* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Review Sheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
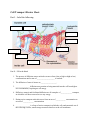
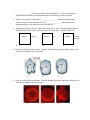
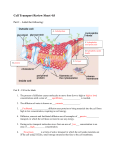
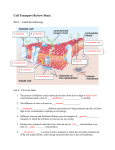
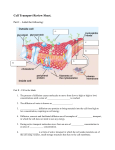
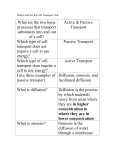
Cell Transport Review Sheet. Part I – Label the following: A. B. F. G. H. C. D. E. Part II – Fill in the blank 1. The process of diffusion causes molecules to move from (low to high or high to low) concentrations until a state of ____________________ is reached. 2. The diffusion of water is known as __________________. 3. ________________ diffusion uses proteins to bring materials into the cell from high to low concentration, requiring no cell energy. 4. Diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of _____________ transport, in which the cell does not need to use any energy. 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of ___________ concentration to an area of ____________ concentration. 6. ________________ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small storage structures that fuse to the cell membrane. 7. _________________ is the reverse of the process named in # 6. The cell membrane wraps around a substance to be brought into the cell forming a vesicle around it. 8. There are two types of endocytosis: __________________ which involves bringing solids or large molecules into the cell, and _________________, which deals with bringing liquids or very small molecules into the cell. 9. In the pictures below each “X” represents a molecule of water. In each diagram indicate which direction water will be moving (mostly in, mostly out, or equally in and out). XXXXX A. XXXXX XXXXX XX XXXXX B. XXXXX XXXXX C. 10. Look at each of the pictures below. Identify whether the picture represents a plant cell in fresh water, distilled water or salt water. A. B. C. 11. Look at each of the pictures below. Identify whether the picture represents a blood cell in fresh water, distilled water or salt water. A. B. C. 12. Why did the potato left in salt water or fresh water lose or gain water? What was different about the amount of water inside and outside the cell, and what state were the potato cells trying to reach? 13. How do facilitated diffusion and active transport differ? Is osmosis an example of facilitated diffusion or active transport? 14. Compare a cell from a unicellular organism with a cell from a multicellular organism in terms of cell specialization. 15. What is the function of active transport in moving small molecules and ions across cell membranes? 16. Explain why a small cell is an efficient cell (in other words, why aren’t cells big)? 17. Explain how diagrams A and B below relate to osmosis. Be sure to discuss how tonicity relates to the movement of water. Also, state which side of the tube is hypertonic/hypotonic.