* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Heredity
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
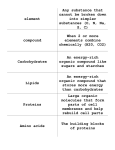
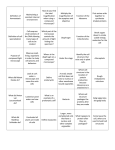
Cells and Heredity Chapter 1 Cell Structure and Function. Section 1-Discovering Cells Section 1 –Discovering Cells: Objectives• Explain how the invention of the microscope contributed to the scientists’ understanding of living things • State the three points of cell theory • Describe how a microscope works, including how a lenses magnifies an object. Vocabulary 1. cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things. 2. microscope An instrument that makes small objects look larger. 3. compound microscope A light microscope that has more than one lens. 4. cell theory A widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. 5. magnification The ability to make things look larger than they are. 6. convex lens A curved lens in which the center is thicker than the edges. 7. resolution The ability to clearly distinguish the individual parts of an object. Notes 1. The invention of the microscope __________________ made it possible for people to discover and learn cells about ________. Names to know Robert Hooke. 1663. One of the first people to observe cells. He observed a thin slice of cork using a compound microscope that he built himself. The cork looked like tiny rectangular rooms, which he called cells. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (around the same time that Hooke made his discovery) Observed tiny objects with microscopes. He made his own lenses to construct simple microscopes He looked at water from a pond and saw onecelled organisms that he called animalcules, meaning “little animals” Matthais Schleiden (1838) –German scientist concluded that all plants are made of cells. Theodor Schwann (1839)-German scientist that concluded that animals are made of cells. Up until this time, people did not understand where cells came from. Most people thought that living things could come from non living matter. German Doctor Rudolf Virchow proposed that cells are only formed from existing cells. The observations of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, and others let to the development of the Cell Theory. 2. The cell theory states: – A. All living things are composed of cells – B. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. – C. All cells are produced from other cells 3. A microscope magnifies an object by Bending the light that passes through them. _______________________________ 4. convex A ____________________lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges. resolution ____________________________ is the sharpness of an image, while magnification _________________________ is making an image appear larger than it really is. 5. Cells and Heredity Chapter 1 Cell Structure and Function Section 2: Looking Inside Cells Section 2-Looking Inside Cells • Identify the roll of the cell membrane and nucleus in the cell • Describe the functions performed by other organelles in the cell • Compare bacterial cells with plant and animal cells • Describe the role of specialized cells in many celled organisms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g FuEo2ccTPA Vocab 8. Organelle A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell. 9. Cell wall A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. 10. cell membrane A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. 11. nucleus A cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s activities. 12. chromatin Material in cells that contains DNA and carries genetic information. 13. cytoplasm The region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane. 14. mitochondria Rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell’s functions. 15. endoplasmic reticulum A cell structure that forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another. 16. ribosome A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made. 17. Golgi body A structure in a cell that receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell. 18. chloroplast A structure in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food. ADD somewhere on vocab page: vacuole A water-filled sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area. 19. lysosome A small round cell structure that contains chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones. Notes 1. Cell membrane The ______________________ protects the cell and controls what substances enter and exit it. nucleus The ______________________ controls all the cell’s activities. 2. 3. See pages 26-27 in your Cells and Heredity Text. Match the organelle to its “City Function”. H 1. Cell Wall: _________ 2. D Cell Membrane ________ 3. J nucleus ________ F 4. chromatin: ________ 5. I mitochondria: _______ 6. C endoplasmic reticulum :___________ 7. B ribosomes: _________ 8. A Golgi Bodies: ________ 9. G chloroplasts: _______ 10. K vacuoles: ________ 11. E lysosomes: _______ 4. The three functions of organelles are: – A. – B. – C. Produce energy Build and transport needed materials Store recycle wastes 5. Bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus ______________________. Cells and Heredity Chapter 1 Cell Structure and Function Section 3: Chemical Compounds in Cells Section 3-Chemical Compounds in Cells • Describe the four main kinds of organic molecules in living things. • Explain how water is important to the functioning of cells. 20. element Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. 21. atom The smallest unit of an element. 22. compound Two or more elements that are chemically combined. 23. molecule The smallest unit of most compounds. 24. organic compound A compound that contains carbon. 25. inorganic compound A compound that does not contain carbon. 26. carbohydrates Energy-rich organic compounds, such as sugars and starches, that are made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 27. proteins Large organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. 28. amino acids Small molecules that are linked together chemically to form proteins. 29. enzyme A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing. 30. lipids Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 31. nucleic acid A very large organic molecule made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus, that contains instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life. 32. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; the genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring. 33. RNA Ribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that plays an important role in the production of proteins. 1. Four main groups of organic compounds: A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. D. proteins nucleic acids 2. Two examples of inorganic compounds: A. H2O - water B. NaCl - Sodium chloride (table salt) 3. Plant cells store excess energy in the starch form of _____________________. 4. Proteins are made from the elements: A. B. carbon hydrogen C. oxygen D. nitrogen E. (and sometimes Sulfur) Enzymes ________________in our saliva speed up digestion by breaking down starches _______________ into sugars __________________. 5. oils fats __________,__________ waxes and __________ are all lipids. 6. water Without ____________ most chemical reactions would not take ___________ 7. place. Cells and Heredity Chapter 1 Cell Structure and Function Section 4: The Cell in Its Environment Section 4- Objectives – Describe 3 methods in which molecules move in and out of cells – Compare passive and active transport. 34. selectively permeable A property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot. 35. diffusion The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. 36. osmosis The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. 37. passive transport The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy. 38. active transport The movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy. Notes 1. Three ways substances can move into and out of cells: diffusion A._______________ osmosis B._______________ Active transport C._______________ Active _______________ transport requires energy, while Passive ____________transport does not. 2. Review-Organic Compounds Graphic Organizer A. carbohydrates B. proteins C. Fats, oils, waxes D. sugar E. DNA