* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download wp-psych-cond - WordPress.com
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
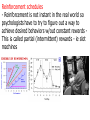
http://www.youtuQDMbe.com/watch?v=nE8pFWP5 Conditioning Based on Classical Conditioning/Pavlovian - Dog and bell experimentJohn B. Watson - Forget all the hidden junk - how do people respond to stimuli in the environment - Psychology should be observable - Behaviorist perspective Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) - The food for the dog Unconditioned response (UCR)- Unlearned response to a stimulus - Dog salivating when food is put into its mouth Conditioned Stimulus (CS) - Something that causes a response because the behavior is learned - The bell for the dog Conditioned Response (CR) - A response due to a stimuli that is learned from - Dog salivating when it hears the bell Conditioned ='s Learned Unconditioned ='s Unlearned Extinction - If the CS is not paired UCS than eventually the CR begins to die out Spontaneous Recovery - If there is a rest period and the CS is reintroduced would lead to a weakened CR - The behavior was suppressed but not eliminated Generalization - If a similar stimulation added it will cause a CR - Dog hears a similar bell - A kid bitten by pit bull may fear all dogs Discrimination - The ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimuli and a irrelevant stimuli - Evolutionary reasons difference between seeing pit bull and a golden retriever Operant Conditioning - Associating behavior w/ consequences - thus they become more likely to repeat rewarded (reinforced) behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors - B. F. Skinner and the skinner box w/ rats - This is how we can tell if dogs are color blind and if babies can discriminate sound - taught teachers to give gradual reinforcers Shaping - Procedure by which reinforcers gradually guide an animal's actions toward desired behaviors - You see this w/ kids or clinics Classical Conditioning - the association between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus. Operant Conditioning - an association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior. Reinforcement - Any event that leads to an increase in the frequency of response - Can be anything - If you're amused when I yell at you you may do something to get me to yell at you Positive Reinforcement - addition of a reinforcing stimulus following a behavior that makes it more likely that the behavior will occur again in the future Example - You get an A on your brain quiz and Mr. Hicks says "good job" http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mt4N9GSBoMI Negative Reinforcement - response or behavior is strengthened by stopping, removing or avoiding a negative outcome or aversive stimulus - something being subtracted from the situation Example - Before heading out for a day at the beach, Victor slathers on sunscreen in order to avoid getting sunburned. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B_9ZZaPDtPk http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fn7-JZq0Yxs Punishment - Any consequence that decreases the frequency of preceding behavior - Opposite of reinforcement - Swift & sure - can lead to aggression, depression, & low self-esteem - it can be effective in the right settings Positive Punishment - presenting an unfavorable outcome or event following an undesirable behavior - An adverse stimulus is added to the situation Example - Ashley's sister calls her during class and she picks it up and gets a severe scolding from Mr. Hicks and a nasty look from Quinn. Negative Punishment - taking something good or desirable away in order to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior - Punishment by removal Anthony refuses to call his sister to wish her a happy birthday and he has phone taken away. Reinforcement schedules - Reinforcement is not instant in the real world so psychologists have to try to figure out a way to achieve desired behaviors w/out constant rewards This is called partial (intermittent) rewards - ie slot machines A. Fixed ratio - Reinforce behavior after a set number of responses - An employee gets money after every 30 products are built - Taking breaks decreases rewards - unions don't like this B. Variable ratio schedules - Reinforcers provided after an unpredictable # of responses - Tends to elicit a high rate of responses - Fishermen and slot jockeys C. Fixed interval schedules - Reinforce the 1st response after a fixed time period - Checking to see if the mail is there as time draws nearer - Pigeons peck more as feeding time draws nearer D. Variable interval schedules - Reinforce 1st response after varying the intervals - Checking to see if you have email - tends to get slow and steady responses