* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.1 Cells and simple cell transport
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
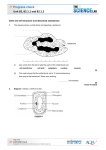
Name: Target Grade: 2.1Cells and Simple Cell Transport Q1. The diagram shows a group of muscle cells from the wall of the intestine. (a) On the diagram, use words from the box to name the structures labelled A, B and C.(3) cell membrane (b) cell wall chloroplast cytoplasm nucleus How are these muscle cells adapted to release a lot of energy? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q2. Diagram 1 shows a cell from a leaf. Diagram 1 (a) How is the leaf cell specialised to carry out photosynthesis? Tick ( ) one box. It has a permanent vacuole. It has many chloroplasts. It has cytoplasm. It has many mitochondria. (1) (b) Diagram 2 shows another type of plant cell. Page 1 Diagram 2 Give two ways in which this cell is different from an animal cell. 1 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Q3. The drawing shows an animal cell, seen at a very high magnification using an electron microscope. (a) (i) Label a mitochondrion [plural = mitochondria]. (ii) What happens in the mitochondria? (1) .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Name and label the structure where you would find chromosomes. (ii) What are chromosomes made of? (1) .......................................................................................................................... (1) (c) What controls the rate of chemical reactions in the cytoplasm? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q4. The diagram shows a bacterium. Page 2 (a) On the drawing, name the structures labelled A, B, C and D. (4) (b) Name one type of cell, other than a plant cell, which also has a cell wall. .................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q5. (a) The diagrams show cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Into which cell, A, B, C or D, will oxygen move the fastest? Write your answer, A, B, C or D, in the box. (b) (1) Draw a ring around the correct word to complete each sentence. diffusion (i) Oxygen is taken into cells by the process of osmosis . respiration (1) breathing (ii) Cells need oxygen for photosynthesis . respiration Page 3 (1) membranes (iii) The parts of cells that use up the most oxygen are the mitochondria . nuclei (1) diffusion (iv) Some cells produce oxygen in the process of photosynthesis . respiration (1) (Total 5 marks) Q6. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell. cell membrane cell wall cytoplasm nucleus vacuole (4) (b) The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D represents: (c) (i) movement of oxygen molecules; .................... (ii) movement of carbon dioxide molecules? .................... (2) Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) [Total 30 marks] Page 4 Page 5 Mark Scheme M1. (a) A nucleus 1 B (cell) membrane 1 C cytoplasm 1 (b) any two from: • (contain mitochondria • many (mitochondria) • respiration (occurs in mitochondria) 2 [5] M2. (a) it has many chloroplasts. 1 (b) (has) cell wall 1 (has) vacuole or large / permanent vacuole do not allow chloroplasts assume plant cell throughout accept converse for animal cell 1 [3] M3. (a) (i) award 1 mark for any of the mitochondria correctly labelled if a number are labelled and one is incorrect award 0 marks 1 Page 6 (ii) respiration or the release or transfer of energy or it contains the enzymes for respiration do not accept energy produced 1 (b) (i) nucleus (named and correctly labelled) arrow or line must touch or go inside the nuclear membrane 1 (ii) DNA or genes or nucleic acids accept protein or histones or nucleotides or ATGC 1 (c) enzymes or nucleus do not accept factors that affect the rate rather than control it eg pH or temperature 1 [5] M4. (a) A – cell membrane 1 B– cytoplasm 1 C– genes / genetic material / chromosome 1 D – cell wall 1 1 (b) Algal or yeast M5. (a) A 1 Page 7 [5] (b) (i) diffusion 1 (ii) respiration 1 (iii) mitochondria 1 (iv) photosynthesis 1 [5] M6. (a) (cell) wall (cell) membrane cytoplasm vacuole for 1 mark each 4 (b) (i) A (ii) B for 1 mark each 2 (c) diffusion (reject osmosis) for 1 mark 1 [7] Page 8