* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 23 Notes Memory and Its Processes Memory
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
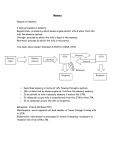
Module 23 Notes Memory and Its Processes • Memory - an active system that receives information from the ___________, organizes and alters it as it ____________ it away, and then ________________ the information from storage. • Processes of Memory: – • Encoding - the set of mental operations that people perform on sensory information to ____________ that information into a form that is usable in the brain's storage systems. Processes of Memory: (continued) – Storage - _______________ onto information for some period of time. – Retrieval - ______________ information that is in storage into a form that can be used. Models of Memory • Information-processing model - model of memory that assumes the ________________ of information for memory storage is similar to the way a computer processes memory in a series of ________________stages. • Levels-of-processing model - model of memory that assumes information that is more “deeply processed,” or ________________ according to its ______________ rather than just the sound or physical characteristics of the word or words, will be remembered more efficiently and for a __________________ period of time. Sensory Memory • Sensory memory - the very ___________ stage of memory, the point at which information enters the __________________ system through the sensory systems. – • Iconic memory - _____________sensory memory, lasting only a fraction of a second. Sensory memory – (continued) – – Iconic memory – (continued) • Capacity - everything that can be seen at one ______________. • Duration - information that has just entered iconic memory will be pushed out very quickly by new information, a process called ________________. Echoic memory - the brief memory of something a person has just _________________. • Capacity - limited to what can be heard at any one ____________ and is ___________ than the capacity of iconic memory. • Duration - lasts ______________ than iconic — about 2 to 4 seconds. Short Term Memory • Short-term memory (STM) - the memory system in which information is held for ___________ periods of time while being ____________. – Selective attention - the ability to focus on only ___________ stimulus from among all sensory input. • Working memory - an active system that ______________ the information in short-term memory. • Digit-span test - memory test in which a series of numbers is read to subjects in the experiment who are then asked to ________________ the numbers in order. – Conclusions are that the capacity of STM is about ________________ items or pieces of information, plus or minus __________ items, or from five to nine bits of information. • “magical number” = 7 • Maintenance rehearsal - _____________ of saying some information to be remembered over and over in one's head in order to maintain it in ________________ memory (STMs tend to be encoded in auditory form). • Duration of STM - lasts from about 12 to 30 seconds without _________________. • STM is susceptible to ___________________ (e.g., if counting is interrupted, have to start over). Long Term Memory • Long-term memory (LTM) - the system of memory into which all the information is placed to be kept more or less _____________________. • Chunking - bits of information are combined into meaningful units, or chunks, so that ___________ information can be held in STM • Elaborative rehearsal - a method of transferring information from STM into LTM by making that information ___________________ in some way. Types of LTM • Procedural (nondeclarative) memory - type of LTM including memory for ________, procedures, habits, and ________________ responses. These memories are not ______________ but are implied to exist because they affect conscious behavior. • Declarative memory - type of LTM containing information that is _________________ and known (memory for _____________). Procedural LTM • _____________ that people know how to do. • Also include emotional associations, _____________, and simple conditioned reflexes that may or may not be in conscious awareness. • Procedural memory often called implicit memory - memory that is ___________ easily brought into conscious awareness. Declarative LTM • All the things that people know. • Semantic memory - type of declarative memory containing general ____________________, such as knowledge of language and information learned in formal ___________________. • Episodic memory - type of declarative memory containing _________________ information not readily available to others, such as daily ________________ and events. • Semantic and episodic memories are forms of _________________ memory - memory that is ______________________ known. Formation of LTM • Memory consists of several ________________ changes. – Changes in the number of receptor _____________. – Changes in the sensitivity of a _______________ through repeated stimulation (called long-term potentiation). – Changes in the __________________ and in the proteins within the neurons. • Consolidation - the changes that take place in the structure and functioning of neurons when an _____________ is formed. • Hippocampus - area of brain responsible for the formation of ________________________.