Freud: Psychoanalysis Freud identified three levels of - Figure B
... Maslow assumed that motivation affects the whole person; it is complete, often unconscious, continual, and applicable to all people People are motivated by four dimensions of needs: conative (willful striving), aesthetic (the need for order and beauty), cognitive (the need for curiosity and knowledg ...
... Maslow assumed that motivation affects the whole person; it is complete, often unconscious, continual, and applicable to all people People are motivated by four dimensions of needs: conative (willful striving), aesthetic (the need for order and beauty), cognitive (the need for curiosity and knowledg ...
Learning - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Law of Effect: behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely & vice versa • Puzzle Box: experiments w/ Cats taught escape learning ...
... • Law of Effect: behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely & vice versa • Puzzle Box: experiments w/ Cats taught escape learning ...
File
... Causes unwanted behaviors to reappear in its absence. 5. Causes aggression towards the agent. 6. Causes one unwanted behavior to appear in place of another. ...
... Causes unwanted behaviors to reappear in its absence. 5. Causes aggression towards the agent. 6. Causes one unwanted behavior to appear in place of another. ...
Organizational Behaviour Prof. Susmita Mukhopadhyay Vinod
... carry the vigor with which you carry a walk forward which may lead to changes in different levels of motivation and here we will discuss with the two main groups of theories under reinforcement theories. The operant conditioning theory and the classical conditioning theory. Point to note over here r ...
... carry the vigor with which you carry a walk forward which may lead to changes in different levels of motivation and here we will discuss with the two main groups of theories under reinforcement theories. The operant conditioning theory and the classical conditioning theory. Point to note over here r ...
chapter - Human Kinetics
... Extinction • Withholding of reinforcement after a response previously reinforced • No consequence following the response • A stimulus (aversive or positive) neither presented nor taken away ...
... Extinction • Withholding of reinforcement after a response previously reinforced • No consequence following the response • A stimulus (aversive or positive) neither presented nor taken away ...
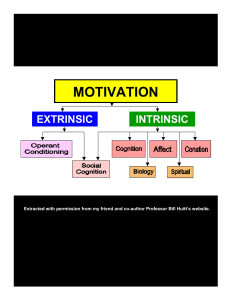
Motivation
... The degree to which carrying out the work activities required by a job results in the individual obtaining direct and clear information about the effectiveness of his or her performance. ...
... The degree to which carrying out the work activities required by a job results in the individual obtaining direct and clear information about the effectiveness of his or her performance. ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences ...
... Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences ...
Quiz
... _____ The initial learning stage in classical conditioning in which the neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with unconditioned stimulus is known as: a. Prompting b. Trial-and-Error learning c. Acquisition d. Insight learning e. Shaping ...
... _____ The initial learning stage in classical conditioning in which the neutral stimulus is repeatedly paired with unconditioned stimulus is known as: a. Prompting b. Trial-and-Error learning c. Acquisition d. Insight learning e. Shaping ...
Names - appsychologykta
... by satisfying consequences become associated with the situation, and are more likely to recur when the situation is subsequently encountered. If the responses are followed by aversive consequences, associations to the situation become weaker. Skinner – reinforcement strengthens behavior Watson – con ...
... by satisfying consequences become associated with the situation, and are more likely to recur when the situation is subsequently encountered. If the responses are followed by aversive consequences, associations to the situation become weaker. Skinner – reinforcement strengthens behavior Watson – con ...
Behavioral Theory rev 2012
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
... Stimulus generalization – somewhat like over generalization in language, people may over generalize a response CER’s – conditioned emotional responses often compound generalization and create problems for discrimination (classically conditioned) Stimulus discrimination – Identifying key elements ...
Learning/Conditioning + Memory – (textbook chapters 8 + 9)
... 5. Maya wants to train her cat to use the toilet instead of the litter box. Describe how she might use shaping to train her cat in five steps/stages to exhibit toilet-using behavior. ...
... 5. Maya wants to train her cat to use the toilet instead of the litter box. Describe how she might use shaping to train her cat in five steps/stages to exhibit toilet-using behavior. ...
Learning
... • No homework in class because everyone’s behavior was on point! ▫ Negative reinforcement – removal of something bad ...
... • No homework in class because everyone’s behavior was on point! ▫ Negative reinforcement – removal of something bad ...
Operant Conditioning
... Cognition and Operant Conditioning Overjustification Effect the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation for performing the task ...
... Cognition and Operant Conditioning Overjustification Effect the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation for performing the task ...
Psych 260 Ch 5 Review - biggerstaffintropsych
... 21. Students generally study very diligently before midterms and slack off immediately afterwards, which is characteristic of behavior reinforced on a _____ schedule. 22. _____ is a formalized technique for promoting the frequency of desirable behaviors and decreasing the incidence of unwanted ones ...
... 21. Students generally study very diligently before midterms and slack off immediately afterwards, which is characteristic of behavior reinforced on a _____ schedule. 22. _____ is a formalized technique for promoting the frequency of desirable behaviors and decreasing the incidence of unwanted ones ...
Notes Part 1 (10 pts)
... Cognitive Map: mental representation of the ____________ of one’s environment o Example: being about to visualize your path between classes Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent until there is an incentive to ...
... Cognitive Map: mental representation of the ____________ of one’s environment o Example: being about to visualize your path between classes Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent until there is an incentive to ...
SR6e Chapter 2
... Focus on identity crisis of adolescence still most relevant Emphasis on rational and adaptive nature Interaction of biological & social influences Weaknesses Sometimes vague and difficult to test Does not explain how development comes about ...
... Focus on identity crisis of adolescence still most relevant Emphasis on rational and adaptive nature Interaction of biological & social influences Weaknesses Sometimes vague and difficult to test Does not explain how development comes about ...
Ecological Theories Derived from Learning Theories
... Sears’s learning model is based on 5 assumptions: Assumption # 1: Initially, every behavior begins as an effort to reduce tension that is associated with some biological need Assumption # 2: Behavior (and development) is a function of interactions between people, especially dyadic (two-person) ...
... Sears’s learning model is based on 5 assumptions: Assumption # 1: Initially, every behavior begins as an effort to reduce tension that is associated with some biological need Assumption # 2: Behavior (and development) is a function of interactions between people, especially dyadic (two-person) ...
Operant Conditioning Notes (teacher version)
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
PowerPoint slides into MS Word
... the next level because she is constantly concerned for her safety. Love and belongingness have to wait until she is no longer cringing in fear. Many in our society cry out for law and order because they do not feel safe enough to go for a walk in their neighborhood. Many people, particularly those i ...
... the next level because she is constantly concerned for her safety. Love and belongingness have to wait until she is no longer cringing in fear. Many in our society cry out for law and order because they do not feel safe enough to go for a walk in their neighborhood. Many people, particularly those i ...
Behaviorism - Dr Matthew J Koehler
... Start simple, increase complexity. -Shape the behavior by starting simple and build up. • Schedules for reward (Skinner): rewards not only create behavior, but also maintain it. If you reinforce on an irregular schedule more likely to be maintained. ...
... Start simple, increase complexity. -Shape the behavior by starting simple and build up. • Schedules for reward (Skinner): rewards not only create behavior, but also maintain it. If you reinforce on an irregular schedule more likely to be maintained. ...
Motivation Theories Essay Assignment
... behavior is changed when we see a person take a specific action and be rewarded for that action. In the future we are more likely to take that same action. This is vicarious learning in which we learn through imitation rather than through direct reinforcement. Bandura’s theory is referred to social- ...
... behavior is changed when we see a person take a specific action and be rewarded for that action. In the future we are more likely to take that same action. This is vicarious learning in which we learn through imitation rather than through direct reinforcement. Bandura’s theory is referred to social- ...