* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biological explanation of schizophrenia (1)
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Irving Gottesman wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
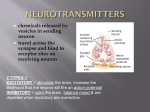
BIOLOGICAL EXPLANATION OF SCHIZOPHRENIA (1) The function of neurotransmitters • What is this? • What does it do? • Where are the neurotransmitters? • Can you name any neurotransmitters? LABEL THE DIAGRAM ON THE FOLLOWING SLIDE. YOU CAN USE THE TEXT BELOW TO HELP. Neurotransmitter molecules are released from the end of the presynaptic cell (the axon) into the space between the two nerve cells (the synapse). Having travelled across the synaptic gap or cleft, molecules may then be ‘taken up’ by specially shaped receptor sites on the postsynaptic nerve cell (the dendrite) and so the chemical message is passed on. The relationship between the neurotransmitter molecule and the receptor site is like a lock and key, molecules will only fit certain receptor sites. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WhowH0kb7n0 LETS REMIND OURSELVES HOW NEUROTRANSMITTERS WORK LETS REMIND OURSELVES HOW NEUROTRANSMITTERS WORK What happens if the neurotransmitt ers are not ‘sponged back up by the presynaptic nerve? What does dopamine do? What do you think the consequence of too much dopamine would be? BACKGROUND • Patients who abused large amounts of amphetamine have often shown positive symptoms of schizophrenia. • Randrup and Munkvad (1966) raised dopamine levels in the brains of rats by injecting them with amphetamine • Rats behaviour changed – psychotic behaviour consistent with that shown in patients with schizophrenia • Research has suggested that the presence of an excess of dopamine receptors and synapses in the brain contributes to schizophrenia • Those treated with dopamine enhancing levodopa for Parkinson's disease can experience psychotic side effects mimicking the symptoms of schizophrenia. • Amphetamine, cocaine and similar drugs increase levels of dopamine in the brain and can cause symptoms which resemble those present in psychosis, particularly after large doses or prolonged use. This is often referred to as "amphetamine psychosis" or "cocaine psychosis," but may produce experiences virtually indistinguishable from the positive symptoms associated with schizophrenia. • Up to 75% of patients with schizophrenia have increased signs and symptoms of their psychosis upon challenge with moderate doses of methylphenidate or amphetamine or other dopamine-like compounds, all given at doses at which control normal volunteers do not have any psychologically disturbing effects Leiberman et al 1987) • Lieberman et al. 1987 – 75% of patients with schizophrenia show new symptoms or increase in symptoms of psychosis after using amphetamine (mimic the action of dopamine) • Not all users of amphetamine suffer from psychotic symptoms – Suggesting there is something different about hope people’s brains react to dopamine The Dopamine hypothesis states that the brain of schizophrenic patients produces more dopamine than normal brains. Schizophrenia symptoms are due to excess activity of the neurotransmitter – dopamine. it is now thought that those with schizophrenia have an abnormally high number of D2 receptors – rather than just high dopamine levels. • Post mortems of brains of people who had have had schizophrenia show a higher density of dopamine receptors is in certain parts of the brain (cerebral cortex) than those who have not suffered from schizophrenia (Owen et al. 1989) • SZ- more sensitive to the action of dopamine • Seeman (2013) People diagnosed with schizophrenia may have a higher number of D2 receptors with a high affinity to dopamine • More likely to bind to the neurotransmitter when it is present in the synapse • More likely to overreact to the presence of the neurotransmitter • This may result • from a combination of increased presynaptic neural pruning, a high release of dopamine • (Howes et al., 2012), altered numbers of dopamine D2 receptors (Seeman, 2013a, in press), • and/or an increased sensitivity of the D2 receptor to dopamine (Seeman, 2011). This view is • supported by the fact that the positive symptoms of delusions and hallucinations are • alleviated in the majority of patients by D2-blocking medications. The positive symptoms of schizophrenia include hallucinations and delusions as a result of increased subcortical release of dopamine, which augments D2 receptor activation The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area (VTA_, which is located in the midbrain, to the nucleus accumbens (NA) Positive symptoms Negative symptoms The negative symptoms of schizophrenia include lack of motivation, avolition, diminished emotional expression, which result from reduced D1 receptor activation in the prefrontal cortex Okubo 1997 EVALUATION • SCOAR • Supporting research • Application – treatment • Reductionist – pg 293 It is further here suggested that dopaminergic overdrive is a necessary step on the path between initial causation and symptom expression. As such, therapeutic interventions need to focus on preventing dopamine overstimulation through a combination of means: biological (dampening dopamine release and transmission), psychological (muting stress that is mediated through dopamine pathways), and sociological (alleviating poverty and discrimination, which raise dopamine activity in large swaths of the population). Seeman 2014