* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A View of the Cell
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
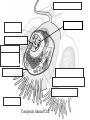
A View of the Cell Cellular Organization • Cell • Tissue – group of cells functioning together. • Organ – group of tissues functioning together. • Organ System – group of organs functioning together. • Organism – group of organ systems functioning together. The History of the Cell • The Cell –The basic unit of an organism –Discovery made possible by the invention of the microscope Microscopes and Cells • 1600’s. –Anton van Leeuwenhoek first described living cells as seen through a simple microscope. Microscopes and Cells –Robert Hooke used the first compound microscope to view thinly sliced cork cells. •Compound scopes use a series of lenses to magnify in steps. •Hooke was the first to use the term “cell”. Microscopes and Cells • 1830’s. –Mathias Schleiden identified the first plant cells and concluded that all plants made of cells. - Thomas Schwann made the same conclusion about animal cells. Cell Theory: • All living things are made up of cells • Each cell has the same essential parts. Cells come in many sizes and shapes. Humans are composed of many cells. And are said to be multicellular. Some organisms such as bacteria, yeast and protozoans are only single celled. Nuclear membrane The Parts of The Cell 1.) Cell Membrane -- Serves as a boundary between the cell and its external environment. -- Allows materials to pass in and out of the cell. 2.) Cell Wall -- Surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells -- Plant cell walls contain cellulose. Gives the plant structure. 3.) Nucleus •Controls the activities of the cell. •Contains chromatin – long tangles of DNA. 4.)Cytoplasm •The jelly-like material that surrounds the organelles. Contains water salts and organic compounds. 5.) Vacuoles •Stores food, fluid, or waste products. 6.) Chloroplasts -- Found in plant cells and some protists. -- Contain chlorophyll – a green pigment that traps light energy and gives plants their green color. Nuclear Membrane Surrounds the nucleus and separates it from the cytoplasm. Composite Animal Cell Composite Animal Cell