* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Cycle
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
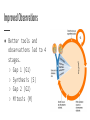
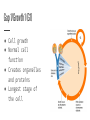
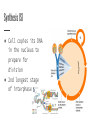
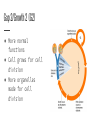
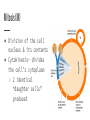
The Cell Cycle Early Observations ● All living things have a life cycle ● Cell cycle- a pattern of eukaryotic cell growth & division ● Early observations saw 2 stages ○ mitosis (cell division) ○ interphase (not division) Improved Observations ● Better tools and observations led to 4 stages. ○ Gap 1 (G1) ○ Synthesis (S) ○ Gap 2 (G2) ○ Mitosis (M) Gap 1/Growth 1 (G1) ● Cell growth ● Normal cell function ● Creates organelles and proteins ● Longest stage of the cell Synthesis (S) ● Cell copies its DNA in the nucleus to prepare for division ● 2nd longest stage of interphase Gap 2/Growth 2 (G2) ● More normal functions ● Cell grows for cell division ● More organelles made for cell division Mitosis (M) ● Division of the cell nucleus & its contents ● Cytokinesis- divides the cell’s cytoplasm ○ 2 identical “daughter cells” produced Chemical Checkpoints ● Exist at the ends of G1 & G2 and in the middle of mitosis ● Makes sure that the cell is ready for the next stage Human Cell Cycle ● On average, cells go through the S, G2, & M stages in 12 hours ● G1 time differs by cell type ○ Shorter for cells that are worn down quickly or during fast growth ■ embryonic cells ■ stomach cells ■ skin cells Human Cell Cycle ● G1 differs by cell type ○ Longer G1 for internal organs that have less wear and tear ■ lung cells ■ kidney cells ■ liver cells G Zero Stage (G0) ● Cells that rarely divide but continue with normal cell function ● No S, G2, or M stages ● Only certain cells have this stage ○ neurons ○ heart muscle cells