* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Organization of Life
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
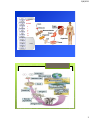
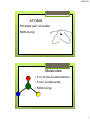
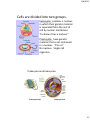
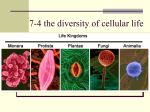
9/8/2015 Levels of Organization of Life Levels of Organization There are many examples of levels of organization that relate to the real world. Please provide one. Place the following levels in order: Ecosystem Atoms Community Molecule Population Cell Organism Biosphere Organ Organ system Organelle Macromolecule Biome Tissue 1 9/8/2015 NON LIVING L I V I N G Levels of Organization 2 9/8/2015 ATOMS • Smallest part of matter • NON-living Molecules • 2 or more bonded atoms • Form compounds • NON-living 3 9/8/2015 Biomolecule/Macromolecule A very large molecule made by joining hundreds of molecules. Organelle Compartments that may be surrounded by membranes. Each carries out a specific function inside the cell. 4 9/8/2015 Cell Smallest functional unit of life, composed of organelles. Tissue A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function. 5 9/8/2015 Organ One or more tissues working as functional unit. Organ System or Body System Two or more organs that work separately but are integrated to perform a specific task. 6 9/8/2015 Organism Individual living thing, made of cells, tissues, organs, organ systems. Population Group of organisms of one type that live in the same area 7 9/8/2015 Community Populations that live together in a defined area Ecosystem Communities and its non-living surroundings 8 9/8/2015 Biosphere Part of the Earth that contains all ecosystems. Which of these organisms has the same levels of organization as we do? Bacteria Cell = Single Cell Plants = Multicellular 9 9/8/2015 What does it mean to be “living”? • • • • • Growth and development Reproduce – asexual and sexual Adapt to their environment. They evolve. Cells. All living things are made of Cells. Energy. All living things require energy. –Metabolism: the sum of all chemical activities in an organism. • Stimulus. All living things respond to a stimulus. • Homeostasis: All living things maintain an internal balance known as homeostasis. 10 9/8/2015 Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms Unicellular Organisms Multicellular Organisms • One celled organisms that perform all cell functions within that one cell. • Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Organisms that consists of more than one cell. • Eukaryotes Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells 11 9/8/2015 Cells are divided into two groups. Eukaryote: contains a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of cell by nuclear membrane. “Eu knew it has a nucleus.” Prokaryote: have genetic material that is not contained in a nucleus. “Pro no” No nucleus. Single cell organism. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Prokaryotic Cell Eukaroytic Cell 12 9/8/2015 Euglena = Protista Bacteria 13