, write the simplest overall equation for photosynthesis. 3. How do CAM plants differ from both C3 and C4 plants? 4. Why does the rate of photosynthesis increase, peak, and then decrease as temperature increases? 5. Critical Thinking Stomata can open and close in response to changes in the CO2 concentration inside the leaf. Would you expect stomata to open or close if the CO2 concentration decreased? Explain. The diagram below summarizes the Calvin cycle. CO2 RuBP ADP ATP PGA ATP ADP PGAL NADPH NADP1 34 Section 6-2 Review HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS In the blank spaces provided in the diagram, indicate the number of molecules of each substance that are involved in each turn of the cycle. Menu Lesson Print 2. Carrier proteins bind to a molecule of the substance on one side of the membrane, change shape, transport the molecule across the membrane, and release the molecule on the other side. 3. The stimuli are stretching of the cell membrane, electrical signals, and chemicals in the cytosol or external environment. 4. Both involve the binding of a specific substance to a particular kind of protein and a change in shape of the protein as the process (transport or chemical reaction) proceeds. After the process is completed, the protein is unchanged. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS 1. a, hypotonic; b, hypertonic; c, isotonic; d, hypertonic; e, isotonic; f, hypotonic Section 5-2 VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Active transport is the movement of materials across a membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. 2. Endocytosis is the process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles. 3. A vesicle is a membrane-bound organelle that pinches off from the cell membrane during endocytosis or fuses with the cell membrane during exocytosis. 4. Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis in which cells ingest large particles or whole cells. HRW material copyrighted under notice appearing earlier in this work. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. b 5. d SHORT ANSWER 1. The mechanism uses energy to move Na1 and K1 up their concentration gradients. 2. The phagocyte forms a pouch in its cell membrane and engulfs bacteria in the pouch. It then pinches off the pouch to form a vesicle. Lysosomes fuse with the vesicle, and lysosomal enzymes destroy the bacteria it contains. 3. Proteins are made on ribosomes and packaged into vesicles by the Golgi apparatus. The vesicles move to the cell membrane and fuse with it, releasing the proteins from the cell through exocytosis. 4. The interior of the lipid bilayer is nonpolar and therefore would repel ions, which are attracted to polar environments. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS 1. The correct order is d, c, f, b, a, e. 2. Na1 ions are released on the external side of the cell membrane. 3. K1 ions are released on the cytosolic side of the cell membrane. Section 6-1 VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Grana are stacks of thylakoids inside a chloroplast; the stroma is the solution that surrounds the thylakoids. 2. Accessory pigments assist chlorophyll a in capturing light energy during photosynthesis. 3. Chemiosmosis is the process by which ATP is made during photosynthesis. The production of ATP is catalyzed by the enzyme ATP synthase. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. a 2. c 3. d 4. b 5. c SHORT ANSWER 1. Photosynthesis involves many chemical reactions linked such that the product of one reaction is consumed in the next reaction. 2. Chloroplasts have an inner membrane system consisting of thylakoids. The pumping of protons into the thylakoids builds up a proton concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane. 3. The energy-carrying products are ATP and NADPH. 4. They help chlorophyll a capture light energy by absorbing energy in wavelengths that chlorophyll a cannot absorb. This enables the photosynthetic cell to capture more of the energy in light. 5. Photosystem II most likely evolved first, because it replaces electrons lost from chlorophyll a with electrons from water. Since photosystem I accepts electrons from photosystem II, it probably evolved after photosystem II. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS a, electrons; b, NADPH; c, ATP; d, H1 Section 6-2 VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. The Calvin cycle is a biochemical pathway that produces organic compounds from carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. 2. Carbon fixation is the incorporation of carbon dioxide into organic compounds. 3. A stoma is a small pore on the surface of a plant through which water, O2, CO2, and other gases enter or leave the plant. 4. The C4 pathway is a carbon fixation pathway in which CO2 is incorporated into four-carbon compounds. 5. CAM is a carbon fixation pathway in which CO2 is incorporated into organic compounds at night and released to enter the Calvin cycle during the day. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. a 2. c 3. d 4. b 5. d SHORT ANSWER 1. In each turn of the cycle, three molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH are used. 2. CO2 + H2O + light energy→(CH2O) + O2 3. CAM plants open their stomata at night, whereas C3 and C4 plants open their stomata during the day. 4. Increasing the temperature initially accelerates the various chemical reactions involved in photosynthesis. At higher temperatures, many of the enzymes that catalyze these reactions become ineffective, and the stomata begin to close. 5. The stomata would open. That would allow more CO2 to enter the leaf from the surrounding air, stimulating photosynthesis. STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS 1. Clockwise from the top: 1 CO2, 2 PGA, 2 ATP, 2 ADP, 2 NADPH, 2 NADP1, 2 PGAL, 1 ATP, 1 ADP, 1 RuBP Modern Biology Study Guide Answer Key 5