* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 8.1 Summary – pages 195
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
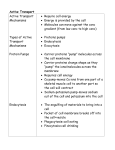
CELLULAR TRANSPORT Chapter 3, Section 2 Osmosis: Diffusion of Water • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • In a cell, water always moves to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. Osmosis: Diffusion of Water • The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. • Regulating the water flow through the cell membrane is an important factor in maintaining homeostasis within a cell. Passive Transport • When a cell uses no energy to move particles across a membrane passive transport occurs. Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Passive Transport by proteins • Passive transport of materials across the membrane using transport proteins is called facilitated diffusion. Channel proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Passive Transport by proteins • Some transport proteins, called channel proteins, form channels that allow specific molecules to flow through. Channel proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Passive transport by proteins • The movement is with the concentration gradient, and requires no energy input from the cell. Carrier proteins Concentration gradient Plasma membrane Step 1 Step 2 Passive transport by proteins • Carrier proteins change shape to allow a substance to pass through the cell membrane. Carrier proteins Concentration gradient Plasma membrane Step 1 Step 2 Passive transport by proteins • In facilitated diffusion by carrier protein, the movement is with the concentration gradient and requires no energy input from the cell. Carrier proteins Concentration gradient Plasma membrane Step 1 Step 2 Active Transport • Movement of materials through a membrane against a concentration gradient is called active transport and requires energy from the cell. Carrier proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Cellular energy Step 1 Step 2 How active transport occurs • In active transport, a transport protein called a carrier protein first binds with a particle of the substance to be transported. Carrier proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Cellular energy Step 1 Step 2 How active transport occurs Click image to view movie. How active transport occurs • Each type of carrier protein has a shape that fits a specific molecule or ion. Carrier proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Cellular energy Step 1 Step 2 How active transport occurs • When the proper molecule binds with the protein, chemical energy allows the cell to change the shape of the carrier protein so that the particle to be moved is released on the other side of the membrane. Carrier proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Cellular energy Step 1 Step 2 How active transport occurs • Once the particle is released, the protein’s original shape is restored. • Active transport allows particle movement into or out of a cell against a concentration gradient. Carrier proteins Plasma membrane Concentration gradient Cellular energy Step 1 Step 2 How active transport occurs Click image to view movie. Transport of Large Particles • Endocytosis is a process by which a cell surrounds and takes in material from its environment. Nucleus Wastes Digestion Endocytosis Exocytosis Transport of Large Particles • The material is engulfed and enclosed by a portion of the cell’s membrane. Nucleus Wastes Digestion Endocytosis Exocytosis Transport of Large Particles • The resulting vacuole with its contents moves to the inside of the cell. Nucleus Wastes Digestion Endocytosis Exocytosis Transport of Large Particles • Exocytosis is the expulsion or secretion of materials from a cell. Nucleus Wastes Digestion Endocytosis Exocytosis Transport of Large Particles • Endocytosis and exocytosis both move masses of material and both require energy. Nucleus Wastes Digestion Endocytosis Exocytosis