* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
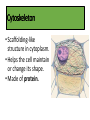
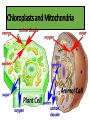
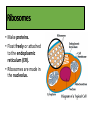
Cells Chapter 1.4 Organelles in Plant and Animal Cells Cell wall • Protects the cell. • Gives the cell its shape. • Found in plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria. Cell/Plasma Membrane • Protective layer around ALL cells. • For cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is inside the cell wall. • Allows food, oxygen, and water into the cell and waste products out of the cell. Cytoskeleton • Scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm. • Helps the cell maintain or change its shape. • Made of protein. Nucleus • Directs all cell activities. • Contains instructions for everything the cell does. • These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA. Nucleolus • Found within the nucleus. • Responsible for the production of ribosomes. Chloroplasts • Contain a green pigment, chlorophyll, that captures light energy from the sun used to produce glucose. • Found only in plant cells. Mitochondria • The powerhouse of a cell. • Energy is released by breaking down glucose. Chloroplasts and Mitochondria Pause and Think Some muscle cells have 20,000 mitochondria. Why would these cells need so many mitochondria? Ribosomes • Make proteins. • Float freely or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). • Ribosomes are made in the nucleolus. Endoplasmic reticulum • A series of folded membranes that move proteins around in a cell. • Smooth ER – ribosomes NOT attached to ER. • Rough ER – ribosomes attached to ER. Golgi apparatus • Stacked and flattened membranes. • Function is to sort, package and ship proteins that are produced in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Vacuoles • Temporary storage spaces. • Store food, water, waste. Vacuole Lysosomes • Membrane-bound sacs containing enzymes responsible for: • The digestion of material in food vacuoles. • The destruction of foreign bodies entering the cell (e.g. bacteria). • The breakdown of cell structures when the cell dies. Homework Cell Organelles: Complete the task sheet by sorting the function cards and memory items. Cut and paste the cards for each corresponding organelle.