* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Your Pre AP biology final exam
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
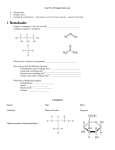
Your Pre AP biology final exam: 100 questions Multiple choice Completely comprehensive – that means it covers the whole semester…August to December. I. Biomolecules: Organic or inorganic? How do you tell?________________________________ Categorize organic or inorganic: What are the 4 classes of compounds? ______________________________ How can you tell the difference between Carbohydrates and everything else? _____________________________ Lipids and everything else? ____________________________________ Proteins and everything else? __________________________________ Nucleic acids and everything else? ______________________________ What kind of bond holds together Carbohydrates - ___________________ Lipids - _____________________ Nucleic acids - ________________ Proteins - ____________________ Categorize Starch Hair DNA Cellulose Plant cell walls Enzymes Organic product of photosynthesis Component of cell membrane Hemoglobin Unsaturated fat Saturated fat Structure Solid at room temp Examples How many different amino acids are possible? __________________________ What determines the order of the amino acids in your proteins? ____________________ II. Cells: Prokaryote Eukaryote Size Age Nucleus Organelles Examples Part Nucleus Function Part Smooth ER Cytoplasm Golgi Body Ribosomes Vacuoles Rough ER Lysosome Plasma membrane Mitochondria Chloroplasts Cell wall Function Plant cell and Animal cell comparison and contrast III. Transport Label the parts of a phospholipid: (polar, nonpolar, phosphate, lipid, hydrophilic, hydrophobic) Label the parts of a bilayer: (polar, nonpolar, phosphate, lipid, hydrophilic, hydrophobic) Use the drawing below to indicate the location of inside the cell, outside of the cell, polar and nonpolar Using the image of a cell membrane below: Color the proteins red Color the polar part green Color the non polar part yellow Add in a channel (transport) protein. Add in a carbohydrate marker on one of the proteins When we say that a lipid bilayer is semipermeable, what do we mean? Passive transport Requires energy Moves molecules Moves molecules Active Transport From low concentration to high concentration With (down) the concentration gradient Define osmosis: Label the following drawings as hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic and draw an arrow to indicate the direction water will move. (The cell membrane is semipermeable but will not allow the particles to move thru…only water) Here are some more examples: Great website activity to review what happens to a human cell (blood cell), a plant cell (elodea) and protist (paramecium) in different solutions: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Indicate which of the following is endocytosis and which is exocytosis. Below each one give an example of a type of substance moved in that manner Indicate which side is hypertonic, hypotonic and the direction water will move. Draw a prediction of what it will look like after sitting for a few hours: before prediction 5% NaCl 2% NaCl 20% sucrose 50% sucrose 70% NaCl 40% NaCl IV. Energy: Is this reaction exergonic or endergonic? How can you tell? Give an example of endergonic and exergonic reactions: What is activation energy? What do the following letters represent in the diagram A: B: C: E: Which line (solid or dashed) represents a reaction with an enzyme? Give some characteristics of an enzyme: Give 3 examples of digestive enzymes and the reactions they catalyze: What’s an easy way to tell if a chemical named is an enzyme? Name 4 things that can affect an enzyme functioning Label the structure of ATP using the following terms: phosphate, bonds with high stored energy, sugar, and adenine What does ATP become when it loses one phosphate? _______________ two phosphates?_______________ All of our energy originates from the ______________________ The first living things to take incoming energy and transform it to chemical energy (glucose) are called _______________ or ____________________. The energy flows from those organisms to ____________________ or ______________________ that must eat to obtain energy Give 3 kinds of organisms that are photosynthetic: What is fermentation? When does it occur and what are the byproducts? Bacteria can only conduct the first part of cellular respiration. What is that called? How many ATP does it produce? Cellular respiration Photosynthesis What Where Who What goes in (reactant) What comes out (product) Reaction (balanced) V. Cell Reproduction: What is a gene? What is a chromosome? What is chromatin? Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: G1, G2, S, cytokinesis, mitosis, interphase *Notice I am giving you more than one diagram so that you can get used various formats. Who knows what I will put on the final (and Rick Perry is the only one that knows what they’re putting on the STAAR) What happens in each of these phases? G1 G2 S Mitosis Cytokinesis What kind of cell never leaves G1 What happens when the cell cycle loses control and begins to rapidly repeat itself? How does cytokinesis differ between a plant cell and an animal cell? Label each of the steps in mitosis: A (before mitosis begins) B C D E F (after cytokinesis) Is there a difference between the two cells labeled F? Is there a difference between the cell labeled A and the two labeled F? What is structure #6? What is structure #13? What is structure #1 What is structure #8? You have 22 pairs of chromosomes called __________________. The 23rd set are called ____________ chromosomes and are either X and X if you are a ___________________ or X and Y if you are a _____________. X chromosome is necessary and everyone has one they got from their _________________. Y chromosome only codes for male sex characteristics and boys get that chromosome from their __________. Girls get their other X from their dads. What is meiosis? Characteristic Parent cell Where # of daughter cells Chromosome # in daughter cells Are they clones? What is a karyotype? Mitosis Meiosis Identify the following karyotypes as male or female and indicate if there are any chromosomal disorders The following problems is genetics portion of the review!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!