* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Chapter 1.2 and Chapter 2 Cells Test
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
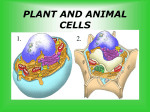
Study Guide for Chapter 1.2 and Chapter 2 Cells Test 1. Chapter 1 Section 2 (p.16-20) Cells – the basic units of all living things Homeostasisan organisms ability to maintain a steady condition no matter what is going on outside the body The size of an organism is due to what? How many cells that organism has, not the size of the cells. The more cells the bigger the organism. 2. Chapter 2 section 1 (p.40-47) 4 parts that all cells have 1. cell membrane 2. cytoplasm 3. DNA 4. Ribosomes Each cell part and it’s function (both plant and animal) Cell Part Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast ER Golgi Body Lysosome Vacuole Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosome Cytoplasm Function Protects cell, and regulates what goes in and out of cell Plants only, gives shape and structure, and protects Plants only, where the plant makes its food (photosynthesis) moves/transports materials around in the cell Sort and package materials for transport out of the cell Helps breaks down food and eliminates waste in the cell. Temporary storage of cellular material such as water, food, and waste Controls the cell and holds information to make new cells Breaks down food to make energy call ATP Makes protein for cell activity Gelatinlike material inside the cell. Most of the cell is made up of cytoplasm Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and examples of each. Prokaryotic does not have a nucleus parts do not have membranes world’s smallest cell example = bacteria Progression from cell to organism: cell tissue organ organ system organism Difference between multicellular organisms and unicellular organisms multicellular made up of several cells and organ systems cells and systems work together to keep the organism alive Eukaryotic has a nucleus has membrane bound parts 10 times larger than prokaryotic example: all cells except bacteria unicellular a one celled organism That one cell performs all the functions to keep it alive Examples of a single cell, tissue, organ, and organ system single cell bacteria one plant cell tissue muscle tissue lining of stomach organ lungs kidney organ system respiratory system digestive system 3. Chapter 2 section 2 (p.49-53) Three parts to the cell theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all organisms 3. All cell come from other cells (cell division) Who was the first scientist to discover cells? Robert Hooke What instrument is used to study cells? Know the two different types of that instrument. -microscopes 1) modern microscopes- can be simple or compound 2) electron microscopes- much stronger magnification 4. Chapter 2 section 3 (p.54-57) What are viruses? Strands of material that are surrounded by a protein. They require a host cell to multiply, they can be helpful, and there are vaccines to help prevent certain viral diseases. Is a virus living or non-living?? non-living