* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.2 Student Notes
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
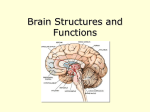
Topic 7.2 Structure & Function of the Brain 7.2.1 brain Label the location of the principal structures of the Brain stem Diencephalon 2 hemispheres of the cerebrum Cerebellum 7.2.2 Label the location of the principal lobes of the cerebrum Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Limbic lobe 7.2.3 Outline blood supply to the brain What goes in the brain? o Oxygen o Carbohydrates o Amino acids o Fats o Hormones o Vitamins What goes out of the brain? o Carbon dioxide o Ammonia o Lactate o Hormones For the brain to function it requires adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. These are supplied through a network of blood vessels. Blood is supplied to the brain by 2 sets of vessels o ____________________________________________________ o ____________________________________________________ Carotid arteries o External______________________________________________ o Internal______________________________________________ Brachiocephalic trunk - artery that supplies blood to right arm, head, and neck Blood-brain barrier o Protects the brain ____________________________________ that may injure the brain o Maintains a constant environment for the brain o Is a highly selective barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain extracellular fluid in the CNS. 7.2.4 Describe the principal source of energy for brain cells Brain obtains energy using _____________________________________, which pass rapidly from the blood to the brain cells. ______________________________ helps to make ATP within the brain. CHO storage in the brain __________________________, so the supply of glucose must be continuous. If blood entering brain is low on glucose or oxygen, we can suffer: _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 7.2.5 Explain the function of the principal parts of the brain. Brain Stem o ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ o Acts as a vehicle for sensory information o Posterior part of brain adjoins the spinal cord o ____________________________________________________ Diencephalon o ____________________________________________________ o ____________________________________________________ Sensation – pain, temperature, pressure, cognition o ____________________________________________________ Control autonomic nervous system (ANS) Heart rate, blood pressure, pituitary gland, body temperature, appetite, thirst, fluid and electrolyte balance, circadian rhythms Cerebrum o Responsible for high level brain functions such as ____________________________________________________ o 3 broad processes: Sensory – receiving sensory impulses Association – interpreting and storing input, and initiating a response Motor – transmitting impulses to effectors Cerebral lobe functions LOBE FUNCTION Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Limbic Lobe limbic system often referred to as the “emotional brain” Cerebellum o ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ o Walnut shaped o Located at the top of the brain stem