* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis Translation
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
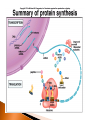
Transcribe the following DNA sequence: TAC-GTA-CGG-TAA-GGC What enzyme is used during transcription? Chapter 10 pg. 207-210 Made of amino acids (monomer) 20 amino acids Sequence of amino acids determines the protein Protein function is based on shape. Making proteins from mRNA Ribosomes read (translate) mRNA to assemble proteins ◦ Occurs in the ribosomes Molecules used: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA Step 1: Initiation Ribosome assembles at the start codon of mRNA ◦ Start codon: AUG ◦ Codes for amino acid: Methionine Codon: set of three nucleotides on mRNA that code for a specific amino acid Step 2: Elongation The ribosome moves down the mRNA one codon (three nucleotides) at a time tRNA has complementary anti-codon that recognizes the codon tRNA adds an amino acid Step 2: Elongation Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids creating a growing polypeptide Polypeptide = protein Protein molecule Step 3: Termination The process continues until a stop codon is reached Ribosome falls apart and protein is created Protein molecule stop codon 1. 2. Ribosome attaches to mRNA at start codon tRNA brings in amino acids from cytoplasm a. tip of tRNA binds to a specific amino acid b. anti-codon on tRNA binds to codon on mRNA 3. Repeat for each codon until stop is reached SECOND BASE U UUU U UUC UUA C LEU UCC UCA UAU SER UAC UAA UAG CUU CCU CAU CUC CCC CAC CUA LEU CCA PRO CAA CUG CCG CAG AUU ACU AAU ACC AAC ILE AUA AUG ACA MET START GUU G UCU UCG AUC A PHE A GUC GUA GUG VAL THR AAG GCU GAU GCA GCG ALA TYR STOP HIS GLN ASN AAA ACG GCC G GAC GAA GAG UGU UGC CYS STOP A UGG TRP G CGU U CGC C CGA ARG CGG AGU AGC ASP GLU AGG GGA GGG U C A ARG GGU GGC A G SER G U GLY What amino acids do you have for the following codons? C UGA AGA LYS U C A G AUG-CUC-AAU-UCC MET LEU ASN SER THIRD BASE FIRST BASE UUG C AUG-GGG-CCC-UUU MET GLY PRO PHE TRANSCRIBE TRANSLATE DNA: mRNA: AA: T-A-C-A-A-T- A-G-G-G-T- C Translation location Molecule made Molecules involved Transcription