* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download asdfs
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
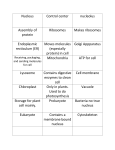
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7 http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/cell.gif Vocab Review Process in which cells change and develop into different kinds of cells doing different jobs Differentiation OR cell specialization Idea that all living things are made of Cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced by existing cells Cell theory Collection of living material enclosed by a barrier that separates it from its surroundings; the basic unit of life cell Log-like structures that pull the chromosomes apart during cell division in animal cells centrioles Membrane protein with sugars attached that help cells identify “self” glycoprotein Movement of water from a higher concentration to lower across a semi-permeable cell membrane osmosis Sac of digestive enzymes used by cells to break down food, cell parts, or whole cells lysosomes Membrane stacks found inside chloroplasts where the enzymes for photosynthesis are found thylakoids Control center of the cell that contains the genetic material nucleus Stack of membranes in cells that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the ER for transport Golgi body (apparatus) DNA with attached proteins found spread out in the nucleus of non-dividing cells chromatin Describes molecules that try to stay away from water… means “water fearing” hydrophobic Transport that does NOT require energy Passive transport Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower until equilibrium is reached diffusion Nucleotide molecules used by cells to store and transfer energy ATP Transport that requires energy Active transport DNA with proteins attached that is scrunched up into compact bodies in the nucleus of dividing cells chromosomes Molecule with a polar head and two hydrophobic tails used to make cell membranes phospholipid Passive movement of specific molecules across a cell membrane with the help of membrane carrier proteins Facilitated diffusion Condition in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is GREATER than inside. HYPERTONIC Kind of passive transport in which proteins form passageways across the membrane for sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride ions ion channels Many, small hair-like structures made of microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement that extend from the surface of cells and help in movement cilia Space used to store water, food, molecules, enzymes, or waste vacuole Condition in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is LESS than inside HYPOTONIC Dark spot in the cell nucleus where RNA for ribosomes is made Nucleolus Network of microtubules and microfilaments that give the cell shape and support it cytoskeleton Organism whose cells have a nucleus and organelles surrounded by membranes eukaryote Gel-like material and the organelles found between the nucleus and cell membrane cytoplasm Double membrane that surrounds the cell nucleus Nuclear envelope OR nuclear membrane Small particles that make proteins ribosomes Membrane system without ribosomes attached involved in lipid synthesis, calcium regulation, and the break down of toxins Smooth ER Power plant of the cell that burns glucose and stores the energy released in ATP mitochondria Folded inner membrane inside a mitochondrion cristae System of membranes with ribosomes attached where proteins are produced and modified Rough ER Organelle where photosynthesis happens chloroplast Bilayer made of phospholipids and proteins which surrounds all cells and controls what enters and leaves Cell membrane Double layer formed when phospholipids line up with their hydrophillic heads to the outside and their hydrophobic tails toward the center bilayer Molecule with an uneven pattern of charges… slightly positive on one side, slightly negative on the other polar Small structure inside eukaryotic cells which carries out a specific function organelle Unicellular organism that does NOT have a nucleus and or organelles surrounded by membranes prokaryote Describes molecules that try to be near water or other polar molecules… means “water loving” hydrophillic Structure found outside the cell membrane that provides support and protection Cell wall Polysaccharide found in plant cell walls that makes them sturdy cellulose Molecule made by joining amino acid subunits that is used to make cell membranes protein Condition in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is equal to the concentration inside isotonic Process in which small molecules or liquids are engulfed and taken into the cell pinocytosis Molecule used to build bacterial cell walls instead of cellulose peptidoglycan State in which the concentration of molecules is equal throughout the available space equilibrium Process in which a vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases its contents to the outside exocytosis Kind of active transport in which ATP provides the energy to a membrane protein that moves sodium ions out and potassium ions into cells Sodium-potassium pump A living thing composed of many organ systems organism Process in which large molecules or whole cells are engulfed and taken into the cell phagocytosis Process in which material is surrounded by the cell membrane and taken into the cell when a piece of cell membrane breaks off and forms a vesicle within the cytoplasm endocytosis Organism made of one cell unicellular A few, long hair-like structures made of microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement that extend from the surface of cells and help in movement flagella Small openings in the nuclear membrane that allow molecules to pass through Nuclear pores Group of different kinds of tissues working together organ Molecule found in the nucleus that carries the genetic code DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid A group of similar cells working together tissue Organism made of many cells multi-cellular Group of different organs working together organ system Protein found in cell membranes which helps molecules get across the membrane Carrier protein Small membrane sac used to transport substances during endocytosis and exocytosis vesicle Programmed cell death; “cell suicide” apoptosis