* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 9 + 10 [genetics]
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
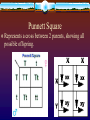
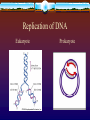
Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 9 Gregor Mendel Monk who lived in early 1860’s. Wanted to know how heredity was passed on from generation to generation. 1800’s theory: Blending Concept Both parents contribute equally to offspring. EX: red flower + white flower = pink Mendel’s Experiment Worked with PEA plants Why: 1. Easy to cultivate 2. Has a short generation time 3. Easily cross pollinated 4. Many varieties Pea Plant Traits Mendel’s Final Theory Particulate Theory of Inheritance: Inheritance is based on the existence of minute particles called genes; these genes are reshuffled from generation to generation. One-Trait Inheritance Chose plants that differed only in ONE trait Parent Generation : P 1st Generation : F1 2nd Generation : F2 Alleles: different forms of genes Letters are assigned for different alleles (traits) Y = yellow y = green Dominant (Y) – visible trait Recessive (y) – hidden trait Homozygous – a trait where 2 alleles are the same (yy or YY) Heterozygous – a trait where 2 alleles are different (Yy) Genotype – the alleles the individual receives Phenotype – the physical appearance Punnett Square Represents a cross between 2 parents, showing all possible offspring. Practice Problem In rabbits, if B = black hair, and b= white hair. When two heterozygous parents are crossed, B b what are the offsprings? B BB Bb b Bb bb -one trait cross- Practice Problem What is the phenotypic ratio?? B b B BB Bb b Bb bb 3:1 3 = black 1 = white Practice Problem In pea plants, if Y = yellow, and y = green peas, and T = tall plant, and t = short plant. When two heterozygous parents are crossed, what are the offsprings? YT -two trait cross- YT YYTT Yt yT yt YYTt YyTT YyTt Yt YYTt YYtt YyTt Yytt yT YyTT YyTt yyTT yyTt yt YyTt Yytt yyTt yytt Practice Problem What is the phenotypic ratio?? 9:3:3:1 9 = yellow & tall 3 = yellow & short 3 = green & tall 1 = green & short YT YT YYTT Yt yT yt YYTt YyTT YyTt Yt YYTt YYtt YyTt Yytt yT YyTT YyTt yyTT yyTt yt YyTt Yytt yyTt yytt DNA Structure Chapter 10 History Mendel knew that inheritance was passed on, but he didn’t know what! Two molecules that were thought to pass on inheritance – DIDN’T KNOW WHICH ONE 1. 2. Proteins DNA DNA Structure Watson and Crick – 1962 Nucleotides bonded together in a double helix 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 different ones A = adenine T = thymine G = guanine C = cytosine A=T G=C Replication of DNA Eukaryote Prokaryote