* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecological Theories Derived from Learning Theories
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Social computing wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Social group wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
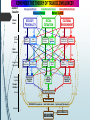
Ecological Theories Derived from Learning Theories Eiman E AlEissa H671 Advanced Theories of Health Behavior 02/11/2016 Outline Social learning Theory (Salkind, 2004) Sears’s Phases of Development Important concepts of SLT Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation (Ryan & Deci, 2000) Social Cognitive Means (Bandura, 2004) SCT Determinants SCT overlap with models of health behavior Social Mediated pathways + examples Self-Management Kernels (Embry & Biglan, 2008) Types of kernel units + examples Selection of consequences Individual Behavior, Culture and Social Change Behavioral Ecological Model (BEM) Basic Terms & Principles of Behavior Stimuli = anything in the environment that affects behavior Response = Behavior produced by the stimuli Unconditioned Stimuli = anything in the environment that causes natural response Conditioned Stimuli = anything in the environment that has an affect through association with the UCS. conditioned Response/ conditional reflex/respondent conditioning = Behavior produced by the CS. Classical conditioning: learning new behaviors through association 3 Basic Terms & Principles of Behavior + Operant conditioning: a response that operates on or changes the environment. The consequences produced by the response/ behavior may cause the behavior to more likely (reinforcement) or less likely (punishment) to occur in the future. Reinforces: Consequences that increase the probability of repeating a behavior (can be negative or positive) Punishers: Consequences that decrease the probability of repeating a behavior The Matching Law: the frequency of a behavior or time allocated to engaging in the behavior is a function of the rate of reinforcement for that behavior relative to the rete of reinforcement for alternative possible behaviors. 4 Reaction Potential: Potential for repeating a response given a particular stimulus Strength of a reaction potential is determined by Drive Intensity of the stimulus Incentive motivation Habit strength – experience Inhibitory potential Consequences of a behavior become the causes of later behavior Over time, experiences take on value as secondary reinforcers 5 Sears’s learning model is based on 5 assumptions: Assumption # 1: Initially, every behavior begins as an effort to reduce tension that is associated with some biological need Assumption # 2: Behavior (and development) is a function of interactions between people, especially dyadic (two-person) interaction Assumption # 3: Drives (similar to intrinsic motivation) that are present at birth provide the foundation for later development Assumption # 4: Behavior is both the cause and the effect of later behavior: behavior does not occur in isolation, it always affect other parts of the individual behavioral system. Assumption # 5: The quality of a behavior (in terms of the reinforcement value positive or negative) is determined by experience and learning 6 Social Learning Model Sears’s phases of development Phase Time frame Focus Rudimentary Behavior Birth -16 months Innate needs/ reduce tension Secondary Behavioral Systems 16 months- 5 years Family-Centered learning Secondary Motivational Systems 5 years + Extra-familial learning Stimulus Response Albert Bandura, 1925Social Cognitive Theory Vicarious Learning: the ability to learn various behaviors through indirect reinforcement/ experience Stimuli Mediation Process Response Bandura’s Bobo Doll Experiment https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pr0OTCVtHbU SLT Important concepts + Mediation Process Attention Attention Retention Reproduction Motivation Motivation Social cognitive learning Retention Reproduction According to Bandura “the processes take place in an overlapping sequence, in any given instance, some of the elements may be stronger than others, but if anyone of them is too weak, the entire learning process is disrupted” SLT Important Concepts + Motivation Intrinsic: doing something because it is inherently interesting or enjoyable Competence Autonomy Extrinsic: to doing something because it is leads to a separable outcome Self efficacy Social Cognitive Means Knowledge Perceived Self-Efficacy foundation of human motivation and action Self-efficacy shape the outcomes people expect their efforts to produce Outcome Expectations: expected cost and benefits for different health habits. Physical outcome Social outcome Self evaluation outcome Perceived social and structural Facilitators & impediments Self-Efficacy Goals Outcomes Facilitators & impediments Overlap of Sociocognitive Determinants in Different Models of Health Behavior Socially Mediated pathways of influence Direct pathway= media promote changes by informing, modelling, motivating and guiding personal change. Socially mediated pathways= media link participants to social networks and community settings (these places provide continued personalized guidance, incentives, and social support) Media Influence Connection to social systems Behavior change Self-Management Model Motivation Proximal goals Incentives Social support 15 Effective prevention programs include 4 major components: information: it informs children of the health risks and benefits of different lifestyle habits. social and self-management skills: for translating the information learned into effective preventive practices. Building resilience sense efficacy to support the exercise of control in the face of difficulties and setbacks. create social support for desired personal change. Examples of Socially mediated pathways Promoting Society-Wide changes Serial Dramas Health Promotion in children through interactive media. Evidence-based Kernels: fundamental units of behavioral influence Kernels: indivisible evidence-based procedures shown through experimental evaluation to produce effects on behavior. Kernels Altering consequences for behavior Verbal praise (increase behavior) Time out (decrease behavior) Kernels affecting behavior via physiology Omega 3 supplementation Kernels affecting behaviors via relational frames Media associating behavior with immediate negative social outcome. Kernels affecting behavior via antecedents Stop lights in school settings Relevance to TTI Motivation Self-Efficacy Self-Management Proximal predictors of behavior ( Levels of Causation) REMEMBER THE THEORY OF TRIADIC INFLUENCE!! Levels of Causation Intrapersonal Stream Biological/Nature BIOLOGY/ PERSONALITY Ultimate Causes 1 Social/ Personal Nexus 7 Self Determination Expectancies & Evaluations 13 8 h Skills: Social+General 14 b c Proximal Predictors j k B C l m u d e n 16 SOCIAL NORMATIVE BELIEFS o 11 w 20 q Values/ Evaluations x v 6 Interactions w/ Social Instit’s p Perceived Norms 15 s 5 f 10 Motivation to Comply 19 A Others’ Beh & Atts 9 i CULTURAL ENVIRONMENT 4 Interpersonal Bonding SELF-EFFICACY t BEHAVIORAL CONTROL Affect and Cognitions Nurture/Cultural 3 a Social Competence g Cultural/Attitudinal Stream SOCIAL SITUATION 2 Sense of Self/Control Distal Influences Decisions Social/Normative Stream Information/ Opportunities Knowledge/ Expectancies 17 F 21 I 22 Trial Behavior EXPERIENCES: Expectancies -- Social Reinforcements -- Psychological/Physiological Experiences 19 18 ATTITUDES TOWARD THE BEHAVIOR DECISIONS/INTENTIONS D E 12 r 23 J K Related Behaviors H G Thank you Questions??