* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 11 - Human Anatomy Lecture
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
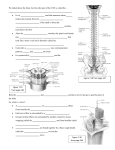
Anatomy 32 Lecture Chapter 14 - Peripheral Nervous System I. Overview A. Introduction to the PNS B. Cranial Nerves C. Spinal Nerves D. Nerve Plexuses E. Reflex Arc II. Introduction to the _____ A. The PNS conveys impulses to and from the ____ and includes the: 1. Sensory ______________ within sensory organs 2. ____________ & their associated ganglia 3. Nerve ____________ B. __________ of the PNS are classified as either 1. _____________ nerves - arise from the brain 2. ____________ nerves - arise from the spinal cord C. The terms sensory, motor, or mixed nerve refer to the _________ nerve impulses are conducted 1. 2. 3. __________ (afferent) nerves conduct impulses toward the CNS _______ (efferent) nerves conduct impulses away from the CNS ________ nerves are composed of both sensory & mixed nerves, thus conduct impulses to & from the CNS III. ______________ - 12 pr. of cranial nerves emerge from the inferior brain surface and pass through skull foramina to ennervate structures in the head, neck, and visceral organs A. Structure & function of the cranial nerves 1. ____ pr. arise from the _________ and the other ___ pr. arise from the __________ & brain _______ 2. Cranial nerves are designated by _________ numerals, which refer to the order the nerves are positioned from the ________ to the ________ of the brain 3. Most cranial nerves are ________ or mostly motor, but some associated with special senses are __________ only. (Remember by: Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big Bras Matter More) 4. Cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in ___________ outside the brain and SC B. The ___ Cranial Nerves (Remember by: On Occasion Our Trusty Truck Acts Funny, Very Good Vehicle AnyHow) 1. _________ - Sensory fibers arise from the olfactory epithelium in nasal cavity, pass through the cribiform plate to synapse in the olfactory _______ and extend posteriorly as the olfactory ____ beneath the frontal lobe; carry impulses for sense of smell 2 2. _______ - Sensory fibers arise from the retina, pass through the optic foramen, converge and partially cross over forming the optic ________, continue as optic _______, enter the thalamus and are relayed to the occipital lobe; carry impulses for vision 3. ___________ - Mixed fibers extend from the midbrain near the pons, through the superior orbital fissure to enervate ______ muscles 4. ____________ - Mixed fibers emerge from the midbrain , pass ventrally through the superior orbital fissures with oculomotor nerves to the ______ muscles (superior oblique) 5. ___________ - largest cranial nerve (mixed), extends from pons to face and forms 3 divisions: a. ____________ - sensory fibers run from the face to pons via superior orbital fissure; conveys impulses from _____, nose, & scalp b. _____________ - sensory fibers run from face to pons via foramen rotundum; conveys impulses from nasal mucosa, palate, upper _________ & lip c. ___________ - mixed fibers pass through skull via foramen ovale; conveys sensory impulses from lower teeth, ______, motor impulses to muscles of mastication 6. __________ - mixed fibers leave inferior pons & enter orbit via superior orbital fissure to _____; supplies motor fibers to lateral rectus muscle and sensory fibers from the muscle proprioceptors 7. _____ - mixed fibers emerge from pons, lateral to abducens and exit via stylomastoid foramen, then branches into the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical; conveys impulses to & from muscles of ______ expression, facial glands & tongue 8. ______________ - sensory fibers arise in the inner _____ and pass through internal auditory meatus to enter pons; forms 2 divisions: a. b. 9. _____________ - transmits impulses for sense of hearing _____________ - transmits impulses for equilibrium _______________ - mixed fibers emerge from medulla, through jugular foramen, to throat; sends motor impulses to _________ muscles, sensory from pharynx & posterior ________ 10. _________ - only CN to extend beyond head & neck; mixed fibers emerge from the medulla, through jugular foramen, descend through neck into thorax & abdomen; branches enervate pharynx, larynx, tongue & visceral _________ 11. ________- mixed fibers formed by union of cranial root (from lateral medulla) & spinal root (C1-C5); enters skull via jugular foramen; cranial enervates larynx, pharynx, & soft palate, spinal enervates trapezius & sternocleidomastoid to move ______ 12. _____________ - mixed fibers arise from medulla, exit skull via hypoglossal canal to ennervate intrisic & extrinsic ________ muscles 3 IV. __________________ A. Each of ___ pr. of spinal nerves is formed by the union of a dorsal and ventral spinal ______ that emerges from the SC through an intervertebral foramen to innervate a part of the body B. Spinal nerves are named according to the __________ they emerge through 1. 8 pr. __________ - C1 is between occipital bone & atlas; C2-C7 leave above their cervical bone, C8 and the rest leave below namesake vertebrae 2. 3. 4. 5. 12 pr. _________ (T1-T12) 5 pr. _________ (L1-L5) 5 pr. _________ (S1-S5) 1 pr. ___________ (C0) C. A spinal nerve is a _______ nerve attached to spinal cord by a 1. __________ (posterior) ______, which contains the dorsal root _____________ - a collection of sensory cell bodies. ________ neurons carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS 2. ___________ (anterior) _______ is composed of _______ fibers that convey impulses away from the CNS to effectors D. After spinal nerves exit a root, they divide into peripheral ______ 1. ______ ________ contains mixed nerves that innervate muscles, joints, & skin of the posterior neck & trunk. 2. _________________ contains mixed nerves that innervate the muscles & skin of the anterior & lateral neck & trunk, as well as the limbs. 3. Rami ______________ are two spinal nerve branches from the ventral ramus to a sympathetic trunk ___________, part of the autonomic nervous system. Communicantes are mixed nerves. V. Nerve Plexuses A. Except for T2-T12 (intercostal nerves), the ___________ of spinal nerves split again & again as nerve networks called plexuses. B. There are four _________; nerves emerging from the plexuses are named according to the structures they innervate or the course they take. 1. _________ plexus - formed by the ventral rami of C1-C4 and part of C5. a. b. 2. Branches innervate the skin & muscles of the _______, head, & shoulders Fibers from the 3rd-5th cervical nerves become the ________ nerve, which innervates the diaphragm ___________ plexus - formed by C5-T1; passes over the 1st rib behind the clavicle and enters the axilla; innervates the upper extremities, and some shoulder & neck muscles. Major subdivisions include: a. ________ - five ventral rami (C5-T1), which unite to form three b. ________ – upper, middle, and lower; each trunk divides into 4 c. _________ – anterior and posterior, then each of the 6 divisions merge to form three d. ______ – posterior, medial, and lateral, which form the following nerve _________ 1) __________ – from the posterior cord, posterior to the humerus neck; innervates the shoulder 2) ___________ – from the posterior cord, wraps around the humerus in the radial groove; innervates the triceps and forearm extensors 3) ____________ – from the medial cord, lies between the radial and ulnar nerves; innervates anterior forearm flexors 4) ________ (funny bone nerve) – from the medial cord, descends along the medial humerus, over the medial epicondyle, then along the medial ulna; innervates the wrist and many hand flexors 5) Musculo____________ – from the lateral cord, descends along the anterior arm to just below the elbow; innervates elbow flexors and lateral forearm 3. ____________ plexus - formed by L1-L4; innervates lower abdomen, anterior & medial lower extremity. Major nerves include: a. b. 4. ___________ - innervates anterior & lateral thigh, medial leg & foot ____________ - innervates medial thigh, adductors of thigh __________ - formed by L4-S4; innervates lower back, pelvis, perineum, posterior thigh & leg, & foot. Major nerves include: a. ___________ - passes through the greater sciatic notch, deep to gluteus maximus and biceps femoris; branches into two nerves 1) ____________ - posterior to tibia; innervates knee flexors and foot plantar flexors 2) _____________ (peroneal) - lateral to fibula; innervates fibularis muscles (Note: Sciatica involves injury to the sciatic nerve, causing pain to radiate from the buttock down the posterior leg; may be caused by herniated disc, dislocated hip, lumbosacral osteoarthritis, pregnancy, and gluteal muscle injection) VI. Components of a ________________ A. A reflex arc implies an ____________, unconscious, protective response in an attempt to maintain homeostasis B. The five components of a reflex arc are: 1. ____________ - dendrite of a sensory neuron and the place the impulse is initiated 2. __________ neuron - relays the impulse through the dorsal root to the CNS 3. __________________ - located in the CNS and usually involves an association neuron (interneuron); here impulses are sent through synapses to other parts of the body 4. 5. ___________ neuron - conducts the impulse to an ____________ - usually a skeletal muscle 5 Chapter 15 - Autonomic Nervous System I. Introduction to the _______ A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the general ___________ division of the PNS, and contains two subdivisions 1. ______________ N.S. – involved in “fight or flight” responses 2. ________sympathetic N.S. – involved in “rest & digest” activities B. Involuntary ___________ (smooth & cardiac muscle and glands) are regulated by autonomic ________ impulses via the ANS C. The autonomic motor pathway involves 2 types of ____________: 1. _______________ (presynaptic) neurons - have their cell bodies in the gray matter of the brain or SC; release _____ neurotransmitter; their axons synapse with 2. ________________ (postsynaptic) neurons - extend from the autonomic ganglia and synapse with an ____________ organ 3. Autonomic _____________ are located in the head, neck, & abdomen, and on each side of the spinal cord (paravertebral) II. Both sympathetic & parasympathetic divisions innervate the _____ organs, but have _____________ effects (see table in text) A. Sympathetic (______________) division - preganglionic neurons exit the spinal cord lateral horns from T1 to L2 1. Involved in “________ or ________” responses: a. Dilates _______ b. Stimulates _______ glands c. Vaso__________ blood vessels to glands and internal organs d. __________ bronchioles and blood vessels to heart & skeletal muscles e. Stimulates ____________ medulla to secrete epinephrine & norepinephrine into the blood stream f. Increases ____________ and force of contraction, as well as blood pressure g. Stimulates break down and release of _______ from liver and lipids from fat cells to supply _________ to blood stream 2. ______transmitters are released by neurons and adrenal glands a. ______________ - most postganglionic sympathetic neurons release ____epinephrine b. Epinephrine (_________) & norepinephrine are released by the adrenal glands when stimulated by the sympathetic sys. 3. ____________ are close to the spinal cord a. _____________ trunk ganglia alongside vertebral column b. _____________ ganglia anterior to vertebral column 4. Preganglionic neurons are _______, postganglionic are ______ 6 B. Parasympathetic (___________) division - preganglionic neurons exit from the midbrain, brain stem and sacrum (cranial nerves III, VII, IX, & X also participate) 1. Involved in _____________ (resting & digesting) functions a. _______ are constricted b. Glands are stimulated to ________ c. Heart rate is ________ and steadied d. Blood vessels to heart and bronchioles are vaso__________ e. Smooth muscle of bladder and digestive organs are contracted, promoting _______________. 2. ___________ - acetylcholine (____) neurotransmitter is released from most parasympathetic postganglionic neurons to effectors 3. ____________ are in or close to the organ served 4. Preganglionic neurons are ______, postganglionic are ______