* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology Midterm Study Guide Chapter 1 and 2: The Science
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Honors Biology Midterm Study Guide Chapter 1 and 2: The Science of Biology Students will be able to… ● identify variables in an experiment ● distinguish between observations and inferences ● match examples to characteristics of living things Mike’s dad always buys bread with preservatives because he says it lasts longer. Mike asks, “Will bread with preservatives stay fresh longer than bread without preservatives?” He hypothesizes that bread with preservatives will not grow mold as quickly as bread without preservatives. In order to test his hypothesis, he obtains one slice of bread containing preservatives and one slice of bread without any preservatives. He dampens two paper towels and folds the paper towels so that they will lay flat inside two separate ziploc bags. One slice of bread is placed in each bag and the bags are sealed and kept in a dark environment for one week. Mike records mold growth once a day for one week. What is Mike’s hypothesis? ______________________________________________________________ What is the independent variable? Dependent variable? Control group? Name 3 controlled variables in Mike’s experiment. “The bread with preservatives has less mold growing on its surface than the bread without preservatives” is an (observation, inference, opinion). “The bread without preservatives tastes better” is an (observation, inference, opinion). “The preservatives in the bread include fungicides” is an (observation, inference, opinion). Distinguish between a hypothesis and a theory. List the 8 characteristics of living things and gives examples of each: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Ch 9: Cellular Inheritance Compare and Contrast Mitosis and Meiosis in terms of where these processes occur, their function or purpose, the number of divisions and daughter cells produced, the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells. Describe what is going on in each phase of the cell cycle picture here: Explain how the cell cycle is regulated and what happens when this system malfunctions (ie. cancer) Meiosis is the formation of sex cells or gametes. What is crossingover? Explain their contribution to genetic diversity. Ch 10: Introduction to Genetics and Ch 12: The Human Genome 1. Explain the experiments done by Gregor Mendel. Why did he use pea plants? Draw Punnett squares to represent the F1 and F2 generations. 2. What is the difference between genes, alleles, and traits? Remember: at least two alleles (one from each parent) make up the gene that determines traits in offspring. 3. Give an example of a dominant allele ____ and a recessive allele ____. How do they influence inheritance of traits? 4. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? Give an example of each. 5. Practice Punnett squares with homozygous inheritance (TT, tt) and heterozygous (Tt) inheritance 6. What kind of cells are represented by the alleles outside the Punnet Square? Inside the Punnett Square? 7. If a parent has the genotype AaBb, what are the different combinations that they can send into the sex cells (gametes)? 8.Define complete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, and incomplete dominance. Give example of each inheritance 9. What are the sex chromosomes? What is the diploid number for humans? Can you explain sexlinked inheritance? 10. Use of pedigree charts to show human inheritance patterns. 11. If Mom has B+ blood and a baby has O blood, what are the possible blood types for the father? 12. Draw a pedigree for an autosomal recessive trait in which the father’s sister expresses the trait, but he and their parents do not. The mother expresses the trait, and their youngest daughter and son express the trait, but the older boy and girl do not. Ch 11: DNA and RNA 1. Compare DNA and RNA by filling out the chart below. DNA Stands for: RNA Deoxyribonucleic acid cDNA complementary strand of DNA Name of Sugar: 4 Nitrogen Bases: Single or Double Stranded: Where is it in the cell? Types of: Purpose: Sketch a picture of the molecule: Master DNA strand: TAC CAT GGG TGA CAA GTC 2. DNA replication: what is it, when does it occur in the cell cycle, why does it occur, how does it occur? Replicate the strand of DNA above: ____________________________________________________ 3. Transcription and translation: how is genetic information encoded in DNA transcribed (copied) as mRNA in the nucleus and translated into a specific protein in the ribosome? Transcribe the master DNA strand into mRNA: ______________________________________________________________ 4. Translation into amino acids using Codon Wheel: __________________________________________________________ 5. Human hair is made of protein. Explain how the processes of DNA replication/transcription/translation, cell cycle with Meiosis all can lead to two people having different colored hair. 6. Explain the differences between chromosomal and gene mutations and their significance on the resulting protein. Ch 14 & 15: Evolution 1. Who is Charles Darwin? Describe his ideas of natural selection and common descent. 2. How can the diversity of living things be explained using the theory of natural selection? 3. What causes genetic variation occur? __________________ & ______________________ 4.How do the processes described in #3 above, provide material in organisms for natural selection to work upon? In other words, how does the absence of the processes described in #3 prevent natural selection from occurring? 5.How does natural selection explain how bacteria causing human diseases become immune to antibiotics used to heal people who have the diseases caused by the bacteria in question. The History of Life: Geologic time Place the major groups of animals and mass extinctions into the appropriate era PALEOZOIC: MESOZOIC: CENOZOIC:






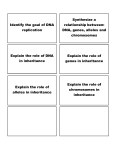




![Ch. 9 + 10 [genetics]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008315130_1-77d900a848f59bba71a4600153ed2e6c-150x150.png)