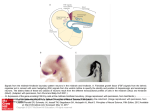
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Empirical theory of perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive model wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stephen Grossberg wikipedia , lookup
Eshkol-Wachman movement notation wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual control theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup