* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 Cells Study Guide
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
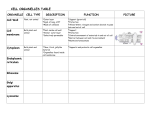
Unit 5 Cells Study Guide Name ______________________________ 1. In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? 2. Name two storage organelles? 3. What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesis? p.176-177 4. How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? p.177 5. What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? p.178 6. How does the membrane of the cell differ from the nuclear membrane? What advantages does this difference have for the nucleus? p.176 7. What do ribosomes do? Are they found freely floating in the cytoplasm? OR are they found attached to another organelle? OR both. Explain why this occurs. 8. What does the endoplasmic reticulum do? p.177 9. What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER? What is the ER doing that is different in each case? p.177-178 10. What are lysosomes? What types of molecules would be found inside a lysosome? p.179 11. Why might a lysosome fuse with or link up with a food vacuole? 12. What molecules move from the ER to the Golgi bodies?p. 178 13. What is meant by “membrane turnover”? THINK 14. In what type of cell (plant or animal) is a centriole found? 15. What is the difference between chromosomes and chromatin? What do they each have to do with DNA? p.176 16. What are microtubules? How do they differ from microfilaments? Name two molecules that are considered microfilaments? p.181 17. What is a flagella? How does it differ in size and number from cilia? What is the function of each of these organelles? (bottom of p.181) 18. How is the composition of cilia and flagella different with reference to microtubules? Sketch that difference below. p.499 & p.501 19. What are centrioles? What is their function? p.181 20. What organelles are ONLY found in plant cells? Why? 21. What is the cell wall made up of? Is the cell wall selectively permeable? p.183 22. What is the function of the cell wall and what takes the place of that function in animal cells? p.183 23. Which organelle can convert sunlight, carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen? p.180 24. Which organelle can convert sugar (glucose) and oxygen into ATP (energy molecule), carbon dioxide and water? p.179 25. What is the process in number 23 called? 26. What is the process in Number 24 called? 27. Do plant cells contain mitochondria? Why? p.179 28. What are plastids? (see the board) 29. What is a chloroplast? 30. What type of vacuole is present in all plant cells?