* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics: Review Variations in Mendel`s Laws Variations in
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
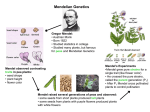
10/28/2011 Genetics: Review 1. Alternative versions of genes (alleles) account for variation in inherited characters 2. For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent 3. If two alleles differ, one is dominant, the other recessive 4. The two alleles for each character segregate (separate) during gamete production. Variations in Mendel’s Laws In incomplete dominance, F1 hybrids have an appearance in between the phenotypes of the two parents. P Generation White rr Red RR Gametes R r F1 Generation Pink R Rr 1 Gametes 1 2R 2 r F2 Generation Sperm 1 1 2R 2 r 1 R 2 Eggs RR Rr 1 r Rr rr 2 Variations in Mendel’s Laws Hypercholesterolemia PHENOTYPE GENOT TYPE •Dangerously high levels of cholesterol in the blood. •Is a human trait that is incompletely dominant. •Heterozygotes have blood cholesterol levels about 2X normal. •Homozygotes have blood cholesterol levels about 5X normal. HH Homozygous for ability to make LDL receptors Hh Heterozygous hh Homozygous for inability to make LDL receptors LDL LDL receptor Cell Normal Mild disease Severe disease 1 10/28/2011 Variations in Mendel’s Laws Multiple Alleles Blood Group Genotypes Red Blood Cells (Phenotype) Carbohydrate A IAIA or IAi A B IBIB or IBi AB IAIB O ii Carbohydrate B Variations in Mendel’s Laws – Pleiotropy is the impact of a single gene on more than one character. Single gene Pleiotropy Multiple traits (e.g., sickle-cell disease) Variations in Mendel’s Laws 2 10/28/2011 Variations in Mendel’s Laws *Epistasis Example: In Drosophila, gene:eyeless *Black (B) is dominant to brown (b) *Second gene responsible for allowing pigment to be deposited d d in hair h C = presence, c = absence (colorless) Variations in Mendel’s Laws – Polygenic inheritance is the additive effects of two or more genes on a single phenotype. Polygenic inheritance Single trait (e.g., skin color) Multiple genes Variations in Mendel’s Laws P Generation aabbcc AABBCC (very light) (very dark) F1 Generation F2 Generation 1 8 1 8 1 8 1 8 1 Eggs 8 1 8 1 8 1 8 1 8 1 64 1 8 AaBbCc AaBbCc Sperm 1 1 1 1 1 8 8 8 8 8 6 64 15 64 20 64 15 64 6 64 1 8 1 64 3 10/28/2011 Variations in Mendel’s Laws *Gene interactions Sex Linkage *1909 Thomas Hunt Morgan II III XY IV or XX *Sex chromosomes *Autosomes Example: In Drosophila and all mammals sex chromosomes designated as X and Y XX=female XY=male Sex Linkage Any gene located on a sex chromosome is called a sex-linked gene. • Most sex-linked genes are found on the X chromosome. 4 10/28/2011 Variations in Mendel’s Laws *Phenotype depends on environment and genes How do we account for genetic variation? *Independent assortment *Crossing over *Random fertilization Cross over: Independent Assortment: 5