* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download basic parts of a cell - Marissa Junior/Senior High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
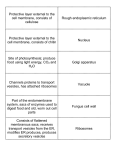
Chapter 4 Cell: the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life. Studied nature Used “light microscope” pg 69 Viewed a thin slice of cork Saw many little boxes CELLS First to observe living cells Microscope lens was 10x that of Hooke Was first able to see unseen world of microorganisms First to view a REAL cell Botanist First to view plant cells Concluded: All plants are composed of cells. Zoologist Concluded: All animals were made of cells. Physician All cells come from other cells. 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. Discovery of cells and cell theory: MICROSCOPE 1. made of organized parts 2. obtain energy from their surroundings 3. perform chemical reactions 4. change with time 5. respond to the environment 6. reproduce In a body: pg 72 Different cells Different shapes Different functions All in same body Shape reflects the different functions PAGE 72 A few types of cells are large enough to be seen without a microscope Ex. Giraffe’s nerve cells: 6 ½ ft long Human egg cell: size of a period MOST cells: 1/500th the size of a period SURFACE AREA-TO-VOLUME RATIO Nutrients and oxygen go in Waste goes out BOTH pass through surface Happens QUICKLY therefore need more surface area to volume page 73 Cells MUST be microscopic!!! 3 basic parts to all cells 1. Cell Membrane 2. 3. Cytoplasm Nucleus Also called the plasma membrane Covers the surface Acts as a barrier All materials enter or exit through this Hold all of the organelles Control center Holds DNA Membrane bound and free floating DNA PROKARYOTES Lack a membrane-bound nucleus Lack membrane-bound organelles May have a nucleoid: concentrated area of DNA DOMAIN Archaea DOMAIN Bacteria EUKARYOTES In organisms made up of one or more cells Contain organelles Larger in size than prokaryotes Page 76 Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Functions: A. Allows only certain molecules to enter or leave the cell B. Separates reactions inside the cell from outside the cell C. Excretes waste D. Interacts with environment Phospholipids Proteins Cell surface markers – emerge from only one side of the membrane Receptor proteins – recognizes and binds to substances outside the cell Transfer proteins – helps substances move across the membrane Enzyme – Houses and protects genetic information Chromosomes: holds DNA Nuclear Envelope: surrounds nucleus Nucleolus: denser area in nucleus Holds organelles Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi aparatus Vesicles Microtubules Microfilaments centrioles Mitochondria: tiny organelles that transfer energy into ATP ATP: Adenosine triphosphate Powers the cell’s chemical reactions HIGH in # in muscle cells! FEW in # in fat cells. Small, roughly spherical organelles Responsible for building protein No membrane Made of protein and RNA Created in nucleus, finished in cytoplasm Found in Cytoplasm Some endoplasmic reticulum Called ER System of tubes and sacs (cisternae) Function as a “highway”: a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another 2 types: Rough Smooth System of interconnected, flattened sacs covered with RIBOSOMES Pg 81 Produces phospholipids and proteins Ribosomes on ER: Produce digestive enzymes that contain proteins Vesicles (sacs) pinch off and store these enzymes until they are released Smooth appearance Builds In ovaries and testes: produces hormones *abundant in liver and kidneys: Long term alcohol and drug abuse: Pg 82 Another system of flattened, membrane sacs Sacs closest to the nucleus receive vesicles from the ER containing newly made proteins or lipids Proteins get “address labels” VESICLE: small sacs that head to the plasma membrane and release contents outside of cell 1. LYSOSOME 2. PEROXISOME 3. others Vesicles from Golgi Apparatus that contain digestive enzymes Breakdown proteins, carbs, fats, bacteria. Responsible for breaking down cell when it is time to die! Abundant in liver and kidney Detoxify alcohol and other drugs Also breakdown fatty acids 1. proteins assembled by ribosomes on rough ER 2. Vesicles transport proteins to the golgi apparatus 3. Golgi modifies the proteins and packages them in new vesicles 4. Vesicles release proteins that have destination outside of cell 5. Vesicles needing to remain inside of cell stay. Network of thin tubes and filaments Give shape to the cell from the inside ex. Tent poles Also acts as a system of internal tracks to allow items to move around in cell Microtubules, Microfilaments, & Intermediate filaments Hollow tubes made of protein called “tubulin” 1. Hold organelles in place 2. Maintain cell’s shape 3. Act as track to guide organelles Finer than microtubules 2 strands of intertwined protein 1. contribute to cell movement 2. muscle contraction 3. maintainance and changing of shape Rods that anchor the nucleus and other organelles to their place Maintain INTERNAL shape of nucleus CILIA Extend from surface of cell Short Large #’s Inner ear: vibrate and help detect sounds Protisits: sweep food into mouthlike opening FLAGELLA Extend from surface of cell Long less #’s Plant cells have 3 additional kinds of structures 1. cell wall 2. large central vacuole 3. plastids Make their own food: photosynthesis Must reach up towards the sun Need to hold water Rigid layer outside of plasma membrane Made of cellulose: a carb that makes the cell like a stiff box 2 layers: Primary wall Secondary wall (wood) Large, fluid-filled organelle Mainly stores water 90% of the plants volume Causes plant to stand upright Used in photosynthesis Use light energy Contain chlorophyll: green pigment that absorbs light and captures the light energy Colored pigment Found in carrots: orange flowers: red, purple, yellow & white