* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology B Trimester Review 6-1
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
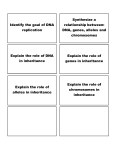
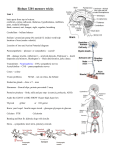
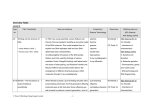
Biology B Trimester Review Chapter 10, 11.4, 248, 334, 612: Cell Cycle + Development 1. Explain the purpose of mitosis. 2. Explain the difference among chromatin, chromosomes, and chromatids. 3. What are the two phases of the cell cycle? 4. Describe the events that take place during G1, S, G2. 5. Describe the events taking place during mitosis and cyokinesis. 6. Compare the daughter cells at the end of mitosis to each other and the parent cell. 7. How is cytokinesis in plants different from that in animal cells? 8. Compare benign tumors to malignant tumors in terms of cell type, danger, mobility, and treatments. 9. Explain the purpose of meiosis. 10. What are homologous chromosomes? 11. What does it mean to be a diploid cell? A haploid cell? 12. What are gametes? 13. If the “n” number of a cell is 24, what would its diploid number be? 14. Be able to explain the different phases of meiosis. 15. What is crossing over, and when does it take place? 16. Identify another way to increase genetic variation in offspring? 17. Compare and contrast the daughter cells produced at the end of meiosis to each other and to the parent cell. 18. What are stem cells? Why are they important? 19. What is a zygote? An embryo? Chapter 11, 334-340: Genetics 1. Explain why the blending hypothesis was eventually rejected as the method of inheritance? 2. Define trait, loci, gene, allele. 3. Describe Mendel’s particulate hypothesis of inheritance. 4. What does it mean to be true-breeding? 5. What characteristics make pea plants ideal organisms for genetic studies? 6. Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes. 7. How many alleles does it take to show a dominant trait? 8. Be able to conduct mono/di-hybrid crosses and determine genotypic/phenotypic ratios. 9. How are testcrosses used to determine unknown genotypes? 10. Explain Mendel’s principle of independent assortment. 11. Be able to conduct Punnett Square crosses involving exceptions to Mendel’s Rules. 12. What is unique about a heterozygous individual exhibiting intermediate inheritance? 13. Why are some alleles written as a letter/symbol as an exponent on a base letter? 14. How does polygenetic inheritance differ from having multiple alleles? 15. How many blood alleles are in the population? Blood phenotypes? 16. Explain the role of the environment in determining an organism’s phenotype. 17. Which chromosome is important to sex-linked inheritance? 18. Why are males often affected by sex-linked disorders? Chapter 12 and 13: DNA and the Language of Life 19. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 20. DNA is composed of what monomer? 21. What are the three units to the above monomer? 22. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 23. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 24. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 25. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 26. What hold base pairs together and how many? 27. What enzyme is involved in attaching nucleotides to form DNA? 28. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 29. Identify and describe the three types of RNA. 30. Why are three nucleotides needed for one codon? 31. For transcription and translation: a. Summarize in one sentence. b. What “materials” are needed? c. Identify the step. d. Where does it take place? 32. Define mutation. 33. What are two main classes of mutations? 34. What is a point mutation? 35. What is the difference between a silent mutation and an expressed mutation? 36. Explain how insertions and deletions are frameshift mutations. Chapter 10.4, 14.3, 15.2-15.4: DNA and Biotechnology 37. What is the Human Genome Project? 38. What is biotechnology? 39. What is recombinant DNA? 40. What is a plasmid? 41. How are restriction enzymes used by biologists? 42. What are pros/cons of genetically modified organisms? 43. What steps are involved in animal cloning? 44. How is gel electrophoresis used by scientists? 45. Why are stem cells important to scientists? Chapter 16, 406, 17.2, 17.3, Chapter 18, 19.1, 459-461: Evolution and Classification 46. Define Evolution and Adaptation 47. What is the smallest level that evolution can act on? 48. What is descent with modification? 49. What is natural selection? 50. How do we age fossils? 51. Compare and contrast homologous structures to analogous structures. 52. What are vestigial structures? 53. Why must variation exist for evolution to occur? 54. What is a gene pool? 55. Describe 2 different types genetic drift that can change a gene pool. 56. What are 2 additional ways? 57. What are two types of macroevolution? 58. Describe how species number can increase by adaptive radiation? 59. Describe the information needed to build a phylogenetic tree. 60. What is cladistics? A clade? 61. Did humans evolve from Apes? Explain.