* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function description
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
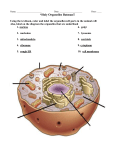
Organelle Function Location 1. Nucleiod Region Where DNA is found in prokaryotes prokaryotes 2. Nucleus Control and manage the cell, DNA synthesis (genetic information) Eukaryotes 3. Nucleolus Inside nucleus – components of ribosomes are produced Eukaryotes 4. Mitochondria Provide energy for the cell- carry out cellular respiration. Chemical energy of food is converted to chemical energy of a molecule called ATP. Eukaryotes 5. Chloroplast make chemical energy (sugars) during photosynthesis Plants and protists (Eukaryotes) 6. Centrioles help organize DNA during cell division Animal 7. Golgi Modify, store, package, and transport macromolecules in and out of the cell Eukaryotes 8. Lysosome Clean cell and break down waste, destroy harmful bacteria, holds digestive enzymes. Vital in embryonic development. Produced by the Rough E.R. and Golgi Animal/ Very few in plant 9. Vacuole Digestion, storage of chemicals (salt, carbs, proteins), cell enlargement and water storage. Large (Central) in Plant/ small in Animal 10. Cell wall added structure support and protection Plants and prokaryotes 11. Ribosome Assemble amino acids into proteins(polypeptides) Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes 12. Cell (plasma) Membrane protective layer that surrounds the cell Eukaryotes/prokaryotes 13. Rough ER Where proteins and more membrane is made /contain ribosomes Eukaryotes 14. Smooth ER Continuous to Rough E.R. –lack ribosomes. Where lipids are made Eukaryotes 15. Cytoskeleton Maintains cell shape and skeletal support – microtubules, microfilament, intermediate filaments Eukaryotes 16. Cytoplasm enclosed within the cell membrane, liquid that contains organelles Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes 17. Flagellum *(Bacterial) Long fingerlike projections for movement Bacteria and some animal cells 18. Pili Short projections for attachment to surfaces Prokaryotes 19. peroxisome A specialized structure inside a cell which helps to rid the body of the host organism of toxins. Breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) Animals cells 20. Cilia Short projections, move debris in multicellular cells, propel protists (eukaryotic) Some eukaryotes 21. Cell junctions Communication between cells, binding of cells; Tight, anchoring, communicating Animal cells 22. Plasmodesmata Channels between cells for communication and connections (Extracellular matrix in animal cells) Plants Organelle Function Location Nucleiod Region Where DNA is found in prokaryotes prokaryotes Nucleus control and manage the cell, DNA synthesis (Genetic information) Eukaryotes Nucleolus Inside nucleus – components of ribosomes are produced Eukaryotes Mitochondria Provide energy for the cell- carry out cellular respiration. Chemical energy of food is converted to chemical energy of a molecule called ATP. Eukaryotes Chloroplast make chemical energy (sugars) during photosynthesis Plants and protists (Eukaryotes) Centrioles help organize DNA during cell division Animal Golgi Modify, store, package, and transport macromolecules in and out of the cell Eukaryotes Lysosome Clean cell and break down waste, destroy harmful bacteria, holds digestive enzymes. Vital in embryonic development. Produced by the Rough E.R. and Golgi Animal/ Very few in plant Vacuole Digestion, storage of chemicals (salt, carbs, proteins), cell enlargement and water storage. Large (Central) in Plant/ small in Animal Cell wall added structure support and protection Plants and prokaryotes Ribosome Assemble amino acids into proteins(polypeptides) Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes Cell (plasma) Membrane protective layer that surrounds the cell Eukaryotes/prokaryotes Rough ER Where proteins and more membrane is made /contain ribosomes Eukaryotes Smooth ER Continuous to Rough E.R. –lack ribosomes. Where lipids are made Eukaryotes Cytoskeleton Maintains cell shape and skeletal support – microtubules, microfilament, intermediate filaments Eukaryotes Cytoplasm enclosed within the cell membrane, liquid that contains organelles Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes Flagellum *(Bacterial) Long fingerlike projections for movement Bacteria and some animal cells Pili Short projections for attachment to surfaces Prokaryotes peroxisome A specialized structure inside a cell which helps to rid the body of the host organism of toxins. Breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H 2O2) Animals cells Cilia Short projections, move debris in multicellular cells, propel protists (eukaryotic) Some eukaryotes Cell junctions Communication between cells, binding of cells; Tight, anchoring, communicating Animal cells Plasmodesmata Channels between cells for communication and connections (Extracellular matrix in animal cells) Plants