* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operant Conditioning
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
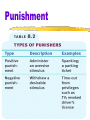
Learning: Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely Operant Conditioning _______________ (1904-1990) elaborated Thorndike’s Law of Effect developed behavioral technology Operant Chamber _____________ chamber with a bar or key that an animal manipulates to obtain a food or water reinforcer contains devices to record responses Operant Conditioning ________ any event that ___________ the behavior it follows __________ operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward _________________________ of a desired goal Punishment ____________ aversive event that __________ the behavior that it follows powerful controller of unwanted behavior Punishment Operant Conditioning Big Bang Theory The Garcia effect People get sick after eating at a restaurant so they won’t eat at that restaurant, even if they know the food was safe. Shaping A procedure in Operant Conditioning in which reinforcers guide behavior closer and closer towards a goal. Principles of Reinforcement _________ Reinforcer __________ reinforcing stimulus i.e., satisfies a biological need Ex: Food, Sleep, Air, Water, Sex ___________ aka Conditioned Reinforcer stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its ____________ with primary reinforcer Ex/ Money, Cars, Grades, Clicker training even… Schedules of Reinforcement Continuous Reinforcement reinforcing the desired response _________ it occurs Partial (Intermitent) Reinforcement reinforcing a response only ______________ results in slower acquisition greater resistance to extinction Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio (FR) reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses faster you respond the more rewards you get different ratios very high rate of responding like piecework pay Schedules of Reinforcement __________ Ratio (VR) reinforces a response after an ___________ number of responses average ratios like gambling, fishing ______________________ because of unpredictability Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Interval (FI) reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed response occurs more frequently as the anticipated time for reward draws near Schedules of Reinforcement Variable Interval (VI) reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals produces slow steady responding like pop quiz Cognition and Operant Conditioning Cognitive Map mental representation of the layout of one’s environment Example: after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it Latent Learning learning that occurs, but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Latent Learning Cognition and Operant Conditioning Overjustification Effect the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation for performing the task Cognition and Operant Conditioning Intrinsic Motivation Desire to perform a behavior for __________________________ Extrinsic Motivation Desire to perform a behavior due to _____________________________ Operant vs Classical Conditioning Observational Learning _____________ Learning learning by _______________ Modeling process of _________ and __________ a specific behavior Prosocial Behavior positive, constructive, helpful behavior _________ of _________ behavior Observational Learning ________________ frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy What is Social Learning Theory? Albert Bandura: Bobo doll. We learn by observing the behavior of others and from imagining the consequences of our own behavior. Social Learning Theory Cont. Modeling: we imitate people who we __________ Identify with View as __________ ________ Reinforcement and Punishment Bobo Doll Experiment Albert Bandura allowed children to watch an adult play with a bobo doll. The experimental group watched a video of an adult playing violently with the doll The control group watched a boring video. The experimental group children imitated the violent behavior.