Classical and Operant Conditioning
... Being influenced by seeing or hearing about the consequences of others’ behaviour ie - if the behaviour is seen to be rewarded then it is more likely to be copied. What influences whether behaviour is modelled or not? ...
... Being influenced by seeing or hearing about the consequences of others’ behaviour ie - if the behaviour is seen to be rewarded then it is more likely to be copied. What influences whether behaviour is modelled or not? ...
Behaviorism What is Learning? - University of California, Irvine
... • Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) • Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
... • Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) • Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
Behaviorism_298 (English) - UC Irvine, OpenCourseWare
... Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
... Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
wp-psych-cond - WordPress.com
... gradually guide an animal's actions toward desired behaviors - You see this w/ kids or clinics ...
... gradually guide an animal's actions toward desired behaviors - You see this w/ kids or clinics ...
Behavior - Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
... Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
... Stimulus Discrimination (but not all bells) Classical Conditioning Explains Only Simple Behavior, Such as Emotional Reactions ...
Applied Behavior Analysis Vocabulary Antecedent stimulus
... Consequence – any stimulus presented contingent on a particular response that follows the occurrence of a behavior Extinction – withholding reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior to reduce the occurrence of the behavior Modeling – demonstrating a desired behavior in order to prompt an im ...
... Consequence – any stimulus presented contingent on a particular response that follows the occurrence of a behavior Extinction – withholding reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior to reduce the occurrence of the behavior Modeling – demonstrating a desired behavior in order to prompt an im ...
Module 22 Powerpoint
... the desire to perform a behavior well for its own sake. The reward is internalized as a feeling of satisfaction. Extrinsic motivation refers to doing a behavior to receive rewards from others. Intrinsic motivation can sometimes be reduced by external rewards, and can be prevented by using contin ...
... the desire to perform a behavior well for its own sake. The reward is internalized as a feeling of satisfaction. Extrinsic motivation refers to doing a behavior to receive rewards from others. Intrinsic motivation can sometimes be reduced by external rewards, and can be prevented by using contin ...
Learning Chapter 7 PowerPoint
... vicarious punishment. vicarious reinforcement. modeling. mirror neurons. ...
... vicarious punishment. vicarious reinforcement. modeling. mirror neurons. ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... ∙The vast majority of reinforcers (or punishers) have little to do with biology. -Secondary reinforcers derive their effectiveness from their association with the primary reinforcers. *example: money starts our as a neutral CS that through association with primary US like buying food and a shelter m ...
... ∙The vast majority of reinforcers (or punishers) have little to do with biology. -Secondary reinforcers derive their effectiveness from their association with the primary reinforcers. *example: money starts our as a neutral CS that through association with primary US like buying food and a shelter m ...
Chapter 13
... to correct (rebalance) the ratio or seek a raise. – In overpayment, workers may change the referent person and readjust their ratio perception. – If inequity persists, workers will often choose to leave the organization. ...
... to correct (rebalance) the ratio or seek a raise. – In overpayment, workers may change the referent person and readjust their ratio perception. – If inequity persists, workers will often choose to leave the organization. ...
LEARNING
... F. Conditioned response (CR) - learned response to a previously neutral stimulus – Salivation in response to tone ...
... F. Conditioned response (CR) - learned response to a previously neutral stimulus – Salivation in response to tone ...
Learning Red
... 10 – classical (involuntary behaviors, stimulus precedes behavior), operant (voluntary behaviors, stimulus follows behavior, rewards and punishments, trial and error) Jack – shaping Queen – negative reinforcement King – negative reinforcement Ace – any example in which a stimulus is presented to inc ...
... 10 – classical (involuntary behaviors, stimulus precedes behavior), operant (voluntary behaviors, stimulus follows behavior, rewards and punishments, trial and error) Jack – shaping Queen – negative reinforcement King – negative reinforcement Ace – any example in which a stimulus is presented to inc ...
Myers Module Twenty One
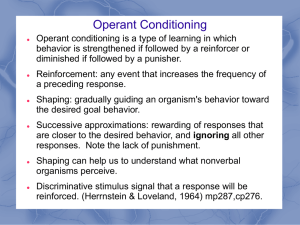
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
path to dependence
... Learning and behavior Learning can be used to modify behavior. Behaviorism was the first scientific paradigm for psychology. JB Watson, BF Skinner Principles widely applied at home, school and workplace. And on the road: seatbelt use ...
... Learning and behavior Learning can be used to modify behavior. Behaviorism was the first scientific paradigm for psychology. JB Watson, BF Skinner Principles widely applied at home, school and workplace. And on the road: seatbelt use ...
Essential Questions, Vocabulary, and Review Charts
... Operant Conditioning - learning in which behaviors are strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Thorndike’s law of effect – behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences becomes less likely Sha ...
... Operant Conditioning - learning in which behaviors are strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Thorndike’s law of effect – behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences becomes less likely Sha ...
File
... OPERANT CHAMBER Skinner Developed the Operant chamber, or the Skinner box Used this to teach animals behaviors that were unlike their natural behavior ...
... OPERANT CHAMBER Skinner Developed the Operant chamber, or the Skinner box Used this to teach animals behaviors that were unlike their natural behavior ...
Learning - Kalyankaari
... Also known as theories of learning, models of learning explain about how individuals learn in their life. The scientific investigation of the learning process was begun at the end of the 19th century by Ivan Pavlov in Russia and Edward Thorndike in the United States. Three models are currently widel ...
... Also known as theories of learning, models of learning explain about how individuals learn in their life. The scientific investigation of the learning process was begun at the end of the 19th century by Ivan Pavlov in Russia and Edward Thorndike in the United States. Three models are currently widel ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
19. The person who studied operant conditioning
... 13. The process in which you break down a desired behavior into smaller steps 14. Spontaneous ____ is when a conditioned response comes back after extinction 17. In Watson's experiment, fear of the write rat was the conditioned ____ 21. Learning to associate a response (our behavior) and its consequ ...
... 13. The process in which you break down a desired behavior into smaller steps 14. Spontaneous ____ is when a conditioned response comes back after extinction 17. In Watson's experiment, fear of the write rat was the conditioned ____ 21. Learning to associate a response (our behavior) and its consequ ...
Skinner
... “Reinforcement indicates a strengthening effect that occurs when operant behaviors have certain consequences. Behavior increases in probability when its outcomes are reinforcing” (Nye, 29-30). ...
... “Reinforcement indicates a strengthening effect that occurs when operant behaviors have certain consequences. Behavior increases in probability when its outcomes are reinforcing” (Nye, 29-30). ...
Chapter 2: Learning Theories
... alters their own behavior based on observations of another person’s behavior • Operant Conditioning: Stimulus + Sr results in learning • With Social-learning observation individuals learn what behaviors are appropriate and get rewarded and which behaviors are not and get ignored or punished through ...
... alters their own behavior based on observations of another person’s behavior • Operant Conditioning: Stimulus + Sr results in learning • With Social-learning observation individuals learn what behaviors are appropriate and get rewarded and which behaviors are not and get ignored or punished through ...
chapter5
... information for improved performance • Define types of rewards, and summarize their relationship to performance • Describe how the effects and consequences of ...
... information for improved performance • Define types of rewards, and summarize their relationship to performance • Describe how the effects and consequences of ...
Theories to know
... Know the background terms and be able to give examples of them (motivation, instinct, homeostasis, etc.) Know the different theories of motivation (evolutionary, drive-reduction theory, optimum arousal) and what provides the motivation for each theory Know each of the levels of Maslow’s Hierar ...
... Know the background terms and be able to give examples of them (motivation, instinct, homeostasis, etc.) Know the different theories of motivation (evolutionary, drive-reduction theory, optimum arousal) and what provides the motivation for each theory Know each of the levels of Maslow’s Hierar ...