* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SI: September 19, 2011 Chapter 7: Part 2 Part I: Warm
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
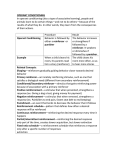
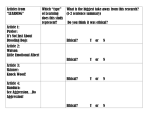
SI: September 19, 2011 Chapter 7: Part 2 Part I: Warm-Up: Define the following vocabulary words: Respondent Behavior: Operant Conditioning: Operant Behavior: Law of Effect: Operant Chamber: Shaping: Reinforcer: Positive Reinforcement: Negative Reinforcement: Primary Reinforcer: Conditioned Reinforcer: Continuous Reinforcement: Partial (Intermittent) Reinforcement: Fixed-Ratio Schedule: Variable-Ration Schedule: Fixed-Interval Schedule: Variable-Interval Schedule: Punishment: Cognitive Map: Latent Learning: Observational Learning: Modeling: Mirror Neurons: Prosocial Behavior: Part II: Matching Reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses. Variable-Interval Schedule Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed. Fixed-Interval Schedule Reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses. Fixed-Ratio Schedule Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals. Variable-Ratio Schedule Part III: Short Answer Give a 1-4 sentence answer for the following questions. Give 3 differences between classical and operant conditioning. What is the difference between respondent behavior and operant behavior? Explain the difference between a positive reinforcement and a negative reinforcement and give an example of each one. Give an example of a primary reinforcer and an example of a conditioned reinforcer (do not use examples from the book) Explain how mirror neurons work. Explain the Bobo the Clown experiment. Part IV: Multiple Choice Choose the correct answer to the following multiple choice questions What kind of behavior is more likely to recur according to the Law of Effect? a. Punished b. Rewarded c. Learned d. None of the Above In shaping, what guides actions towards a desired behavior? a. Reinforcers b. Punishers c. Conditioned Behaviors d. All of the Above True/False: Reinforcers are universal. Mary’s mom took her to get ice cream after Mary finished cleaning her room. This is an example of what kind of reinforcement? a. Primary Reinforcer b. Conditioned Reinforcer c. Negative Reinforcer d. Positive Reinforcer True/False: Delayed reinforcers are effective. True/False: Negative reinforcement punishes an individual and reinforces that behavior to not happen again. Continuous reinforcement reinforces the action how many times? a. Every other time b. Never c. Every time it occurs d. Whenever you feel like it True/False: Spanking a child always works in reinforcing a negative behavior. True/False: Just like classical conditioning, operant conditioning is constrained by biology. What decreases the frequency of a preceding behavior? a. Negative Reinforce b. Punisher c. None of the above d. All of the above Both classical and operant conditioning involve a. Acquisition b. Extinction c. Generalization d. All of the above Prosocial models can have what kind of effects? a. Prosocial effects b. Antisocial effects c. Negative effects d. No effect Matt was abused as a child, and witnessed his father beat his mother when he was young. What is likely to happen to Matt when he grows up? a. He will learn from his father, and not beat his wife and kids. b. He will not beat his children, because he knows how bad it hurts. c. He will likely beat his wife and children. d. We cannot predict Matt’s future. It is all destiny. Part V: Fill in the Blank Fill in the blanks with the correct words or phrases. Any event that strengthens a preceding response is called ___________________________________________. _____________________________________ reinforcers are unlearned. Continuous reinforcement is desired because ______________________________________________________________, ultimately allowing a behavior to be mastered. ______________________________________________________ reinforcement produces greater resistance to extinction. The ability to infer another’s mental state is called ________________________________________________. Models are most effective when their actions and words are ___________________________________. Violence-viewing effects stems from _____________________________________ and _______________________________. Part VI: LOOK OVER THE FOLLOWING IN YOUR BOOK: Figure 7.10 Figure 7.11 Table 7.1 Table 7.2 Table 7.3 Table 7.4 *Understand the Skinner Box *Understand Successive Approximation *Understand cognitive maps and latent learning *Understand instinctive drift