* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 6
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Negative affectivity wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
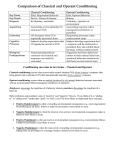
2/19/2014 EDU501 : LECTURE 6 OPERANT CONDITIONING THE A‐B‐C MODEL legacee.com Operant Conditioning: Skinner Box A matter of training using rewards and punishments. In this system a correct system a correct behavior results in a reward of food and an incorrect behavior triggers a punishment of an electric shock. Operant Conditioning Operant conditioning is simply learning from the consequences of your behavior marysbiologypage.blogspot.com Operant Conditioning • Operant Conditioning – learning in which a voluntary response is strengthened or weakened, depending on its positive or negative consequences positive or negative consequences • Thorndike’s Law of Effect Key Aspects of Operant Conditioning • In operant conditioning, the stimulus is a cue, it does not elicit the response • Operant responses are voluntary – responses that are satisfying are more likely to be repeated, and those that are not satisfying are less likely to be repeated 1 2/19/2014 Key Terms of Operant Conditioning • Reinforcement is any procedure that increases the response • Punishment is any procedure that decreases the response Positive Reinforcers, Negative Reinforcers, and Punishment • Positive Reinforcer – added to the environment that brings about an increase in a preceding response Teacher: Who can define the word culture for us? Mere : Culture is our way of life. Teacher : Good Mere. That is correct. ( positive reinforcement) Negative Reinforcer – unpleasant stimulus whose removal leads to an increase in the probability that a preceding response will occur again in the future Teacher : Arti, Tomu, Aliti and Ram ..you have not done your homework so you will not go out for recess..instead d you will stay in the classroom and do ll h l dd your homework . “One has to do their homework to avoid staying in the classroom during recess.” What has been taken away from the students? Will it increase or decrease the desired ( doing homework) behaviour? NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT Negative reinforcement occurs when a behavior is reinforced by removal of a stimulus. The word "negative" does not mean "unpleasant." It means a stimulus is removed or "subtracted" from the situation as a form of reinforcement. Negative reinforcement negative refers to something unpleasant, It is not a form of punishment. Negative reinforcement is a form of reinforcement. It increases the frequency or probability of a behavior by "taking away something bad." 2 2/19/2014 Negative reinforcement occurs when a student shows an appropriate behavior in order to make the threat of punishment go away. The student shows the correct behavior to avoid being punished if s/he doesn't Shaping: Reinforcing What Doesn’t Come Naturally • Shaping – the process of teaching a complex behavior by rewarding closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior Negative reinforcement is the removal of something awful (or the threat of it) if the student shows an appropriate behavior. Punishment • Punishment defined – A negative consequence of a behavior, which leads to a decrease in the frequency of the behavior that produces it – punishment should be used as a last resort in behavior management ; positive and negative reinforcement should be used first Time –out ‐ students offered time in a safe space or a cool‐ down space to think through problems ‐another form of removal (negative) punisher ‐ Helps restore order and relive the teacher ‐ Used as a punishment to reduce specific U d ih tt d ifi undesirable behavior Punisher – A consequence of behavior that weakens or decreases behavior Positive punisher – any event that decreases the frequency of the behavior e.g. Student talking and not paying attention ‐ detention, extra homework, sending student to the Principal’s office (puts an end to the behavior) Negative punisher – any event when taken away decreases the frequency of the behavior e.g. Teacher removing child from the playground after the child has punched a classmate. Teacher takes away the child’s playground privileges in order to punish ( decrease) the aggression DECREASING UNDESIRABLE BEHAVIOUR 1. VERBAL REPRIMANDS – Teachers brief statements to draw attention to misbehavior e.g. stop that! , get back to work! 2. RESPONSE COST – possible lost of the reward e g Peter : Teacher can we go and play in our free e.g. Peter : Teacher can we go and play in our free period? Teacher : you only will be allowed to play if you finish your task sheet . (Unfinished work will cost them their chance to play) 3