* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS- - Uplift Summit International
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
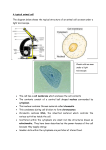
Biology Ch 3- Cell Structure History: Cells first observed by – Robert Hooke in 1665 Described as _______________ (Tiny animals)/ Single celled organisms by – Anton Van Leewenhoek in 1675 Measuring cell structures: SI system – International system of measurement Based on powers of 10 *** Refer to the 4 tables included in your Ch2 packet MICROSCOPES Light microscope light passes through one or more lenses to produce an enlarged image of specimen can view living cells Compound microscope – Light microscope with __________ lenses (________________, ___________________) Electron microscope Uses a beam of electrons instead of light Can’t view living things as it uses a vacuum chamber 200000 X maximum magnification Transmission Electron microscope Black and white images only Electron beam is directed at a very thin slice of a specimen stained with metal ions Scanning Electron microscope Black and white images only Electron beam is focused on a specimen coated with a very thin layer of metal and it produces 3D images Scanning Tunneling microscope Uses needle like probe to measure differences in voltage caused by electrons that leak, or tunnel from the surface of an object Micrographs Types of micrographs Light Micrographs Transmission Electron Micrographs Scanning Electron Micrographs Properties of a microscope: Magnification - Resolution- Size of objects- CELL THEORY Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow All living things are made of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms All cells arise from pre existing cells Cell Size Smaller cells function better than larger cells Can exchange substances more readily due to higher surface area to volume ratio Common features of cells Cell membrane Cytoplasm Regulates what enters/leaves the cell e.g. gases, water, nutrients Ribosomes DNA Cytoskeleton PROKARYOTES Single celled organism with no nucleus or compartments EUKARYOTES Not many specialized functions Nucleus houses DNA, Organelles carry specific activities in the cell Cytoplasm outside nucleus, inside cell membrane Size: Size: e.g. e.g. Lived 3.5 billion years ago Lived 2.5 billion years ago Cells have nucleus Genetic material - single circular molecule of DNA Cell wall surrounds cell membrane-gives structure/support Has polysaccharides and short chains of amino acids Capsule-helps cling to things like food etc. Flagella - long threadlike structures that enable movement Flagella - for movement Cilia- propel cell through environment Cytoskeleton-made of protein fibers/holds cell membrane from collapsing Cytosol -fluid surrounding cytoplasm's organelles etc. Vesicles- formed from membranes-moves proteins from one place to another CYTOSKELETON Framework of animal cell Protein fibers Supports the shape of cell/holds nucleus and organelles in place Types of cytoskeleton fibers Actin fibers-long, slender microfilaments Microtubules-hollow tubes Intermediate fibers-thick ropes of protein CELL MEMBRANESelectively permeable due to phospholipids LIPID BILAYER Membrane proteins e.g. Marker proteins- indicate cell type e.g. liver cell Receptor proteins-recognizes/binds to substances outside cells Enzymes-speed up chemical reactions Transport proteins-move substances across the cell membrane CELL ORGANELLES(Refer to the table at the end of packet) Nucleus Nuclear envelope/nuclear membrane Nuclear pore Nucleolus DNA Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum(ER) Rough ER Smooth ER Vesicle Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Mitochondria PLANT CELL Following are the unique features of a plant cell: Cell wall Chloroplasts Central vacuole