* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
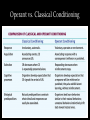
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
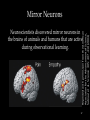
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Operant Chamber • Thorndike's law of effect = starting point for Skinner • Skinner developed the Operant chamber, Skinner box, to study operant conditioning. Walter Dawn/ Photo Researche 1 Shaping • Shaping = process of guiding animal to desired behavior 2 Types of Reinforcers • Reinforcer or Reinforcement • 2 Types… 3 Primary & Secondary Reinforcers 1. Primary Reinforcer: An innately reinforcing stimulus like food or drink. 2. Conditioned Reinforcer: A learned reinforcer that gets its reinforcing power through association with the primary reinforcer. 4 Immediate & Delayed Reinforcers 1. Immediate Reinforcer: – Ex: Dog gets treat for sitting down – Instant Gratification 2. Delayed Reinforcer – Ex: A paycheck – Delayed Gratification 5 Reinforcement Schedules 1. Continuous Reinforcement: 2. Partial Reinforcement: • Which one leads to quicker learning? • Which one is more resistant to extinction? 6 Ratio Schedules (Partial Reinforcement) 1. Fixed-ratio schedule: reinforcer after fixed # of responses 2. Variable-ratio schedule: Reinforcer after an unpredictable number of responses. • Impact of unpredictability? 7 Interval Schedules (Partial Reinforcement) 1. Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforcer after a specified time has elapsed. 2. Variable-interval schedule: Reinforcer at unpredictable time intervals • Impact of unpredictability? 8 Schedules of Reinforcement 9 Punishment An aversive event that decreases the behavior it follows. 10 Cognition & Operant Conditioning • BF Skinner shunned cognition during conditioning – Many people disagreed • Examples of cognition during conditioning: – Cognitive Map – Latent Learning 11 Motivation Intrinsic Motivation: The desire to perform a behavior for its own sake. Extrinsic Motivation: The desire to perform a behavior due to promised rewards or threats of punishments. 12 Biological Predisposition Biological constraints predispose organisms to learn associations that are naturally adaptive. Photo: Bob Bailey Marian Breland Bailey 13 Operant vs. Classical Conditioning 14 Punishment Although there may be some justification for occasional punishment (Larzelaere & Baumrind, 2002), it usually leads to negative effects. 1. 2. 3. 4. Results in unwanted fears. Conveys no information to the organism. Justifies pain to others. Causes unwanted behaviors to reappear in its absence. 5. Causes aggression towards the agent. 6. Causes one unwanted behavior to appear in place of another. 15 Learning by Observation ©Herb Terrace The monkey on the right imitates the monkey on the left in touching the pictures in a certain order to obtain a reward. © Herb Terrace Higher animals, especially humans, learn through observing and imitating others. 16 Mirror Neurons Reprinted with permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Subiaul et al., Science 305: 407-410 (2004) Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brains of animals and humans that are active during observational learning. 17 Meltzoff, A.N. (1998). Imitation of televised models by infants. Child Development, 59 1221-1229. Photos Courtesy of A.N. Meltz Imitation Onset Learning by observation begins early in life. This 14-month-old child imitates the adult on TV in pulling a toy apart. 18 Bandura's Bobo doll study (1961) indicated that individuals (children) learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Courtesy of Albert Bandura, Stanford University Bandura's Experiments 19 Applications of Observational Learning Unfortunately, Bandura’s studies show that antisocial models (family, neighborhood or TV) may have antisocial effects. 20 Positive Observational Learning Bob Daemmrich/ The Image Works Fortunately, prosocial (positive, helpful) models may have prosocial effects. 21 Gentile et al., (2004) shows that children in elementary school who are exposed to violent television, videos, and video games express increased aggression. Ron Chapple/ Taxi/ Getty Images Television and Observational Learning 22 Modeling Violence Children modeling after pro wrestlers Glassman/ The Image Works Bob Daemmrich/ The Image Works Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. 23